
Vascularization in plants occurs through.
(a) Differentiation of procambium followed by primary phloem and then primary xylem
(b) Differentiation of procambium followed by the development of xylem and phloem
(c) Simultaneous differentiation of procambium, xylem, and phloem
(d) Differentiation of procambium is immediately followed by the development of secondary xylem and secondary phloem
Answer
590.1k+ views
Hint: Vascularisation in plants occurs at two stages primary and secondary. The primary growth involves the formation of procambium, xylem, and phloem, while the secondary growth involves the formation of secondary or vascular cambium leading to the formation of secondary vascular bundles.
Complete answer:
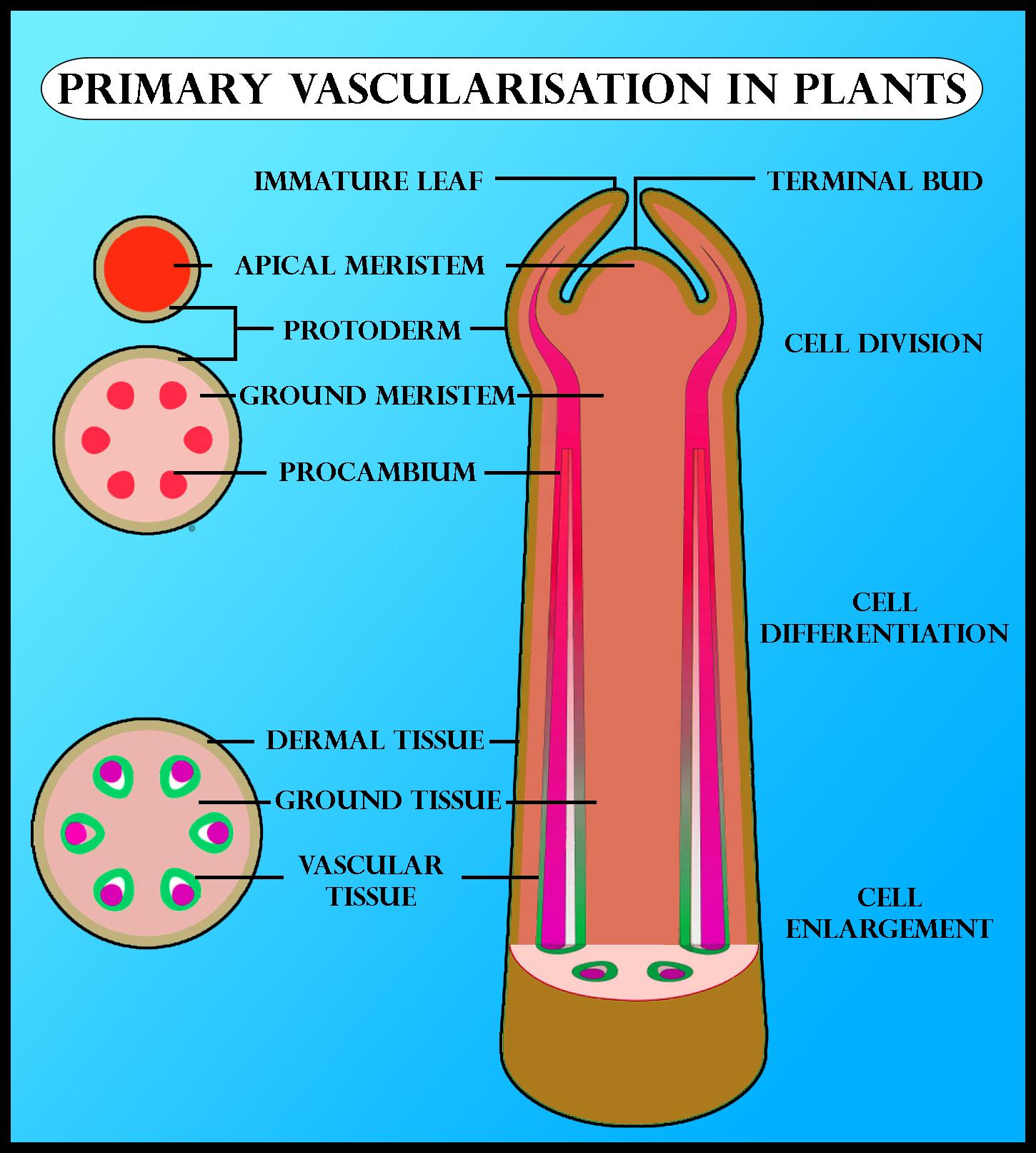
Vascularization in plants occurs through differentiation of procambium followed by the development of xylem and phloem. Vascular plants grow and develop by the activity of organ forming regions, the growing points. The mechanical support and additional conductive pathways required due to increased bulk is provided by the enlargement of the older parts of the shoot and root axes. New cells are added to the vascular bundles through the activity of special tissues called ‘meristems’. The process by which the vascular tissues of plants namely xylem and phloem are formed is called ‘vascularization’ and the meristematic tissue involved in providing the primary tissues of the vascular system is called ‘procambium.’ During the primary growth of the plants, the procambium is formed first followed by the formation of xylem. Phloem development succeeds in the formation of procambium and xylem.
So, the correct answer is, ‘Differentiation of procambium followed by the development of xylem and phloem.’
Note: During the development of primary vascular bundles in plants, a meristematic tissue called procambium is formed in the form of strands. These stands are positioned related to the leaves, in the form of leaf traces. The primary xylem matures in or near a leaf. It further differentiates basipetally in the axis and acropetally in the leaf. On the other hand phloem cells differentiate from procambial cells in a continuous, acropetal fashion.
Complete answer:
Vascularization in plants occurs through differentiation of procambium followed by the development of xylem and phloem. Vascular plants grow and develop by the activity of organ forming regions, the growing points. The mechanical support and additional conductive pathways required due to increased bulk is provided by the enlargement of the older parts of the shoot and root axes. New cells are added to the vascular bundles through the activity of special tissues called ‘meristems’. The process by which the vascular tissues of plants namely xylem and phloem are formed is called ‘vascularization’ and the meristematic tissue involved in providing the primary tissues of the vascular system is called ‘procambium.’ During the primary growth of the plants, the procambium is formed first followed by the formation of xylem. Phloem development succeeds in the formation of procambium and xylem.
So, the correct answer is, ‘Differentiation of procambium followed by the development of xylem and phloem.’
Note: During the development of primary vascular bundles in plants, a meristematic tissue called procambium is formed in the form of strands. These stands are positioned related to the leaves, in the form of leaf traces. The primary xylem matures in or near a leaf. It further differentiates basipetally in the axis and acropetally in the leaf. On the other hand phloem cells differentiate from procambial cells in a continuous, acropetal fashion.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




