
What are dictyosomes?
Answer
560.4k+ views
Hint: Dictyosomes are structures that make up an important cell organelle found in most prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, and are responsible for the storage and modifications of biomolecules necessary for building the cell.
Complete answer:
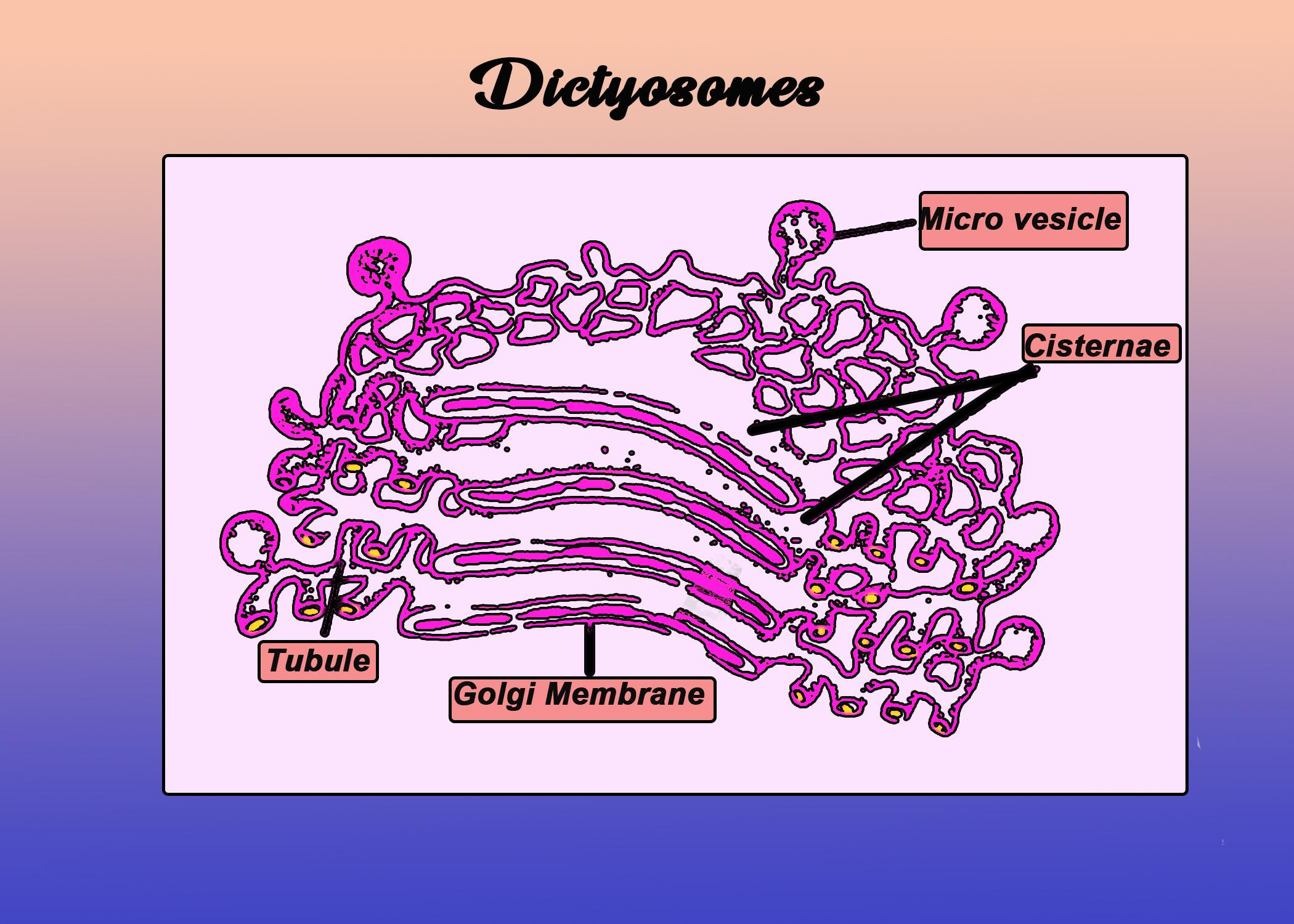
- Dictyosomes are net-like structures of flat, membrane-bound cavities called cisternae that comprise the Golgi apparatus. They are synonymous with the Golgi apparatus in their function.
- In the plant cells, the dictyosome helps in plate formation during cell division.
- Dictyosomes are sites for proteins to be stored, modified, sorted, and packed into vesicles (which are further closed off as Golgi vesicles).
- The difference between the dictyosomes of the animal and plant cells is that dictyosomes in animal cells are stacked tightly together while the dictyosomes in plant cells are dispersed in the cytoplasm, making them difficult to identify as the Golgi apparatus.
Additional Information:
- Plant cells have a few hundred dictyosomes while lower organisms have around four or fewer.
- The Golgi apparatus has two poles. They are (a) The cis-face (or forming face) located near the endoplasmic reticulum and (b) The trans face (or maturing face) that acts as the receiving and shipping departments of the Golgi apparatus.
- Products of the endoplasmic reticulum, such as proteins, are modified during transport from the cis pole to the trans pole of the Golgi apparatus.
Note:
- The term dictyosome was first used by the English biologist John Edmund Sharrock Moore.
- The Golgi apparatus is the organelle that is composed of cisternae and is involved in glycosylation, packaging of molecules for secretion, transporting of lipids within the cell, and giving rise to lysosomes.
Complete answer:
- Dictyosomes are net-like structures of flat, membrane-bound cavities called cisternae that comprise the Golgi apparatus. They are synonymous with the Golgi apparatus in their function.
- In the plant cells, the dictyosome helps in plate formation during cell division.
- Dictyosomes are sites for proteins to be stored, modified, sorted, and packed into vesicles (which are further closed off as Golgi vesicles).
- The difference between the dictyosomes of the animal and plant cells is that dictyosomes in animal cells are stacked tightly together while the dictyosomes in plant cells are dispersed in the cytoplasm, making them difficult to identify as the Golgi apparatus.
Additional Information:
- Plant cells have a few hundred dictyosomes while lower organisms have around four or fewer.
- The Golgi apparatus has two poles. They are (a) The cis-face (or forming face) located near the endoplasmic reticulum and (b) The trans face (or maturing face) that acts as the receiving and shipping departments of the Golgi apparatus.
- Products of the endoplasmic reticulum, such as proteins, are modified during transport from the cis pole to the trans pole of the Golgi apparatus.

Note:
- The term dictyosome was first used by the English biologist John Edmund Sharrock Moore.
- The Golgi apparatus is the organelle that is composed of cisternae and is involved in glycosylation, packaging of molecules for secretion, transporting of lipids within the cell, and giving rise to lysosomes.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




