
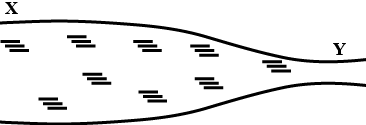
Water flows through a horizontal tube of variable cross-section (figure). The area of cross-section at $x$ and $y$ are $40m{m^2}$ and $20m{m^2}$ ,respectively. If $10cc$ of water enters per second through $x$, find (i) the speed of water at $x$ , (ii) the speed of water at $y$ and (iii) the pressure difference ${P_x} - {P_y}$.

Answer
491.1k+ views
Hint: This question is based on the concept of Bernoulli’s theorem which states that an increase in the speed of a fluid always occurs simultaneously with a decrease in static pressure of the fluid or a decrease in the fluid's potential energy.
Complete step by step answer:
Given,
The area of cross section at $x$,
${a_1} = 40m{m^2}$
On converting it into ${m^2}$, we get,
${a_1} = 4 \times {10^{ - 5}}{m^2}$
The area of cross section at $y$,
${a_2} = 20m{m^2}$
On converting it into ${m^2}$, we get,
${a_2} = 2 \times {10^{ - 5}}{m^2}$
The rate of flow of volume $ = 10cc$
On converting it into $\dfrac{{{m^3}}}{s}$,
The rate of flow of volume $ = {10^{ - 5}}\dfrac{{{m^3}}}{s}$
(a) We know that the volume rate flow,
$Q = {a_1}{v_1}$
${v_1} = \dfrac{Q}{{{a_1}}}$
${v_1} = \dfrac{{{{10}^{ - 5}}}}{{4 \times {{10}^{ - 5}}}}$
On further solving, we get,
${v_1} = 0.25\dfrac{m}{s}$
So, the speed of water at $x$ is ${v_1} = 0.25\dfrac{m}{s}$.
(b) We know that the volume rate flow,
$Q = {a_2}{v_2}$
${v_2} = \dfrac{Q}{{{a_2}}}$
${v_2} = \dfrac{{{{10}^{ - 5}}}}{{2 \times {{10}^{ - 5}}}}$
On further solving, we get,
\[{v_2} = 0.5\dfrac{m}{s}\]
So, the speed of water at $y$ is \[{v_2} = 0.5\dfrac{m}{s}\].
(c) According to the Bernoulli’s theorem,
$\dfrac{{{P_x}}}{\rho } + \dfrac{{v_x^2}}{2} = \dfrac{{{P_y}}}{\rho } + \dfrac{{v_y^2}}{2}$
On rearranging the above equation,
$\dfrac{{{P_x}}}{\rho } - \dfrac{{{P_y}}}{\rho } = \dfrac{{v_y^2}}{2} - \dfrac{{v_x^2}}{2}$
${P_x} - {P_y} = \dfrac{\rho }{2}\left( {v_x^2 - v_y^2} \right)$
On putting the required values, we get,
${P_x} - {P_y} = \dfrac{{1000}}{2}\left( {{{0.5}^2} - {{0.25}^2}} \right)$
${P_x} - {P_y} = 500\left( {{{0.5}^2} - {{0.25}^2}} \right)$
On further solving,
${P_x} - {P_y} = 93.8Pa$
So, the pressure difference ${P_x} - {P_y}$ is $93.8Pa$.
Note: While solving such questions, it is important to note that the rate of flow of water across a section is always equal whether it is a big or a small cross-section. In this question, we have taken the units in the SI system of units, which could also be taken in the CGS system too. The answers will come out the same. If the speed of any fluid increases, this will lead to a decrease in the potential energy of the fluid.
Complete step by step answer:
Given,
The area of cross section at $x$,
${a_1} = 40m{m^2}$
On converting it into ${m^2}$, we get,
${a_1} = 4 \times {10^{ - 5}}{m^2}$
The area of cross section at $y$,
${a_2} = 20m{m^2}$
On converting it into ${m^2}$, we get,
${a_2} = 2 \times {10^{ - 5}}{m^2}$
The rate of flow of volume $ = 10cc$
On converting it into $\dfrac{{{m^3}}}{s}$,
The rate of flow of volume $ = {10^{ - 5}}\dfrac{{{m^3}}}{s}$
(a) We know that the volume rate flow,
$Q = {a_1}{v_1}$
${v_1} = \dfrac{Q}{{{a_1}}}$
${v_1} = \dfrac{{{{10}^{ - 5}}}}{{4 \times {{10}^{ - 5}}}}$
On further solving, we get,
${v_1} = 0.25\dfrac{m}{s}$
So, the speed of water at $x$ is ${v_1} = 0.25\dfrac{m}{s}$.
(b) We know that the volume rate flow,
$Q = {a_2}{v_2}$
${v_2} = \dfrac{Q}{{{a_2}}}$
${v_2} = \dfrac{{{{10}^{ - 5}}}}{{2 \times {{10}^{ - 5}}}}$
On further solving, we get,
\[{v_2} = 0.5\dfrac{m}{s}\]
So, the speed of water at $y$ is \[{v_2} = 0.5\dfrac{m}{s}\].
(c) According to the Bernoulli’s theorem,
$\dfrac{{{P_x}}}{\rho } + \dfrac{{v_x^2}}{2} = \dfrac{{{P_y}}}{\rho } + \dfrac{{v_y^2}}{2}$
On rearranging the above equation,
$\dfrac{{{P_x}}}{\rho } - \dfrac{{{P_y}}}{\rho } = \dfrac{{v_y^2}}{2} - \dfrac{{v_x^2}}{2}$
${P_x} - {P_y} = \dfrac{\rho }{2}\left( {v_x^2 - v_y^2} \right)$
On putting the required values, we get,
${P_x} - {P_y} = \dfrac{{1000}}{2}\left( {{{0.5}^2} - {{0.25}^2}} \right)$
${P_x} - {P_y} = 500\left( {{{0.5}^2} - {{0.25}^2}} \right)$
On further solving,
${P_x} - {P_y} = 93.8Pa$
So, the pressure difference ${P_x} - {P_y}$ is $93.8Pa$.
Note: While solving such questions, it is important to note that the rate of flow of water across a section is always equal whether it is a big or a small cross-section. In this question, we have taken the units in the SI system of units, which could also be taken in the CGS system too. The answers will come out the same. If the speed of any fluid increases, this will lead to a decrease in the potential energy of the fluid.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




