
How do you verify ${\cos ^2}x - {\sin ^2}x = 1 - 2{\sin ^2}x$?
Answer
562.8k+ views
Hint: Here we need to use the trigonometric properties where we must know that in the right angles triangle $\sin \theta = \dfrac{{{\text{perpendicular }}}}{{{\text{hypotenuse}}}}$ and $\cos \theta = \dfrac{{{\text{base}}}}{{{\text{hypotenuse}}}}$ where $\theta $ is the angle between the base and the hypotenuse. So we can derive from it the property that ${\cos ^2}x + {\sin ^2}x = 1$ and then get the desired result.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Here we are given that we need to verify ${\cos ^2}x - {\sin ^2}x = 1 - 2{\sin ^2}x$
So let us take the right angled triangle $ABC$ right angles at $B$
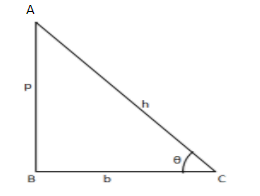
We know that $\sin \theta = \dfrac{{{\text{perpendicular }}}}{{{\text{hypotenuse}}}}$ and $\cos \theta = \dfrac{{{\text{base}}}}{{{\text{hypotenuse}}}}$
So we can say that according to the figure:
$\sin \theta = \dfrac{{{\text{perpendicular }}}}{{{\text{hypotenuse}}}} = \dfrac{p}{h}$$ - - - - (1)$
$\cos \theta = \dfrac{{{\text{base}}}}{{{\text{hypotenuse}}}} = \dfrac{b}{h} - - - - - (2)$
Squaring (1) and (2) and adding we get:
$\Rightarrow$ ${\sin ^2}\theta + {\cos ^2}\theta = \dfrac{{{p^2} + {b^2}}}{{{h^2}}}$
Now we know that according to the Pythagoras theorem we have:
$\Rightarrow$ ${p^2} + {b^2} = {h^2}$
So we can say that:
$
{\sin ^2}\theta + {\cos ^2}\theta = \dfrac{{{h^2}}}{{{h^2}}} = 1 \\
\Rightarrow {\sin ^2}\theta + {\cos ^2}\theta = 1 \\
$
So we get that ${\sin ^2}x + {\cos ^2}x = 1$
So we get that ${\cos ^2}x = 1 - {\sin ^2}x - - - - - (3)$
Now we need to find the value of ${\cos ^2}x - {\sin ^2}x$
Put the value in it from the equation (3):
So we will get:
$1 - {\sin ^2}x - {\sin ^2}x = 1 - 2{\sin ^2}x$
Hence we get the required verification by just using the trigonometric identities and using them to convert into the type as we need in the proof. So we need to utilise our mind in order to know and judge which formula we need to apply in order to get the result that is required.
For example: If we are given that we need to prove ${\cos ^2}x - {\sin ^2}x = 2{\cos ^2}x - 1$
So we just need to think that we need to get the terms in cosine in our proof so we will try to eliminate the terms that contain sin and we will get the desired proof.
Here we will substitute ${\sin ^2}x = 1 - {\cos ^2}x$ instead of ${\cos ^2}x = 1 - {\sin ^2}x$.
Note: In these types of problems where we need to prove or verify the left hand side and the right hand side of the problem, we need to just know the properties and formulae of the trigonometric identities and get the desired proof by using substitution in the correct way.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Here we are given that we need to verify ${\cos ^2}x - {\sin ^2}x = 1 - 2{\sin ^2}x$
So let us take the right angled triangle $ABC$ right angles at $B$

We know that $\sin \theta = \dfrac{{{\text{perpendicular }}}}{{{\text{hypotenuse}}}}$ and $\cos \theta = \dfrac{{{\text{base}}}}{{{\text{hypotenuse}}}}$
So we can say that according to the figure:
$\sin \theta = \dfrac{{{\text{perpendicular }}}}{{{\text{hypotenuse}}}} = \dfrac{p}{h}$$ - - - - (1)$
$\cos \theta = \dfrac{{{\text{base}}}}{{{\text{hypotenuse}}}} = \dfrac{b}{h} - - - - - (2)$
Squaring (1) and (2) and adding we get:
$\Rightarrow$ ${\sin ^2}\theta + {\cos ^2}\theta = \dfrac{{{p^2} + {b^2}}}{{{h^2}}}$
Now we know that according to the Pythagoras theorem we have:
$\Rightarrow$ ${p^2} + {b^2} = {h^2}$
So we can say that:
$
{\sin ^2}\theta + {\cos ^2}\theta = \dfrac{{{h^2}}}{{{h^2}}} = 1 \\
\Rightarrow {\sin ^2}\theta + {\cos ^2}\theta = 1 \\
$
So we get that ${\sin ^2}x + {\cos ^2}x = 1$
So we get that ${\cos ^2}x = 1 - {\sin ^2}x - - - - - (3)$
Now we need to find the value of ${\cos ^2}x - {\sin ^2}x$
Put the value in it from the equation (3):
So we will get:
$1 - {\sin ^2}x - {\sin ^2}x = 1 - 2{\sin ^2}x$
Hence we get the required verification by just using the trigonometric identities and using them to convert into the type as we need in the proof. So we need to utilise our mind in order to know and judge which formula we need to apply in order to get the result that is required.
For example: If we are given that we need to prove ${\cos ^2}x - {\sin ^2}x = 2{\cos ^2}x - 1$
So we just need to think that we need to get the terms in cosine in our proof so we will try to eliminate the terms that contain sin and we will get the desired proof.
Here we will substitute ${\sin ^2}x = 1 - {\cos ^2}x$ instead of ${\cos ^2}x = 1 - {\sin ^2}x$.
Note: In these types of problems where we need to prove or verify the left hand side and the right hand side of the problem, we need to just know the properties and formulae of the trigonometric identities and get the desired proof by using substitution in the correct way.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




