
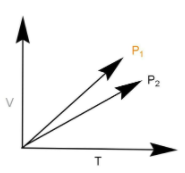
V vs T curves at different pressure \[{{\text{P}}_1}{\text{ and }}{{\text{P}}_2}\] for an ideal gas shown below. Which one of the following is correct?
A.\[{{\text{P}}_1} > {{\text{P}}_2}\]
B.\[{{\text{P}}_1} < {\text{ }}{{\text{P}}_2}\]
C.\[{{\text{P}}_1} = {\text{ }}{{\text{P}}_2}\]
D.Relation between \[{{\text{P}}_1}{\text{ and }}{{\text{P}}_2}\] depends on the gas.

Answer
573.6k+ views
Hint: With the help of an ideal gas equation we will form a linear equation. Using the value of slope from there we will compare both the pressure.
Formula used:
\[{\text{PV}} = {\text{nRT}}\]
Here P is pressure, V is volume, n is number of moles, R is universal gas constant and T is temperature.
Complete step by step solution:
We have been given the graph between volume and temperature, with volume being on y axis and temperature being on x axis. We can rewrite the ideal gas equation as:
\[{\text{V}} = \dfrac{{{\text{nR}}}}{{\text{P}}}{\text{T}}\]
The general equation for a straight line is \[{\text{y}} = {\text{mx}} + {\text{c}}\]
Here y is the coordinate on y axis, x is the coordinate of x axis, m is the slope and c is the intercept made on y axis. Since in our case the line passes through the origin hence the intercept will be zero.
The equation will reduce to: \[{\text{y}} = {\text{mx}}\]
If we compare this equation to ideal gas equation then we will get y as V and x as T and the slope will be:
\[{\text{m}} = \dfrac{{{\text{nR}}}}{{\text{P}}}\]
According to the above formula slope and pressure are inversely proportional to each other. Now it is clear that the slope of \[{{\text{P}}_1}\] line is more than the slope of \[{{\text{P}}_2}\] . Slope represents tangent of angle. The line \[{{\text{P}}_1}\] makes a greater angle and hence has higher slope. Thus the pressure \[{{\text{P}}_1}\] will be lesser than \[{{\text{P}}_2}\] .
Thus, the correct option is B.
Note:
The ideal gas equation is made up using the basic laws such as Boyle’s law, Charles’ law etc. If we keep the temperature constant the product of pressure and volume will also become constant which signifies Boyle's law. Similarly other laws can be proved.
Formula used:
\[{\text{PV}} = {\text{nRT}}\]
Here P is pressure, V is volume, n is number of moles, R is universal gas constant and T is temperature.
Complete step by step solution:
We have been given the graph between volume and temperature, with volume being on y axis and temperature being on x axis. We can rewrite the ideal gas equation as:
\[{\text{V}} = \dfrac{{{\text{nR}}}}{{\text{P}}}{\text{T}}\]
The general equation for a straight line is \[{\text{y}} = {\text{mx}} + {\text{c}}\]
Here y is the coordinate on y axis, x is the coordinate of x axis, m is the slope and c is the intercept made on y axis. Since in our case the line passes through the origin hence the intercept will be zero.
The equation will reduce to: \[{\text{y}} = {\text{mx}}\]
If we compare this equation to ideal gas equation then we will get y as V and x as T and the slope will be:
\[{\text{m}} = \dfrac{{{\text{nR}}}}{{\text{P}}}\]
According to the above formula slope and pressure are inversely proportional to each other. Now it is clear that the slope of \[{{\text{P}}_1}\] line is more than the slope of \[{{\text{P}}_2}\] . Slope represents tangent of angle. The line \[{{\text{P}}_1}\] makes a greater angle and hence has higher slope. Thus the pressure \[{{\text{P}}_1}\] will be lesser than \[{{\text{P}}_2}\] .
Thus, the correct option is B.
Note:
The ideal gas equation is made up using the basic laws such as Boyle’s law, Charles’ law etc. If we keep the temperature constant the product of pressure and volume will also become constant which signifies Boyle's law. Similarly other laws can be proved.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




