
How do you use the unit circle to find the exact value of \[\cos \left( \dfrac{7\pi }{3} \right)\]?
Answer
559.5k+ views
Hint: To solve these types of problems, we should know some of the trigonometric properties. The first one is, \[\cos (2\pi +x)=\cos x\]. This is true because when a point completes one rotation and comes back in the first quadrant its reference angle equals \[\theta -2\pi \], where \[\theta \] is the total angle rotated by the point.
Complete answer:
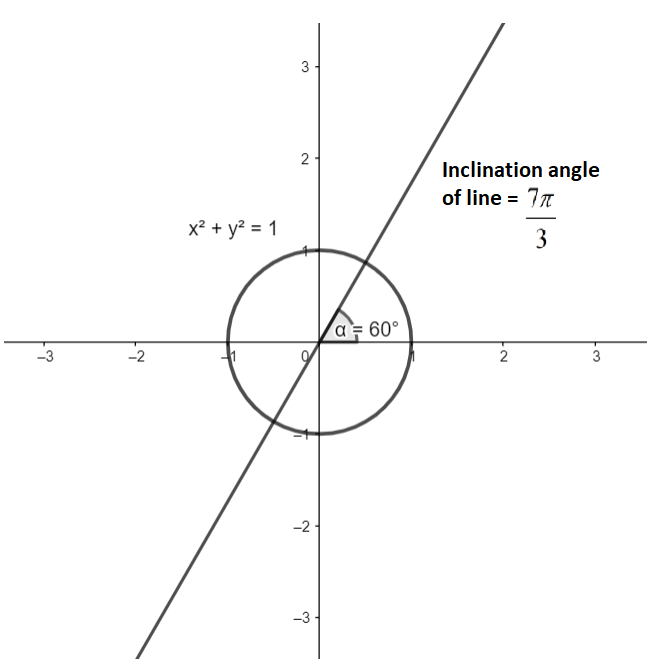
We are asked to find the value of the \[\cos \left( \dfrac{7\pi }{3} \right)\]. From the given figure we can see that the unit circle and the coordinate axes have divided the coordinate plane into 4 sectors. Each of those sectors is the quadrant of the coordinate axes.
As we can see that the line with the inclination \[\dfrac{7\pi }{3}\], lies in the first quadrant. As it has completed a full rotation before coming back in the first sector. The angle can be written in the form of \[2\pi +x\]. Comparing this with the inclination of the line, we get
\[\Rightarrow 2\pi +x=\dfrac{7\pi }{3}\]
Subtracting \[2\pi \] from both sides of the above equation, we get
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow 2\pi +x-2\pi =\dfrac{7\pi }{3}-2\pi \\
& \Rightarrow x=\dfrac{\pi }{3} \\
\end{align}\]
we want to find the value of \[\cos \left( \dfrac{7\pi }{3} \right)\]. As we have seen the angle \[\dfrac{7\pi }{3}\] can also be written as \[2\pi +\dfrac{\pi }{3}\]. Using this in the evaluation of the value of the \[\cos \left( \dfrac{7\pi }{3} \right)\], we get
\[\Rightarrow \cos \left( \dfrac{7\pi }{3} \right)=\cos \left( 2\pi +\dfrac{\pi }{3} \right)\]
We know the property \[\cos (2\pi +x)=\cos x\], using this in the for the above expression we get
\[\Rightarrow \cos \left( 2\pi +\dfrac{\pi }{3} \right)=\cos \left( \dfrac{\pi }{3} \right)\]
As we know that the value of \[\cos \left( \dfrac{\pi }{3} \right)\] is \[\dfrac{1}{2}\].
Hence, the value of \[\cos \left( \dfrac{7\pi }{3} \right)\] equals \[\dfrac{1}{2}\].
Note: The line drawn in the figure is just for reference, it is to show the angle of inclination \[\dfrac{7\pi }{3}\]. The question can be solved without it. Also, to solve these types of problems, one should know the trigonometric properties of the ratios.
Complete answer:

We are asked to find the value of the \[\cos \left( \dfrac{7\pi }{3} \right)\]. From the given figure we can see that the unit circle and the coordinate axes have divided the coordinate plane into 4 sectors. Each of those sectors is the quadrant of the coordinate axes.
As we can see that the line with the inclination \[\dfrac{7\pi }{3}\], lies in the first quadrant. As it has completed a full rotation before coming back in the first sector. The angle can be written in the form of \[2\pi +x\]. Comparing this with the inclination of the line, we get
\[\Rightarrow 2\pi +x=\dfrac{7\pi }{3}\]
Subtracting \[2\pi \] from both sides of the above equation, we get
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow 2\pi +x-2\pi =\dfrac{7\pi }{3}-2\pi \\
& \Rightarrow x=\dfrac{\pi }{3} \\
\end{align}\]
we want to find the value of \[\cos \left( \dfrac{7\pi }{3} \right)\]. As we have seen the angle \[\dfrac{7\pi }{3}\] can also be written as \[2\pi +\dfrac{\pi }{3}\]. Using this in the evaluation of the value of the \[\cos \left( \dfrac{7\pi }{3} \right)\], we get
\[\Rightarrow \cos \left( \dfrac{7\pi }{3} \right)=\cos \left( 2\pi +\dfrac{\pi }{3} \right)\]
We know the property \[\cos (2\pi +x)=\cos x\], using this in the for the above expression we get
\[\Rightarrow \cos \left( 2\pi +\dfrac{\pi }{3} \right)=\cos \left( \dfrac{\pi }{3} \right)\]
As we know that the value of \[\cos \left( \dfrac{\pi }{3} \right)\] is \[\dfrac{1}{2}\].
Hence, the value of \[\cos \left( \dfrac{7\pi }{3} \right)\] equals \[\dfrac{1}{2}\].
Note: The line drawn in the figure is just for reference, it is to show the angle of inclination \[\dfrac{7\pi }{3}\]. The question can be solved without it. Also, to solve these types of problems, one should know the trigonometric properties of the ratios.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




