
How do I use Pascal's triangle to expand ${{\left( x-1 \right)}^{5}}$ ?
Answer
546.9k+ views
Hint: When expanding the above expression ${{\left( x-1 \right)}^{5}}$we will use binomial expansion and Pascal's triangle formulas. By using both we can easily expand these types of expression. The given equation ${{\left( x-1 \right)}^{5}}$ is in the form of${{\left( a+b \right)}^{n}}$, where let $a$ is equals to $x$ and $b$ is equals to $\left( -1 \right)$ and $n$ is equals to the power of expression which is$\left( 5 \right)$. In mathematics, the binomial expansion describes the algebraic expansion of powers of a binomial. The expression of the binomial expansion is: ${{\left( a+b \right)}^{n}}{{=}^{n}}{{c}_{0}}{{a}^{n}}{{b}^{0}}{{+}^{n}}{{c}_{1}}{{a}^{n-1}}{{b}^{1}}+.................{{+}^{n}}{{c}_{n}}{{a}^{0}}{{b}^{n}}$, where $^{n}{{c}_{0}}{{,}^{n}}{{c}_{1,}}..........{{,}^{n}}{{c}_{n}}$ are the combinations. The combination's general formula is: ${{c}_{n,k}}=\dfrac{n!}{k!\left( n-k \right)!}$, where $n=population$ and $k=picks$ . By using the combinations formula we can rewrite the binomial expansion as: ${{\left( a+b \right)}^{n}}={{a}^{n}}+n{{a}^{n-1}}b+\dfrac{n\left( n-1 \right)}{2!}{{a}^{n-2}}{{b}^{2}}+....................+{{b}^{n}}$.
Complete step by step solution:
Now we will expand the given expression ${{\left( x-1 \right)}^{5}}$by using binomial expansion, then we get
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow {{\left( x-1 \right)}^{5}}={{x}^{5}}+5{{x}^{4}}\left( -1 \right)+\dfrac{5\left( 5-1 \right)}{2!}{{x}^{3}}{{\left( -1 \right)}^{2}}+\dfrac{5\left( 5-1 \right)}{2!}{{x}^{2}}{{\left( -1 \right)}^{^{3}}}+5x{{\left( -1 \right)}^{4}}+{{\left( -1 \right)}^{5}} \\
& \Rightarrow {{\left( x-1 \right)}^{5}}={{x}^{5}}-5{{x}^{4}}+10{{x}^{3}}-10{{x}^{2}}+5x-1 \\
\end{align}$
Hence by using binomial expansion we get the expanded form of ${{\left( x-1 \right)}^{5}}$ is ${{x}^{5}}-5{{x}^{4}}+10{{x}^{3}}-10{{x}^{2}}+5x-1$.
Now we can also apply Pascal's triangle formula for expanding ${{\left( x-1 \right)}^{5}}$. Recall that the first row of Pascal's triangle is:${{\left( a+b \right)}^{0}}$. The Pascal's triangle is a never ending equilateral triangle of numbers which follows a rule of adding the two numbers above to get the number below. So for ${{\left( x-1 \right)}^{5}}$we are looking for the 6th row of Pascal's triangle for coefficients:
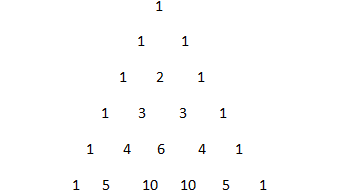
Now expanding the given expression ${{\left( x-1 \right)}^{5}}$by Pascal's triangle formula we get, $\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow {{\left( x-1 \right)}^{5}}=1\cdot {{x}^{5}}+5{{x}^{4}}{{\left( -1 \right)}^{1}}+10{{x}^{3}}{{\left( -1 \right)}^{2}}+10{{x}^{2}}{{\left( -1 \right)}^{3}}+5x{{\left( -1 \right)}^{4}}+{{\left( -1 \right)}^{5}} \\
& \Rightarrow {{\left( x-1 \right)}^{5}}={{x}^{5}}-5{{x}^{4}}+10{{x}^{3}}-10{{x}^{2}}+5x-1 \\
\end{align}$
…Hence we get the expanded form of ${{\left( x-1 \right)}^{5}}$is${{\left( x-1 \right)}^{5}}={{x}^{5}}-5{{x}^{4}}+10{{x}^{3}}-10{{x}^{2}}+5x-1$.
Note:
It is not hard to find the expanded form of any expressions. Here we discussed two methods of finding the expanded form of any type of expression. We only made mistakes in the calculation part, so whenever we solve these types of expressions we are careful.
Complete step by step solution:
Now we will expand the given expression ${{\left( x-1 \right)}^{5}}$by using binomial expansion, then we get
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow {{\left( x-1 \right)}^{5}}={{x}^{5}}+5{{x}^{4}}\left( -1 \right)+\dfrac{5\left( 5-1 \right)}{2!}{{x}^{3}}{{\left( -1 \right)}^{2}}+\dfrac{5\left( 5-1 \right)}{2!}{{x}^{2}}{{\left( -1 \right)}^{^{3}}}+5x{{\left( -1 \right)}^{4}}+{{\left( -1 \right)}^{5}} \\
& \Rightarrow {{\left( x-1 \right)}^{5}}={{x}^{5}}-5{{x}^{4}}+10{{x}^{3}}-10{{x}^{2}}+5x-1 \\
\end{align}$
Hence by using binomial expansion we get the expanded form of ${{\left( x-1 \right)}^{5}}$ is ${{x}^{5}}-5{{x}^{4}}+10{{x}^{3}}-10{{x}^{2}}+5x-1$.
Now we can also apply Pascal's triangle formula for expanding ${{\left( x-1 \right)}^{5}}$. Recall that the first row of Pascal's triangle is:${{\left( a+b \right)}^{0}}$. The Pascal's triangle is a never ending equilateral triangle of numbers which follows a rule of adding the two numbers above to get the number below. So for ${{\left( x-1 \right)}^{5}}$we are looking for the 6th row of Pascal's triangle for coefficients:
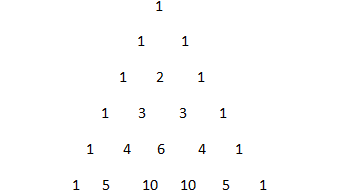
Now expanding the given expression ${{\left( x-1 \right)}^{5}}$by Pascal's triangle formula we get, $\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow {{\left( x-1 \right)}^{5}}=1\cdot {{x}^{5}}+5{{x}^{4}}{{\left( -1 \right)}^{1}}+10{{x}^{3}}{{\left( -1 \right)}^{2}}+10{{x}^{2}}{{\left( -1 \right)}^{3}}+5x{{\left( -1 \right)}^{4}}+{{\left( -1 \right)}^{5}} \\
& \Rightarrow {{\left( x-1 \right)}^{5}}={{x}^{5}}-5{{x}^{4}}+10{{x}^{3}}-10{{x}^{2}}+5x-1 \\
\end{align}$
…Hence we get the expanded form of ${{\left( x-1 \right)}^{5}}$is${{\left( x-1 \right)}^{5}}={{x}^{5}}-5{{x}^{4}}+10{{x}^{3}}-10{{x}^{2}}+5x-1$.
Note:
It is not hard to find the expanded form of any expressions. Here we discussed two methods of finding the expanded form of any type of expression. We only made mistakes in the calculation part, so whenever we solve these types of expressions we are careful.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




