
Use the following data to calculate ${\Delta _{lattice}}$ ${H^\Theta }$ for NaBr.
${\Delta _{sub}}$ ${H^\Theta }$ for sodium metal $ = 108.4kJmo{l^{ - 1}}$
Ionization enthalpy of sodium $ = 496kJmo{l^{ - 1}}$
Electron gain enthalpy of bromine $ = - 325kJmo{l^{ - 1}}$
Bond dissociation enthalpy of bromine $ = 192kJmo{l^{ - 1}}$
${\Delta _f}{H^\Theta }$ for NaBr (s) $ = - 360.1kJmo{l^{ - 1}}$
Answer
550.8k+ views
Hint: In this question using the values given , make a Born Haber's cycle for the given data and with the help of Born Haber's cycle lattice enthalpy ${\Delta _{lattice}}$ ${H^\Theta }$ for NaBr can be calculated.
Now from the question
We have the following given values :
${\Delta _{sub}}$ ${H^\Theta }$ for sodium metal $ = 108.4kJmo{l^{ - 1}}$
Ionization enthalpy of sodium IE $ = 496kJmo{l^{ - 1}}$
Electron gain enthalpy of bromine $ = - 325kJmo{l^{ - 1}}$
${\Delta _{eg}}{H^\Theta } = - 325kJmo{l^{ - 1}}$
Bond dissociation enthalpy of bromine $ = 192kJmo{l^{ - 1}}$
${\Delta _{diss}}{H^\Theta } = 192kJmo{l^{ - 1}}$
${\Delta _f}{H^\Theta }$ for NaBr (s) $ = - 360.1kJmo{l^{ - 1}}$
And $ - U\left( {LatticeEnthalpy} \right)$
Constructing Born Haber's Cycle
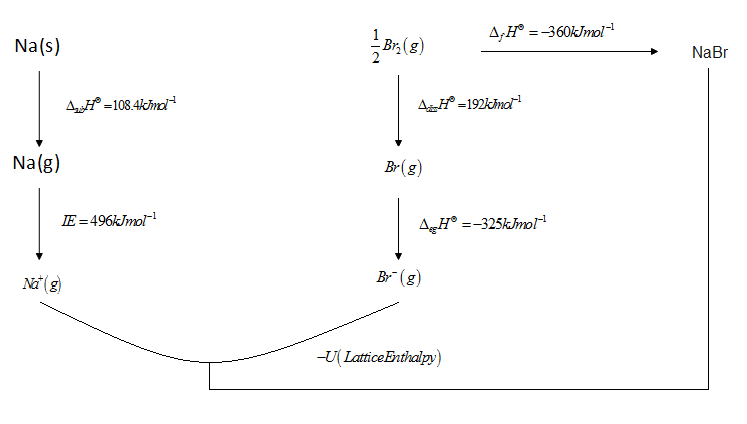
By applying Hess's Law
${\Delta _f}{H^\Theta } = IE + {\Delta _{diss}}{H^\Theta } + U$
$ - 360.1 = 108.4 + 496 + 96 + \left( { - 325} \right) - U$
$U = + 735.5kJmo{l^{ - 1}}$
This is the lattice enthalpy for NaBr ${\Delta _{lattice}}{H^\Theta } = 735.5kJmo{l^{ - 1}}$
Note:
BORN HABER CYCLE :- Born Haber process or generally known as Born Haber cycle is a method which allows us to observe and analyze energies in a chemical reaction. It mostly helps to describe the formation of ionic compounds from different elements. This method also allows us to understand the overall reaction process in a series of steps.
In 1919 a German scientist named Fritz Haber and Max Born introduced the Born-Haber cycle . The Born Haber cycle is mostly used to calculate the lattice energy. It contains many steps or processes which are electron affinity, ionization energy, sublimation energy, the heat of formation and dissociation energy.
HESS LAW:- As it is known that enthalpy is a state function, therefore, it is independent of the path taken to reach the final state starting from the initial state. Now According to Hess’s law, for any reaction involving many steps, the standard reaction enthalpy is independent of the path or number of steps taken, it is the sum of standard enthalpies of all the intermediate reactions occured at the same temperature.
Hess’s law is used to measure the enthalpies of neutralization for many acid-base reactions, using that information and Hess’s law to determine the reaction enthalpies for two salts in aqueous solution.
Now from the question
We have the following given values :
${\Delta _{sub}}$ ${H^\Theta }$ for sodium metal $ = 108.4kJmo{l^{ - 1}}$
Ionization enthalpy of sodium IE $ = 496kJmo{l^{ - 1}}$
Electron gain enthalpy of bromine $ = - 325kJmo{l^{ - 1}}$
${\Delta _{eg}}{H^\Theta } = - 325kJmo{l^{ - 1}}$
Bond dissociation enthalpy of bromine $ = 192kJmo{l^{ - 1}}$
${\Delta _{diss}}{H^\Theta } = 192kJmo{l^{ - 1}}$
${\Delta _f}{H^\Theta }$ for NaBr (s) $ = - 360.1kJmo{l^{ - 1}}$
And $ - U\left( {LatticeEnthalpy} \right)$
Constructing Born Haber's Cycle

By applying Hess's Law
${\Delta _f}{H^\Theta } = IE + {\Delta _{diss}}{H^\Theta } + U$
$ - 360.1 = 108.4 + 496 + 96 + \left( { - 325} \right) - U$
$U = + 735.5kJmo{l^{ - 1}}$
This is the lattice enthalpy for NaBr ${\Delta _{lattice}}{H^\Theta } = 735.5kJmo{l^{ - 1}}$
Note:
BORN HABER CYCLE :- Born Haber process or generally known as Born Haber cycle is a method which allows us to observe and analyze energies in a chemical reaction. It mostly helps to describe the formation of ionic compounds from different elements. This method also allows us to understand the overall reaction process in a series of steps.
In 1919 a German scientist named Fritz Haber and Max Born introduced the Born-Haber cycle . The Born Haber cycle is mostly used to calculate the lattice energy. It contains many steps or processes which are electron affinity, ionization energy, sublimation energy, the heat of formation and dissociation energy.
HESS LAW:- As it is known that enthalpy is a state function, therefore, it is independent of the path taken to reach the final state starting from the initial state. Now According to Hess’s law, for any reaction involving many steps, the standard reaction enthalpy is independent of the path or number of steps taken, it is the sum of standard enthalpies of all the intermediate reactions occured at the same temperature.
Hess’s law is used to measure the enthalpies of neutralization for many acid-base reactions, using that information and Hess’s law to determine the reaction enthalpies for two salts in aqueous solution.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




