
What is the value of ${{\sin }^{2}}x+{{\cos }^{2}}x=$____?
(a) 1
(b) -1
(c) 0
(d) $-\sqrt{2}$
Answer
622.5k+ views
Hint: Consider any right-angled triangle. Use the fact that sine of any angle is the ratio of the perpendicular to the hypotenuse and cosine of any angle is the ratio of the base to the hypotenuse. Simplify the expression using the Pythagoras Theorem of the right – angled triangle to calculate the value of the given trigonometric expression.
Complete step by step answer:
We have to calculate the value of ${{\sin }^{2}}x+{{\cos }^{2}}x$.
Let’s consider a right-angled triangle $\Delta ABC$, right-angled at B. Let the length of sides be $AB=c,BC=a,AC=b$ and $\angle ACB=x$ , as shown in the figure.
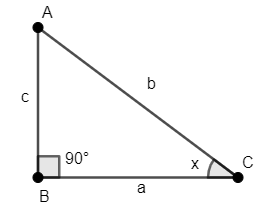
We will use Pythagorean Theorem in the $\Delta ABC$. Thus, we have ${{a}^{2}}+{{c}^{2}}={{b}^{2}}.....\left( 1 \right)$.
We know that sine of any angle is the ratio of the perpendicular to the hypotenuse. Thus, we have $\sin \left( \angle ACB \right)=\sin x=\dfrac{c}{b}$.
Squaring the above equation on both sides, we have ${{\sin }^{2}}x=\dfrac{{{c}^{2}}}{{{b}^{2}}}.....\left( 2 \right)$.
Similarly, we know that cosine of any angle is the ratio of the base to the hypotenuse. Thus, we have $\cos \left( \angle ACB \right)=\cos x=\dfrac{a}{b}$.
Squaring the above equation on both sides, we have ${{\cos }^{2}}x=\dfrac{{{a}^{2}}}{{{b}^{2}}}.....\left( 3 \right)$.
Adding equation (2) and (3), we have ${{\sin }^{2}}x+{{\cos }^{2}}x=\dfrac{{{c}^{2}}}{{{b}^{2}}}+\dfrac{{{a}^{2}}}{{{b}^{2}}}$.
Simplifying the above equation, we have ${{\sin }^{2}}x+{{\cos }^{2}}x=\dfrac{{{c}^{2}}}{{{b}^{2}}}+\dfrac{{{a}^{2}}}{{{b}^{2}}}=\dfrac{{{c}^{2}}+{{a}^{2}}}{{{b}^{2}}}.....\left( 4 \right)$.
Substituting equation (1) in equation (4), we have ${{\sin }^{2}}x+{{\cos }^{2}}x=\dfrac{{{c}^{2}}+{{a}^{2}}}{{{b}^{2}}}=\dfrac{{{b}^{2}}}{{{b}^{2}}}=1$.
Hence, the value of ${{\sin }^{2}}x+{{\cos }^{2}}x$ is 1, which is option (a).
Note: We can also solve this question by taking the polar coordinates of a unit circle of the form $\left( \cos x,\sin x \right)$ and then substituting it in the equation of the unit circle which is ${{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}=1$. One must keep in mind that ${{\sin }^{2}}x+{{\cos }^{2}}x=1$ is a trigonometric identity, i.e., it holds for all possible values of ‘x’.
Complete step by step answer:
We have to calculate the value of ${{\sin }^{2}}x+{{\cos }^{2}}x$.
Let’s consider a right-angled triangle $\Delta ABC$, right-angled at B. Let the length of sides be $AB=c,BC=a,AC=b$ and $\angle ACB=x$ , as shown in the figure.

We will use Pythagorean Theorem in the $\Delta ABC$. Thus, we have ${{a}^{2}}+{{c}^{2}}={{b}^{2}}.....\left( 1 \right)$.
We know that sine of any angle is the ratio of the perpendicular to the hypotenuse. Thus, we have $\sin \left( \angle ACB \right)=\sin x=\dfrac{c}{b}$.
Squaring the above equation on both sides, we have ${{\sin }^{2}}x=\dfrac{{{c}^{2}}}{{{b}^{2}}}.....\left( 2 \right)$.
Similarly, we know that cosine of any angle is the ratio of the base to the hypotenuse. Thus, we have $\cos \left( \angle ACB \right)=\cos x=\dfrac{a}{b}$.
Squaring the above equation on both sides, we have ${{\cos }^{2}}x=\dfrac{{{a}^{2}}}{{{b}^{2}}}.....\left( 3 \right)$.
Adding equation (2) and (3), we have ${{\sin }^{2}}x+{{\cos }^{2}}x=\dfrac{{{c}^{2}}}{{{b}^{2}}}+\dfrac{{{a}^{2}}}{{{b}^{2}}}$.
Simplifying the above equation, we have ${{\sin }^{2}}x+{{\cos }^{2}}x=\dfrac{{{c}^{2}}}{{{b}^{2}}}+\dfrac{{{a}^{2}}}{{{b}^{2}}}=\dfrac{{{c}^{2}}+{{a}^{2}}}{{{b}^{2}}}.....\left( 4 \right)$.
Substituting equation (1) in equation (4), we have ${{\sin }^{2}}x+{{\cos }^{2}}x=\dfrac{{{c}^{2}}+{{a}^{2}}}{{{b}^{2}}}=\dfrac{{{b}^{2}}}{{{b}^{2}}}=1$.
Hence, the value of ${{\sin }^{2}}x+{{\cos }^{2}}x$ is 1, which is option (a).
Note: We can also solve this question by taking the polar coordinates of a unit circle of the form $\left( \cos x,\sin x \right)$ and then substituting it in the equation of the unit circle which is ${{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}=1$. One must keep in mind that ${{\sin }^{2}}x+{{\cos }^{2}}x=1$ is a trigonometric identity, i.e., it holds for all possible values of ‘x’.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 10 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
State and explain Ohms law class 10 physics CBSE

Write a letter to the editor of a newspaper explaining class 10 english CBSE

Distinguish between soap and detergent class 10 chemistry CBSE

a Why did Mendel choose pea plants for his experiments class 10 biology CBSE

What is a "free hit" awarded for in limited-overs cricket?

Draw the diagram of the sectional view of the human class 10 biology CBSE




