
Vertex is $\left( 4,3 \right)$ and the directrix is $3x+2y-7=0$, then the equation of latus rectum is?
Answer
575.1k+ views
Hint: We will look at a rough diagram of a parabola that shows its directrix, latus rectum and other components. We will first find the slope of the latus rectum using the equation of the directrix. Then we will find the coordinates of the focus, that is the point at which the latus rectum intersects the axis of the parabola. Using the focus and the slope of the latus rectum, we will find its equation using the slope-point form.
Complete step by step answer:
Let us look at a rough diagram that shows the parabola along with its axis, directrix, and other components.
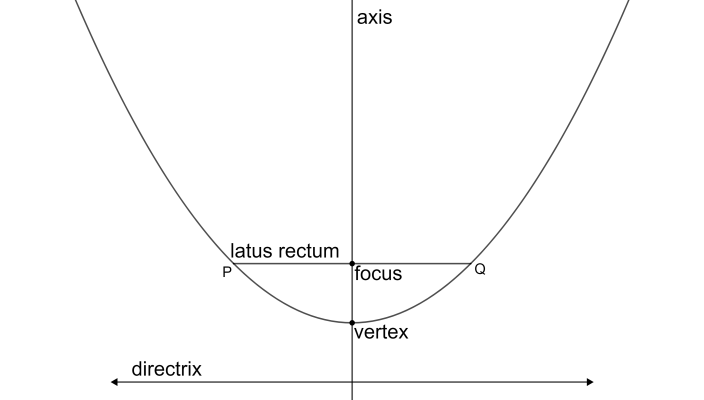
The equation of directrix is given as $3x+2y-7=0$. So, the slope of the directrix is $-\dfrac{3}{2}$. Now, from the figure, we can see that the directrix is parallel to the latus rectum. So the slope of the latus rectum is the same as that of the directrix.
Now, we will find the coordinates of the focus and then use the slope-point form to find the equation of the latus rectum. We know that the coordinates of the vertex are $V=\left( 4,3 \right)$. Let us assume that the coordinates of the focus are given by $F=\left( x,y \right)$. The focus and the vertex lie on the axis. Since the axis is perpendicular to the latus rectum, we know that
$\text{slope of latus rectum }\times \text{ slope of axis = }-1$
Therefore, we have that the $\text{slope of axis = }\dfrac{-1}{\text{slope of latus rectum}}=\dfrac{-1}{\left( \dfrac{-3}{2} \right)}=\dfrac{2}{3}$.
We can find the slope of the axis using the coordinates of the vertex and focus in the following manner,
$\text{slope of axis =}\dfrac{y-3}{x-4}$
Hence, from the above two expressions, we get
$\dfrac{y-3}{x-4}=\dfrac{2}{3}$
Simplifying the above expression by cross multiplication, we get
$3y-9=2x-8$
Shifting the expression from LHS to RHS, we obtain
$\begin{align}
& 2x-3y-8+9=0 \\
& \Rightarrow 2x-3y=-1.....(i) \\
\end{align}$
Now, we know that the distance between a line $ax+by+c=0$ and a point $\left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)$ is given by
$d=\dfrac{|a{{x}_{1}}+b{{y}_{1}}+c|}{\sqrt{{{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}}}$
We will use this formula to find the distance between the directrix and the vertex. The equation of the directrix is $3x+2y-7=0$ and the coordinates of the vertex are $V=\left( 4,3 \right)$. Substituting these values in the above formula we get,
$\begin{align}
& d=\dfrac{|3\cdot 4+2\cdot 3-7|}{\sqrt{{{3}^{2}}+{{2}^{2}}}} \\
& \Rightarrow d=\dfrac{|12+6-7|}{\sqrt{9+4}} \\
& \Rightarrow d=\dfrac{11}{\sqrt{13}} \\
\end{align}$
Now, we know that the distance between the directrix and the vertex is the same as the distance between the vertex and the focus. So, the distance between the focus and the directrix is twice the distance between the vertex and the directrix.
$\text{distance between focus and directrix = 2}d$
Using the above formula to find the distance between the focus and the directrix, we get
$\begin{align}
& \text{distance between focus and directrix = }\dfrac{|3\cdot x+2\cdot y-7|}{\sqrt{{{3}^{2}}+{{2}^{2}}}} \\
& \Rightarrow \text{distance between focus and directrix = }\dfrac{3x+2y-7}{\sqrt{13}} \\
\end{align}$
Substituting these values in the above equation, we get
$\dfrac{3x+2y-7}{\sqrt{13}}=2\times \dfrac{11}{\sqrt{13}}$
Simplifying the above expression, we get
$\begin{align}
& 3x+2y-7=22 \\
& \Rightarrow 3x+2y=29....(ii) \\
\end{align}$
Now, we will solve the equation $(i)$ and $(ii)$ simultaneously. From equation $(i)$, we have $x=\dfrac{3y-1}{2}$. Substituting this value in equation $(ii)$, we get
$3\times \dfrac{3y-1}{2}+2y=29$
Simplifying this equation we get,
$\begin{align}
& 9y-3+4y=58 \\
& \Rightarrow 13y=61 \\
& \therefore y=\dfrac{61}{13} \\
\end{align}$
Substituting this value of $y$ in equation $(i)$, we get
$2x-3\times \dfrac{61}{13}=-1$
Simplifying the above expression, we get
$\begin{align}
& 26x-183=-13 \\
& \Rightarrow 26x=170 \\
& \Rightarrow x=\dfrac{170}{26} \\
& \therefore x=\dfrac{85}{13} \\
\end{align}$
So, the coordinates of the focus are $F=\left( \dfrac{85}{13},\dfrac{61}{13} \right)$. The slope of the latus rectum is $-\dfrac{3}{2}$.
Using the slope-point form, the equation of the latus rectum will be
$y-\dfrac{61}{13}=-\dfrac{3}{2}\left( x-\dfrac{85}{13} \right)$
Simplifying the above equation, we get
\[\begin{align}
& \dfrac{13y-61}{13}=-\dfrac{3}{2}\left( \dfrac{13x-85}{13} \right) \\
& \Rightarrow 2\left( 13y-61 \right)=-3\left( 13x-85 \right) \\
& \Rightarrow 26y-122=-39x+255 \\
& \Rightarrow 39x+26y=377 \\
& \therefore 3x+2y=29 \\
\end{align}\]
Hence, the equation of the latus rectum is $3x+2y=29$.
Note: It is important that we understand the definitions of the elements associated with the conics section like the directrix, focus, etc. In this type of question, it is useful to know the formulae for distances between a line and a point or two points, etc. Since there are many calculations involved, it is better to write all these calculations explicitly to avoid making any errors.
Complete step by step answer:
Let us look at a rough diagram that shows the parabola along with its axis, directrix, and other components.

The equation of directrix is given as $3x+2y-7=0$. So, the slope of the directrix is $-\dfrac{3}{2}$. Now, from the figure, we can see that the directrix is parallel to the latus rectum. So the slope of the latus rectum is the same as that of the directrix.
Now, we will find the coordinates of the focus and then use the slope-point form to find the equation of the latus rectum. We know that the coordinates of the vertex are $V=\left( 4,3 \right)$. Let us assume that the coordinates of the focus are given by $F=\left( x,y \right)$. The focus and the vertex lie on the axis. Since the axis is perpendicular to the latus rectum, we know that
$\text{slope of latus rectum }\times \text{ slope of axis = }-1$
Therefore, we have that the $\text{slope of axis = }\dfrac{-1}{\text{slope of latus rectum}}=\dfrac{-1}{\left( \dfrac{-3}{2} \right)}=\dfrac{2}{3}$.
We can find the slope of the axis using the coordinates of the vertex and focus in the following manner,
$\text{slope of axis =}\dfrac{y-3}{x-4}$
Hence, from the above two expressions, we get
$\dfrac{y-3}{x-4}=\dfrac{2}{3}$
Simplifying the above expression by cross multiplication, we get
$3y-9=2x-8$
Shifting the expression from LHS to RHS, we obtain
$\begin{align}
& 2x-3y-8+9=0 \\
& \Rightarrow 2x-3y=-1.....(i) \\
\end{align}$
Now, we know that the distance between a line $ax+by+c=0$ and a point $\left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)$ is given by
$d=\dfrac{|a{{x}_{1}}+b{{y}_{1}}+c|}{\sqrt{{{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}}}$
We will use this formula to find the distance between the directrix and the vertex. The equation of the directrix is $3x+2y-7=0$ and the coordinates of the vertex are $V=\left( 4,3 \right)$. Substituting these values in the above formula we get,
$\begin{align}
& d=\dfrac{|3\cdot 4+2\cdot 3-7|}{\sqrt{{{3}^{2}}+{{2}^{2}}}} \\
& \Rightarrow d=\dfrac{|12+6-7|}{\sqrt{9+4}} \\
& \Rightarrow d=\dfrac{11}{\sqrt{13}} \\
\end{align}$
Now, we know that the distance between the directrix and the vertex is the same as the distance between the vertex and the focus. So, the distance between the focus and the directrix is twice the distance between the vertex and the directrix.
$\text{distance between focus and directrix = 2}d$
Using the above formula to find the distance between the focus and the directrix, we get
$\begin{align}
& \text{distance between focus and directrix = }\dfrac{|3\cdot x+2\cdot y-7|}{\sqrt{{{3}^{2}}+{{2}^{2}}}} \\
& \Rightarrow \text{distance between focus and directrix = }\dfrac{3x+2y-7}{\sqrt{13}} \\
\end{align}$
Substituting these values in the above equation, we get
$\dfrac{3x+2y-7}{\sqrt{13}}=2\times \dfrac{11}{\sqrt{13}}$
Simplifying the above expression, we get
$\begin{align}
& 3x+2y-7=22 \\
& \Rightarrow 3x+2y=29....(ii) \\
\end{align}$
Now, we will solve the equation $(i)$ and $(ii)$ simultaneously. From equation $(i)$, we have $x=\dfrac{3y-1}{2}$. Substituting this value in equation $(ii)$, we get
$3\times \dfrac{3y-1}{2}+2y=29$
Simplifying this equation we get,
$\begin{align}
& 9y-3+4y=58 \\
& \Rightarrow 13y=61 \\
& \therefore y=\dfrac{61}{13} \\
\end{align}$
Substituting this value of $y$ in equation $(i)$, we get
$2x-3\times \dfrac{61}{13}=-1$
Simplifying the above expression, we get
$\begin{align}
& 26x-183=-13 \\
& \Rightarrow 26x=170 \\
& \Rightarrow x=\dfrac{170}{26} \\
& \therefore x=\dfrac{85}{13} \\
\end{align}$
So, the coordinates of the focus are $F=\left( \dfrac{85}{13},\dfrac{61}{13} \right)$. The slope of the latus rectum is $-\dfrac{3}{2}$.
Using the slope-point form, the equation of the latus rectum will be
$y-\dfrac{61}{13}=-\dfrac{3}{2}\left( x-\dfrac{85}{13} \right)$
Simplifying the above equation, we get
\[\begin{align}
& \dfrac{13y-61}{13}=-\dfrac{3}{2}\left( \dfrac{13x-85}{13} \right) \\
& \Rightarrow 2\left( 13y-61 \right)=-3\left( 13x-85 \right) \\
& \Rightarrow 26y-122=-39x+255 \\
& \Rightarrow 39x+26y=377 \\
& \therefore 3x+2y=29 \\
\end{align}\]
Hence, the equation of the latus rectum is $3x+2y=29$.
Note: It is important that we understand the definitions of the elements associated with the conics section like the directrix, focus, etc. In this type of question, it is useful to know the formulae for distances between a line and a point or two points, etc. Since there are many calculations involved, it is better to write all these calculations explicitly to avoid making any errors.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




