
What is $ v - t $ graph? Derive $ x = {v_0}t + \dfrac{1}{2}a{t^2} $ using $ v - t $ graph.
Answer
543.3k+ views
Hint :In order to solve this question, first of all define the velocity time graphs using the explanation of variation of velocity. After that, construct a $ v - t $ graph and take the area under it as the distance, let the initial and final velocities for the considered case in the graph be $ {v_0} $ and $ v $ respectively.
$ s = areaofABCD $
Where $ are ABE = \dfrac{1}{2} \times B \times H $
And the $ area of ECD = L \times B $
The first equation of motion
$ v = {v_0} + at \\
\Rightarrow v - {v_0} = at \\ $
Complete Step By Step Answer:
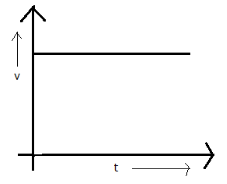
A velocity –time graph is the representation of variation of velocity of a moving body with respect to the dimension time. This graph could be of any type. For the accelerated motion, the line will not be parallel to any of the axes. However, for any other graph that is with zero acceleration, the line will be parallel to the time axis.
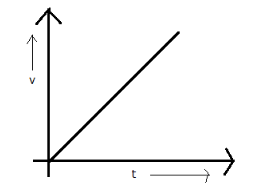
This is a velocity-time graph for the accelerated motion
And for the motion with zero acceleration
Now consider this graph
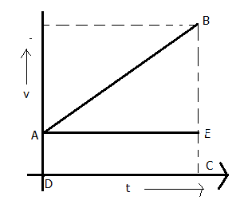
We know that the distance covered by a body is equal to the area under this graph,
$ s = area of ABC $
$ s = areaofABCD \\
\Rightarrow s = areaofABE + areaofAECD \\
\Rightarrow s = \dfrac{1}{2} \times B \times H + L \times B \\
\Rightarrow s = \dfrac{1}{2} \times AE \times BE + AE \times EC \\ $
Now if $ t $ is the total time taken, and $ v $ is the final velocity, and $ {v_0} $ be the initial velocity i.e. at point A
So,
$ AE = t \\
BE = v - {v_0} \\
EC = {v_0} \\ $
Now putting these values in the relation
$ \Rightarrow s = \dfrac{1}{2} \times t \times \left( {v - {v_0}} \right) + t \times {v_0} $
Now as we know that, according to the first equation of motion
$ v = {v_0} + at \\
\Rightarrow v - {v_0} = at \\ $
Using this value in the relation above
$ \Rightarrow s = {v_0}t + \dfrac{1}{2}a{t^2} $
Hence, derived.
Note :
The variable $ a $ in the above equations is the acceleration of the body in motion that we have considered which depends on the slope of the graph that we have drawn. It is important to note that the area under all the $ v - t $ graphs is always equal to the distance travelled by the body under motion.
$ s = areaofABCD $
Where $ are ABE = \dfrac{1}{2} \times B \times H $
And the $ area of ECD = L \times B $
The first equation of motion
$ v = {v_0} + at \\
\Rightarrow v - {v_0} = at \\ $
Complete Step By Step Answer:
A velocity –time graph is the representation of variation of velocity of a moving body with respect to the dimension time. This graph could be of any type. For the accelerated motion, the line will not be parallel to any of the axes. However, for any other graph that is with zero acceleration, the line will be parallel to the time axis.
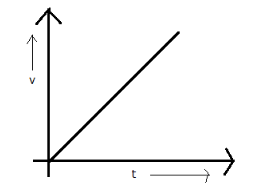
This is a velocity-time graph for the accelerated motion
And for the motion with zero acceleration

Now consider this graph

We know that the distance covered by a body is equal to the area under this graph,
$ s = area of ABC $
$ s = areaofABCD \\
\Rightarrow s = areaofABE + areaofAECD \\
\Rightarrow s = \dfrac{1}{2} \times B \times H + L \times B \\
\Rightarrow s = \dfrac{1}{2} \times AE \times BE + AE \times EC \\ $
Now if $ t $ is the total time taken, and $ v $ is the final velocity, and $ {v_0} $ be the initial velocity i.e. at point A
So,
$ AE = t \\
BE = v - {v_0} \\
EC = {v_0} \\ $
Now putting these values in the relation
$ \Rightarrow s = \dfrac{1}{2} \times t \times \left( {v - {v_0}} \right) + t \times {v_0} $
Now as we know that, according to the first equation of motion
$ v = {v_0} + at \\
\Rightarrow v - {v_0} = at \\ $
Using this value in the relation above
$ \Rightarrow s = {v_0}t + \dfrac{1}{2}a{t^2} $
Hence, derived.
Note :
The variable $ a $ in the above equations is the acceleration of the body in motion that we have considered which depends on the slope of the graph that we have drawn. It is important to note that the area under all the $ v - t $ graphs is always equal to the distance travelled by the body under motion.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




