
How is the wall of the small intestine adapted for performing the function of absorption of food?
Answer
478.5k+ views
Hint: Small intestine is the largest part of the alimentary canal where the majority of the absorption of food takes place. It contains a specialised feature that helps in increasing the surface area of the absorption of nutrients.
Complete answer:
The wall of the alimentary canal from the oesophagus to the rectum possesses four layers namely serosa, muscularis, submucosa and mucosa. Serosa is the outermost layer and is made up of a thin mesothelium with some connective tissues. Muscularis is the second layer that is generally formed by smooth muscles that are arranged into an inner circular and an outer longitudinal layer. In some regions, an oblique muscle layer may be present.
The submucosal layer is the next layer after mucosa that is formed of loose connective tissues containing nerves, blood and lymph vessels. In the duodenum, glands are also present in the submucosa. The mucosa is the innermost layer lining the lumen of the alimentary canal.
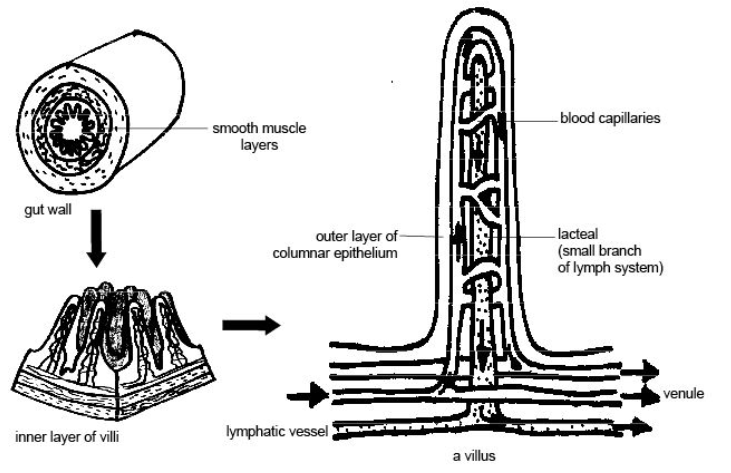
Absorption mainly occurs in the small intestine. For this purpose, the internal surface area of the small intestine is greatly enlarged by its enormous length, folds, villi, and microvilli. The folds are a close-set longitudinal or transverse projection of the mucosa into the lumen of the intestine.
The villi are numerous small, finger-shaped projections of the mucosa. These are found in birds and mammals. Each villus contains abundant blood capillaries, a lymph vessel twist and shortened to quicken absorption by causing circulation of blood and lymph in them. Movements of villi are accelerated by a hormone villikinin secreted by intestinal mucosa in the response to the presence of food in the intestine.
Mechanical mixing of food by muscular contraction of the intestinal wall facilitates absorption as it keeps renewing the fluid directly in contact with the absorptive surface.
Note: The major four lining of the alimentary canal contains some modification in different parts of the body. One such case can be seen with the layer called mucosal. The mucosal epithelium has goblet cells that secrete mucus that helps in lubrication. Mucosa forms glands in the stomach and crypts in between the basis of villi in the intestine that are present.
Complete answer:
The wall of the alimentary canal from the oesophagus to the rectum possesses four layers namely serosa, muscularis, submucosa and mucosa. Serosa is the outermost layer and is made up of a thin mesothelium with some connective tissues. Muscularis is the second layer that is generally formed by smooth muscles that are arranged into an inner circular and an outer longitudinal layer. In some regions, an oblique muscle layer may be present.
The submucosal layer is the next layer after mucosa that is formed of loose connective tissues containing nerves, blood and lymph vessels. In the duodenum, glands are also present in the submucosa. The mucosa is the innermost layer lining the lumen of the alimentary canal.
Absorption mainly occurs in the small intestine. For this purpose, the internal surface area of the small intestine is greatly enlarged by its enormous length, folds, villi, and microvilli. The folds are a close-set longitudinal or transverse projection of the mucosa into the lumen of the intestine.
The villi are numerous small, finger-shaped projections of the mucosa. These are found in birds and mammals. Each villus contains abundant blood capillaries, a lymph vessel twist and shortened to quicken absorption by causing circulation of blood and lymph in them. Movements of villi are accelerated by a hormone villikinin secreted by intestinal mucosa in the response to the presence of food in the intestine.
Mechanical mixing of food by muscular contraction of the intestinal wall facilitates absorption as it keeps renewing the fluid directly in contact with the absorptive surface.

Note: The major four lining of the alimentary canal contains some modification in different parts of the body. One such case can be seen with the layer called mucosal. The mucosal epithelium has goblet cells that secrete mucus that helps in lubrication. Mucosa forms glands in the stomach and crypts in between the basis of villi in the intestine that are present.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




