
How do you use the epsilon delta definition to find the limit of \[\left( {\dfrac{{{x^2} + x - 6}}{{x - 2}}} \right)\]as \[x\] approaches \[2\]\[?\]
Answer
525.3k+ views
Hint: Here we have to check that the given function is defined or not at \[x = 2\]. If it is defined, then by the definition epsilon delta finds the relationship between epsilon and delta to prove the limit of the given function as \[x\]approaches to \[2\] it exists and is unique.
Complete step by step solution:
The epsilon-delta definition of limits says that the limit of \[f(x)\]at \[x = c\]is \[L\] if for any \[\varepsilon > 0\] there exists a \[\delta > 0\] such that if the distance of \[x\] from \[c\] is less than \[\delta \], then the distance of f(x) from \[L\] is less than \[\varepsilon \].
Graphical representation of the epsilon-delta definition:
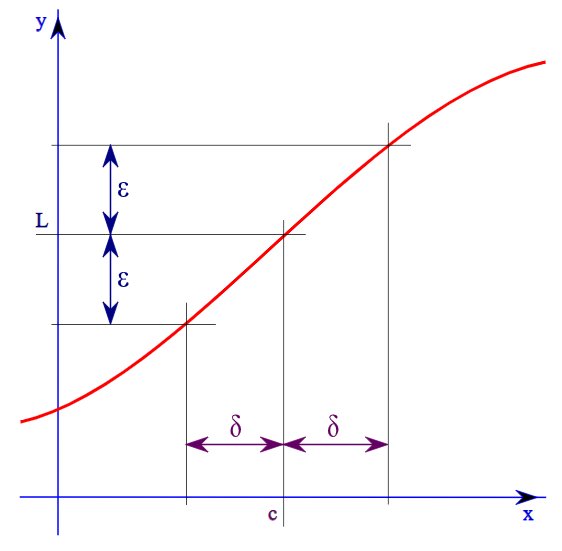
Let the given function say \[f(x) = \left( {\dfrac{{{x^2} + x - 6}}{{x - 2}}} \right)\] and \[L\] be the limit of the given function.
At \[x = 2\], the given function approaches infinity. So, rewriting the given above function, we get \[f(x) = x + 3\]. Hence at \[x = 2\],\[f(2) = 5\].
\[ \Rightarrow \] \[\mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to 2} \left( {\dfrac{{{x^2} + x - 6}}{{x - 2}}} \right) = 5\]
We prove by the epsilon delta definition, for any \[\varepsilon > 0\] there exists a \[\delta > 0\] such that
If \[\left| {x - 2} \right| < \delta \] \[ \Rightarrow \] \[\left| {f(x) - L} \right| < \varepsilon \]
\[ \Rightarrow \left| {x + 3 - 5} \right| < \varepsilon \]
On simplification,
\[ \Rightarrow \left| {x + 2} \right| < \varepsilon \]
\[ \Rightarrow \left| {x + 2} \right| < \delta \]
From the above two equations, we can say
\[ \delta = \varepsilon \]
Hence the limit of \[\left( {\dfrac{{{x^2} + x - 6}}{{x - 2}}} \right)\]as \[x\] approaches \[2\] is \[5\].
Note:
Note that If the limit of the given function at the given point exists then the limit is unique and finite. A function is continuous if you can draw its graph without lifting the pencil. Every differentiable function is continuous but converse is not true.
Complete step by step solution:
The epsilon-delta definition of limits says that the limit of \[f(x)\]at \[x = c\]is \[L\] if for any \[\varepsilon > 0\] there exists a \[\delta > 0\] such that if the distance of \[x\] from \[c\] is less than \[\delta \], then the distance of f(x) from \[L\] is less than \[\varepsilon \].
Graphical representation of the epsilon-delta definition:

Let the given function say \[f(x) = \left( {\dfrac{{{x^2} + x - 6}}{{x - 2}}} \right)\] and \[L\] be the limit of the given function.
At \[x = 2\], the given function approaches infinity. So, rewriting the given above function, we get \[f(x) = x + 3\]. Hence at \[x = 2\],\[f(2) = 5\].
\[ \Rightarrow \] \[\mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to 2} \left( {\dfrac{{{x^2} + x - 6}}{{x - 2}}} \right) = 5\]
We prove by the epsilon delta definition, for any \[\varepsilon > 0\] there exists a \[\delta > 0\] such that
If \[\left| {x - 2} \right| < \delta \] \[ \Rightarrow \] \[\left| {f(x) - L} \right| < \varepsilon \]
\[ \Rightarrow \left| {x + 3 - 5} \right| < \varepsilon \]
On simplification,
\[ \Rightarrow \left| {x + 2} \right| < \varepsilon \]
\[ \Rightarrow \left| {x + 2} \right| < \delta \]
From the above two equations, we can say
\[ \delta = \varepsilon \]
Hence the limit of \[\left( {\dfrac{{{x^2} + x - 6}}{{x - 2}}} \right)\]as \[x\] approaches \[2\] is \[5\].
Note:
Note that If the limit of the given function at the given point exists then the limit is unique and finite. A function is continuous if you can draw its graph without lifting the pencil. Every differentiable function is continuous but converse is not true.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




