
What is velocity of the bob of simple pendulum at its mean position, if it is able to rise to vertical height of $10cm$ ? (Take $g = 9.8\,m{\sec ^{ - 2}}$ )
A. $0.6\,m{\sec ^{ - 1}}$
B. $1.4\,m{\sec ^{ - 1}}$
C. $1.8\,m{\sec ^{ - 1}}$
D. $2.2\,m{\sec ^{ - 1}}$

Answer
500.7k+ views
Hint: In order to solve this question we need to understand energy conservation. Energy conservation states that only when the work done by mechanical force is zero then increase in kinetic energy is equal to decrease in potential energy or decrease in kinetic energy is equal to increase its potential energy. Energy only changes form, it is neither constructive nor destructive in nature.
Complete step by step answer:
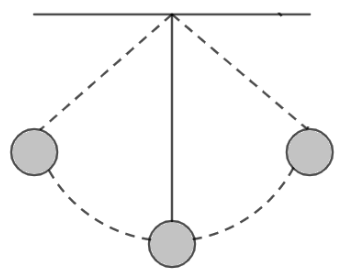
Since, the work done by mechanical force is zero because there is no dissipative force which acts on the bob and thereby restricting its motion, also gravitational force is a conservative force. So the energy conservation principle could be applied.Let the bob has velocity, $u$ $m{\sec ^{ - 1}}$ at its mean position. Since the bob raises by a height $h = 10\,cm = 0.1\,m$.
So increase in potential energy is,
$\Delta U = mgh$
Here, “m” is mass of simple pendulum and “g” is acceleration due to gravity
Also, at maximum height, simple pendulum stops so, final velocity of pendulum is,
$v = 0\,m{\sec ^{ - 1}}$
So decrease in kinetic energy is,
$\Delta K.E = \dfrac{1}{2}m{u^2} - \dfrac{1}{2}m{v^2}$
$\Rightarrow \Delta K.E = \dfrac{1}{2}m{u^2}$
So according to energy conservation law, we have,
$\Delta K.E = \Delta U$
Putting values we get,
$\dfrac{1}{2}m{u^2} = mgh$
$\Rightarrow {u^2} = 2gh$
So speed is, $u = \sqrt {2gh} $
Putting values we get,
$u = \sqrt {(2 \times 9.8 \times 0.1)} m{\sec ^{ - 1}}$
$\therefore u = 1.4\,m{\sec ^{ - 1}}$
The correct option is B.
Note: It should be remembered that while calculating potential difference we have set a reference a point at the mean position and consider it at zero height, so potential difference at reference point is zero, so change in potential energy is equal to potential energy at height up to which it rises. If no net force acts on the body then its momentum is conserved.
Complete step by step answer:
Since, the work done by mechanical force is zero because there is no dissipative force which acts on the bob and thereby restricting its motion, also gravitational force is a conservative force. So the energy conservation principle could be applied.Let the bob has velocity, $u$ $m{\sec ^{ - 1}}$ at its mean position. Since the bob raises by a height $h = 10\,cm = 0.1\,m$.
So increase in potential energy is,
$\Delta U = mgh$
Here, “m” is mass of simple pendulum and “g” is acceleration due to gravity
Also, at maximum height, simple pendulum stops so, final velocity of pendulum is,
$v = 0\,m{\sec ^{ - 1}}$
So decrease in kinetic energy is,
$\Delta K.E = \dfrac{1}{2}m{u^2} - \dfrac{1}{2}m{v^2}$
$\Rightarrow \Delta K.E = \dfrac{1}{2}m{u^2}$
So according to energy conservation law, we have,
$\Delta K.E = \Delta U$
Putting values we get,
$\dfrac{1}{2}m{u^2} = mgh$
$\Rightarrow {u^2} = 2gh$
So speed is, $u = \sqrt {2gh} $
Putting values we get,
$u = \sqrt {(2 \times 9.8 \times 0.1)} m{\sec ^{ - 1}}$
$\therefore u = 1.4\,m{\sec ^{ - 1}}$
The correct option is B.
Note: It should be remembered that while calculating potential difference we have set a reference a point at the mean position and consider it at zero height, so potential difference at reference point is zero, so change in potential energy is equal to potential energy at height up to which it rises. If no net force acts on the body then its momentum is conserved.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




