
What is the velocity ratio of a single movable pulley?
A. 1
B. 0.5
C. 2
D. 1.5
Answer
611.7k+ views
- Hint:- The ratio of the distance moved by the effort force applied to the object and the distance moved by the object load under is known as the Velocity ratio of any body.
Formula Used :- Velocity ratio = \[\dfrac{{{\text{Distance travelled by the effort}}}}{{{\text{Distance travelled by the load}}}}\]
Complete step-by-step solution -
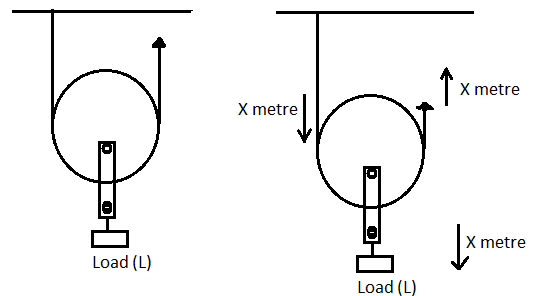
Let us first, draw the diagram for the single movable pulley.
Now let the load L be attached to the single movable pulley.
So, the rope must be fixed at a point in the ceiling such that it passes through the movable pulley.
Now if we had to lift the load L attached to the pulley by distance X metres. We had to apply the effort F to travel a distance of 2X metres. Effort had to travel the 2 times the distance because X metre travelled to the effort rope of one side of the pulley and another X metre travelled to the effort rope of another side of the pulley.
But the distance travelled by the load will be only X metre.
Now as we know that velocity ratio is defined as the ratio of distance travelled by the effort to the distance travelled by the load.
So, velocity ratio of the single moveable pulley will be = \[\dfrac{{{\text{Distance travelled by the effort F}}}}{{{\text{Distance travelled by the load L}}}} = \dfrac{{2X}}{X} = 2\]
As the velocity ratio is ratio. So, it will be unitless.
Hence, the correct option will be C.
Note:- Whenever we come up with this type of problem we should remember that when a load is lifted down by some distance then the force by which it is lifted must be applied for the double distance because when any object attached with pulley is lifted then force is applied on the ropes on different side of the pulley because one side rope move upward and other side rope moves downward by the same distance.
Formula Used :- Velocity ratio = \[\dfrac{{{\text{Distance travelled by the effort}}}}{{{\text{Distance travelled by the load}}}}\]
Complete step-by-step solution -
Let us first, draw the diagram for the single movable pulley.
Now let the load L be attached to the single movable pulley.
So, the rope must be fixed at a point in the ceiling such that it passes through the movable pulley.
Now if we had to lift the load L attached to the pulley by distance X metres. We had to apply the effort F to travel a distance of 2X metres. Effort had to travel the 2 times the distance because X metre travelled to the effort rope of one side of the pulley and another X metre travelled to the effort rope of another side of the pulley.
But the distance travelled by the load will be only X metre.

Now as we know that velocity ratio is defined as the ratio of distance travelled by the effort to the distance travelled by the load.
So, velocity ratio of the single moveable pulley will be = \[\dfrac{{{\text{Distance travelled by the effort F}}}}{{{\text{Distance travelled by the load L}}}} = \dfrac{{2X}}{X} = 2\]
As the velocity ratio is ratio. So, it will be unitless.
Hence, the correct option will be C.
Note:- Whenever we come up with this type of problem we should remember that when a load is lifted down by some distance then the force by which it is lifted must be applied for the double distance because when any object attached with pulley is lifted then force is applied on the ropes on different side of the pulley because one side rope move upward and other side rope moves downward by the same distance.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




