
How do you use the Pythagorean theorem to determine if the following three numbers could represent the measures of the sides of a right triangle: 20, 6, 21?
Answer
531.9k+ views
Hint: Here in this question, we have to check whether the given sides of a right angled triangle using a Pythagoras's theorem, as we know the formula of Pythagoras theorem i.e., \[A{C^2} = A{B^2} + B{C^2}\] , where AB, BC, AC are the sides of the right angled triangle if the given sides satisfied the condition by showing Left hand side is equal to right hand side. Then it’s a right angle triangle otherwise not a right angled triangle.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Pythagoras's theorem is a fundamental relation in Euclidean geometry among the three sides of a right triangle. It states that the area of the square whose side is the hypotenuse (the side opposite the right angle) is equal to the sum of the areas of the squares on the other two sides. This theorem can be written as an equation relating the lengths of the sides a, b and c, often called the Pythagorean equation:
\[{c^2} = {a^2} + {b^2}\]
where c represents the length of the hypotenuse and a and b the lengths of the triangle's other two sides.
Consider the given measures 20, 6, 21
We have to show the given measurements are right angled triangle
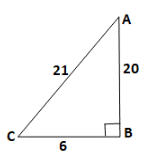
Assume \[\Delta \,ABC\] is a right angled triangle, \[AC = 21\] is the hypotenuse side because in the right angle triangle The Hypotenuse has to be longer than the other two sides otherwise you could not construct the triangle.
\[AB = 20\] and \[BC = 6\] are the measurements of the other two sides of the triangle.
Consider the equation of Pythagoras’s theorem for \[\Delta \,ABC\] is given by:
\[ \Rightarrow \,\,A{C^2} = A{B^2} + B{C^2}\]
On substituting the values, we get
\[ \Rightarrow \,\,{21^2} = {20^2} + {6^2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \,\,441 = 400 + 36\]
\[ \Rightarrow \,\,441 \ne 436\]
these values can not be equal
Hence, the given three measurements of sides does not contain a right angle triangle.
Note: All of the lengths in the above problem represent the lengths of the sides of a triangle. Recall the Triangle Inequality Theorem from geometry which states: The length of a side in a triangle is less than the sum of the other two sides.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Pythagoras's theorem is a fundamental relation in Euclidean geometry among the three sides of a right triangle. It states that the area of the square whose side is the hypotenuse (the side opposite the right angle) is equal to the sum of the areas of the squares on the other two sides. This theorem can be written as an equation relating the lengths of the sides a, b and c, often called the Pythagorean equation:
\[{c^2} = {a^2} + {b^2}\]
where c represents the length of the hypotenuse and a and b the lengths of the triangle's other two sides.
Consider the given measures 20, 6, 21
We have to show the given measurements are right angled triangle

Assume \[\Delta \,ABC\] is a right angled triangle, \[AC = 21\] is the hypotenuse side because in the right angle triangle The Hypotenuse has to be longer than the other two sides otherwise you could not construct the triangle.
\[AB = 20\] and \[BC = 6\] are the measurements of the other two sides of the triangle.
Consider the equation of Pythagoras’s theorem for \[\Delta \,ABC\] is given by:
\[ \Rightarrow \,\,A{C^2} = A{B^2} + B{C^2}\]
On substituting the values, we get
\[ \Rightarrow \,\,{21^2} = {20^2} + {6^2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \,\,441 = 400 + 36\]
\[ \Rightarrow \,\,441 \ne 436\]
these values can not be equal
Hence, the given three measurements of sides does not contain a right angle triangle.
Note: All of the lengths in the above problem represent the lengths of the sides of a triangle. Recall the Triangle Inequality Theorem from geometry which states: The length of a side in a triangle is less than the sum of the other two sides.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is BLO What is the full form of BLO class 8 social science CBSE

Citizens of India can vote at the age of A 18 years class 8 social science CBSE

Full form of STD, ISD and PCO

What are the 12 elements of nature class 8 chemistry CBSE

Convert 40circ C to Fahrenheit A 104circ F B 107circ class 8 maths CBSE

Right to vote is a AFundamental Right BFundamental class 8 social science CBSE





