
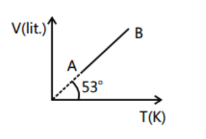
V-T curve for 2 moles of a gas is a straight line as shown in the graph here. Find the pressure of gas at A

Answer
581.1k+ views
Hint
Since we have a V-T curve, by using the gas equation and equation of a straight line, we can find the pressure at any point of the line.
$\Rightarrow PV = nRT$
Complete step by step answer
We can see the graph, the line is passing through the origin hence the pressure is constant
We know $PV = nRT$, where P is the pressure, n is the number of moles , R is the gas constant and T is temperature
Rearranging above equation in the form of equation of line $y = mx$, where m is the slope
So, equation becomes $V = \left( {\dfrac{{nR}}{P}} \right)T$
Comparing it with the equation of line, slope of V-T graph is $\left( {\dfrac{{nR}}{P}} \right)$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{4}{3} = \left( {\dfrac{{nR}}{P}} \right)$
$\Rightarrow P = \dfrac{3}{4} \times 2 \times \dfrac{{25}}{3}J/litre = \dfrac{{25}}{2}\dfrac{J}{{{{10}^{ - 3}}{m^3}}} = 12.5 \times {10^3}J/{m^3} = 1.25 \times {10^4}N/{m^2}$
Hence the pressure at point A is $1.25 \times {10^4}N/{m^2}$.
Additional Information
An isobaric process is a process in which pressure remains constant . In thermodynamics ,$\partial P = 0$ for isobaric processes. In case of an ideal gas , if the pressure is constant it implies that the volume of a given sample of gas is proportional to its temperature. This is also called the Charles law. In this condition the work done by the gas is equal to the area under the curve. It can be mathematically represented as
$\Rightarrow W = P\Delta V$, where W represents the work done by the gas.
Universal gas constant R has same value for all gases $R = 8.32J/mol.K$
Note
We take 1 gram-molecule or 1 mole of the gas so that the value of the gas constant becomes the same for all gases. For ‘n’ number of moles , the product of pressure and volume becomes n times of gas constant and temperature product. The ideal gas equation holds true for any single gas or mixture of different gases provided it has low gas density.
Since we have a V-T curve, by using the gas equation and equation of a straight line, we can find the pressure at any point of the line.
$\Rightarrow PV = nRT$
Complete step by step answer
We can see the graph, the line is passing through the origin hence the pressure is constant
We know $PV = nRT$, where P is the pressure, n is the number of moles , R is the gas constant and T is temperature
Rearranging above equation in the form of equation of line $y = mx$, where m is the slope
So, equation becomes $V = \left( {\dfrac{{nR}}{P}} \right)T$
Comparing it with the equation of line, slope of V-T graph is $\left( {\dfrac{{nR}}{P}} \right)$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{4}{3} = \left( {\dfrac{{nR}}{P}} \right)$
$\Rightarrow P = \dfrac{3}{4} \times 2 \times \dfrac{{25}}{3}J/litre = \dfrac{{25}}{2}\dfrac{J}{{{{10}^{ - 3}}{m^3}}} = 12.5 \times {10^3}J/{m^3} = 1.25 \times {10^4}N/{m^2}$
Hence the pressure at point A is $1.25 \times {10^4}N/{m^2}$.
Additional Information
An isobaric process is a process in which pressure remains constant . In thermodynamics ,$\partial P = 0$ for isobaric processes. In case of an ideal gas , if the pressure is constant it implies that the volume of a given sample of gas is proportional to its temperature. This is also called the Charles law. In this condition the work done by the gas is equal to the area under the curve. It can be mathematically represented as
$\Rightarrow W = P\Delta V$, where W represents the work done by the gas.
Universal gas constant R has same value for all gases $R = 8.32J/mol.K$
Note
We take 1 gram-molecule or 1 mole of the gas so that the value of the gas constant becomes the same for all gases. For ‘n’ number of moles , the product of pressure and volume becomes n times of gas constant and temperature product. The ideal gas equation holds true for any single gas or mixture of different gases provided it has low gas density.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




