
Water is dripping out of the conical funnel of semi vertical angle \[\dfrac{\pi }{4}\] at the uniform rate of $2c{{m}^{2}}/\sec $ through a tiny hole at the vertex at the bottom. When the slant height of the water is 4 cm, find the rate of decrease of the slant height of the water.
Answer
612.9k+ views
Hint:Use properties of triangles to find relation between h and relation between $\dfrac{dh}{dt}$ and $\dfrac{dr}{dt}$ . The finally use ${{l}^{2}}={{r}^{2}}+{{h}^{2}}$ and further differentiate it to get value of $\dfrac{dl}{dt}$ .
Complete step-by-step answer:
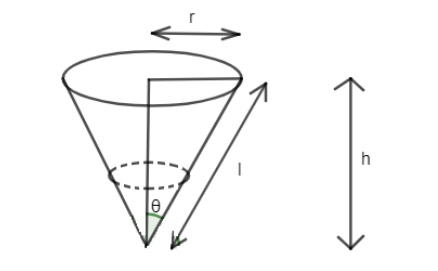
In the question, we are informed that water is dripping out from a conical funnel of semi vertical angle $\dfrac{\pi }{4}$, at the uniform rate $2c{{m}^{2}}/\sec $ through a tiny hole at the vertex at the bottom. We have to find the rate of decrease of the slant height of the water when the slant height is 4 cm.
Let ‘r’ be radius, ‘h’ be height and ‘l’ be slant height at any time ‘t’.
Rate at which area is changing can be represented as $\dfrac{d}{dt}\left( \pi rl \right)$ which can be further written as,
$2\pi r\dfrac{dr}{dt}$
We know the value is $-2$ . So,
$2\pi r\dfrac{dr}{dt}=-2$ ……………………………………….(i)
Now, on observing figure we can see a relation that,
$\tan \theta =\dfrac{r}{h}$
So, $r=h\tan \theta $
Now, on differentiating both the sides with respect to ‘t’ we get,
$\dfrac{dr}{dt}=\dfrac{dh}{dt}\tan \theta $
Also, we can say that,
$\sin \theta =\dfrac{r}{l}$
Here $\theta =\dfrac{\pi }{4}$. So, $\sin \theta =\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}}$
Hence, $\dfrac{r}{l}=\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}}$
As we know that $l=4cm$ which is given, so $r=\dfrac{4}{\sqrt{2}}=2\sqrt{2}cm$
As we know $r=h\tan \theta $ , where $\theta =\dfrac{\pi }{4}$. So, $\tan \theta =1$
Hence, $h=2\sqrt{2}cm$ as $r=2\sqrt{2}cm$
Now putting value of r in (i), we get
$\dfrac{dr}{dt}=\dfrac{-2}{2\pi \times 2\sqrt{2}}=\dfrac{-1}{2\sqrt{2}\pi }$
As we know that,
$\dfrac{dr}{dt}=\dfrac{dh}{dt}$ as $\tan \theta =1$
So, $\dfrac{dh}{dt}=\dfrac{-1}{2\sqrt{2}\pi }$
Now we know the relation of l, h, r which is ${{l}^{2}}={{r}^{2}}+{{h}^{2}}$
Now, we will differentiate with respect to ‘t’ we get,
$2l\dfrac{dl}{dt}=2h\dfrac{dh}{dt}+2r\dfrac{dr}{dt}$
Here substituting $l=4cm,h=2\sqrt{2}cm,r=2\sqrt{2}cm,\dfrac{dh}{dt}=\dfrac{dr}{dt}=\dfrac{-1}{2\sqrt{2}\pi }$
So, we get
$2\times 4\dfrac{dl}{dt}=2\times 4\times \left( \dfrac{-1}{2\sqrt{2}\pi } \right)+2\times 4\times \left( \dfrac{-1}{2\sqrt{2}\pi } \right)$
On simplification, we get
$\dfrac{dl}{dt}=\dfrac{-1}{2\pi }cm/\sec $
Hence, the rate of decrease of slant height is $\dfrac{1}{2\pi }cm/\sec $.
Note: Student can do alternative by taking $\dfrac{ds}{dt}=-2c{{m}^{2}}/\sec $
$s=\pi rl=\pi l\sin \dfrac{\pi }{4}l$
$\Rightarrow s=\dfrac{\pi }{\sqrt{2}}{{l}^{2}}$
So, $\dfrac{ds}{dt}=\dfrac{2\pi }{\sqrt{2}}l\cdot \dfrac{dl}{dt}=\sqrt{2}\pi l\cdot \dfrac{dl}{dt}$
At $l=4$ cm substitute it to find $\dfrac{dl}{dt}$.
Complete step-by-step answer:

In the question, we are informed that water is dripping out from a conical funnel of semi vertical angle $\dfrac{\pi }{4}$, at the uniform rate $2c{{m}^{2}}/\sec $ through a tiny hole at the vertex at the bottom. We have to find the rate of decrease of the slant height of the water when the slant height is 4 cm.
Let ‘r’ be radius, ‘h’ be height and ‘l’ be slant height at any time ‘t’.
Rate at which area is changing can be represented as $\dfrac{d}{dt}\left( \pi rl \right)$ which can be further written as,
$2\pi r\dfrac{dr}{dt}$
We know the value is $-2$ . So,
$2\pi r\dfrac{dr}{dt}=-2$ ……………………………………….(i)
Now, on observing figure we can see a relation that,
$\tan \theta =\dfrac{r}{h}$
So, $r=h\tan \theta $
Now, on differentiating both the sides with respect to ‘t’ we get,
$\dfrac{dr}{dt}=\dfrac{dh}{dt}\tan \theta $
Also, we can say that,
$\sin \theta =\dfrac{r}{l}$
Here $\theta =\dfrac{\pi }{4}$. So, $\sin \theta =\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}}$
Hence, $\dfrac{r}{l}=\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}}$
As we know that $l=4cm$ which is given, so $r=\dfrac{4}{\sqrt{2}}=2\sqrt{2}cm$
As we know $r=h\tan \theta $ , where $\theta =\dfrac{\pi }{4}$. So, $\tan \theta =1$
Hence, $h=2\sqrt{2}cm$ as $r=2\sqrt{2}cm$
Now putting value of r in (i), we get
$\dfrac{dr}{dt}=\dfrac{-2}{2\pi \times 2\sqrt{2}}=\dfrac{-1}{2\sqrt{2}\pi }$
As we know that,
$\dfrac{dr}{dt}=\dfrac{dh}{dt}$ as $\tan \theta =1$
So, $\dfrac{dh}{dt}=\dfrac{-1}{2\sqrt{2}\pi }$
Now we know the relation of l, h, r which is ${{l}^{2}}={{r}^{2}}+{{h}^{2}}$
Now, we will differentiate with respect to ‘t’ we get,
$2l\dfrac{dl}{dt}=2h\dfrac{dh}{dt}+2r\dfrac{dr}{dt}$
Here substituting $l=4cm,h=2\sqrt{2}cm,r=2\sqrt{2}cm,\dfrac{dh}{dt}=\dfrac{dr}{dt}=\dfrac{-1}{2\sqrt{2}\pi }$
So, we get
$2\times 4\dfrac{dl}{dt}=2\times 4\times \left( \dfrac{-1}{2\sqrt{2}\pi } \right)+2\times 4\times \left( \dfrac{-1}{2\sqrt{2}\pi } \right)$
On simplification, we get
$\dfrac{dl}{dt}=\dfrac{-1}{2\pi }cm/\sec $
Hence, the rate of decrease of slant height is $\dfrac{1}{2\pi }cm/\sec $.
Note: Student can do alternative by taking $\dfrac{ds}{dt}=-2c{{m}^{2}}/\sec $
$s=\pi rl=\pi l\sin \dfrac{\pi }{4}l$
$\Rightarrow s=\dfrac{\pi }{\sqrt{2}}{{l}^{2}}$
So, $\dfrac{ds}{dt}=\dfrac{2\pi }{\sqrt{2}}l\cdot \dfrac{dl}{dt}=\sqrt{2}\pi l\cdot \dfrac{dl}{dt}$
At $l=4$ cm substitute it to find $\dfrac{dl}{dt}$.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 9 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Trending doubts
Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell

Fill the blanks with the suitable prepositions 1 The class 9 english CBSE

Who is eligible for RTE class 9 social science CBSE

Which places in India experience sunrise first and class 9 social science CBSE

What is pollution? How many types of pollution? Define it

Name 10 Living and Non living things class 9 biology CBSE





