
What are bridge elements?
Answer
510.3k+ views
Hint :Bridge elements are those elements which show the diagonal relationship with the element of the neighboring period. Period 2 elements are referred to as bridge elements. For example, $ Be $ is a bridge element as it shows diagonal relationship with $ Al $ .
Complete Step By Step Answer:
Bridge elements are those elements which show the diagonal relationship with the element of neighboring period. Diagonal relationship describes the similarity in certain properties between two elements which placed diagonally when we move from left to right in two neighbouring periods. These properties include comparable atomic size, the polarization of atoms, electronegativity and so on. The elements which show diagonal relationship are illustrated in the following diagram.
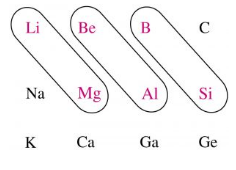
Period 2 elements are referred to as bridge elements. These are so called because these elements bridge the gap between metals on one side (group 1 and 2) and nonmetals/metalloids on the other side (group 13-18). Therefore, from the above diagram we conclude that Lithium $ \left( Li \right) $ , beryllium $ \left( Be \right) $ and boron $ \left( B \right) $ are bridge elements.
Additional Information:
Diagonal relationship arises because moving along the period and down the period has opposite effects. For instance, as we move down the group, atomic size increases. In contrast, when we move along the period, atomic size decreases.
Note :
It is important to note that bridge elements are those elements which show the diagonal relationship with the element of the neighboring period. Diagonal relationship describes the similarity in certain properties between two elements which are placed diagonally when we move from left to right in two neighbouring periods. Lithium $ \left( Li \right) $ , beryllium $ \left( Be \right) $ and boron $ \left( B \right) $ are examples of bridge elements.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
Bridge elements are those elements which show the diagonal relationship with the element of neighboring period. Diagonal relationship describes the similarity in certain properties between two elements which placed diagonally when we move from left to right in two neighbouring periods. These properties include comparable atomic size, the polarization of atoms, electronegativity and so on. The elements which show diagonal relationship are illustrated in the following diagram.

Period 2 elements are referred to as bridge elements. These are so called because these elements bridge the gap between metals on one side (group 1 and 2) and nonmetals/metalloids on the other side (group 13-18). Therefore, from the above diagram we conclude that Lithium $ \left( Li \right) $ , beryllium $ \left( Be \right) $ and boron $ \left( B \right) $ are bridge elements.
Additional Information:
Diagonal relationship arises because moving along the period and down the period has opposite effects. For instance, as we move down the group, atomic size increases. In contrast, when we move along the period, atomic size decreases.
Note :
It is important to note that bridge elements are those elements which show the diagonal relationship with the element of the neighboring period. Diagonal relationship describes the similarity in certain properties between two elements which are placed diagonally when we move from left to right in two neighbouring periods. Lithium $ \left( Li \right) $ , beryllium $ \left( Be \right) $ and boron $ \left( B \right) $ are examples of bridge elements.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




