
Vector $M$ of magnitude $5$ cm, is at ${36.9^ \circ }$ counter clockwise from the +X axis. It is added to vector $N$ , and the resultant is a vector of magnitude $5$ cm at ${53.1^ \circ }$ clockwise from +X axis. Find the magnitude of $N$
A. $5\sqrt 2 $
B. $9\sqrt 2 $
C. $3\sqrt 2 $
D. $7\sqrt 2 $
Answer
508.2k+ views
Hint: To find the magnitude of $N$ , we have to draw the vectors on the graph and find the angle between the vectors to find the magnitude of the vectors by using Pythagoras’ theorem. We use the concept of positive and negative angles from the origin.
Complete step by step answer:
We are given that, vector $M$ of magnitude $5$ cm is ${36.9^ \circ }$ counter clockwise from +X axis is added to vector $N$, the resultant vector is of magnitude $5$ cm is ${53.1^ \circ }$ clockwise from +X axis. Representing these vectors, we have
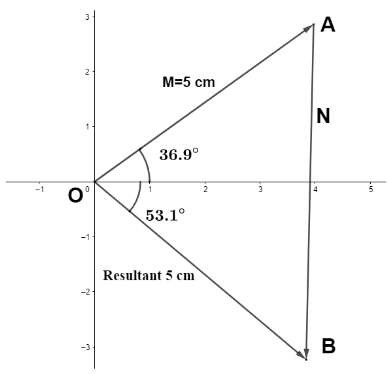
Vector $M$, $N$ and the resultant of $M\& N$ makes a right angled triangle.So, using Pythagoras’ theorem in $\Delta AOB$, we have
Magnitude of vector $N$= $\therefore \left| N \right| = \sqrt {O{A^2} + O{B^2}} $
$\left| N \right| = \sqrt {{5^2} + {5^2}} $
$\therefore \left| N \right| = 5\sqrt 2 $ cm
The magnitude of $N$ is $5\sqrt 2 $ cm.
Hence, option A is correct.
Note: We should use the positive and negative angles notation for counterclockwise and clockwise angles, respectively. We can also use the triangle law of addition of the vectors which states that when two vectors are represented as two sides of the triangle with the order of magnitude and direction, then the third side of the triangle represents the magnitude and direction of the resultant vector.
Complete step by step answer:
We are given that, vector $M$ of magnitude $5$ cm is ${36.9^ \circ }$ counter clockwise from +X axis is added to vector $N$, the resultant vector is of magnitude $5$ cm is ${53.1^ \circ }$ clockwise from +X axis. Representing these vectors, we have

Vector $M$, $N$ and the resultant of $M\& N$ makes a right angled triangle.So, using Pythagoras’ theorem in $\Delta AOB$, we have
Magnitude of vector $N$= $\therefore \left| N \right| = \sqrt {O{A^2} + O{B^2}} $
$\left| N \right| = \sqrt {{5^2} + {5^2}} $
$\therefore \left| N \right| = 5\sqrt 2 $ cm
The magnitude of $N$ is $5\sqrt 2 $ cm.
Hence, option A is correct.
Note: We should use the positive and negative angles notation for counterclockwise and clockwise angles, respectively. We can also use the triangle law of addition of the vectors which states that when two vectors are represented as two sides of the triangle with the order of magnitude and direction, then the third side of the triangle represents the magnitude and direction of the resultant vector.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




