
How do I use Pascal's triangle to expand ${{\left( x+2 \right)}^{5}}$ ?
Answer
546.6k+ views
Hint: To solve these types of questions which are given above ${{\left( x+2 \right)}^{5}}$ we will use a binomial expansion formula. In elementary algebra, the binomial expansion describes the algebraic expansion of powers of binomials.
Complete step by step solution:
The formula of binomial expansion is: ${{\left( a+b \right)}^{n}}{{=}^{n}}{{c}_{0}}{{a}^{n}}{{b}^{0}}{{+}^{n}}{{c}_{1}}{{a}^{n-1}}{{b}^{1}}+...............{{+}^{n}}{{c}_{n}}{{a}^{0}}{{b}^{n}}$ where $a$ and \[b\] are integers and the $^{n}{{c}_{k}}=\dfrac{n!}{k!\left( n-k \right)!}$, where $n$ is equal to power of the expansion and $k$ is equal to picks and this is the combinations general formula. So we can also write binomial expansion by putting the values of combinations. Therefore the formula becomes: ${{\left( a+b \right)}^{n}}={{a}^{n}}+n{{a}^{n-1}}b+\dfrac{n\left( n-1 \right)}{2!}{{b}^{2}}{{a}^{n-2}}+..........+{{b}^{n}}$. So by using this above expression we will solve our given expression${{\left( x+2 \right)}^{5}}$. Now we will expand this expression by using this ${{\left( a+b \right)}^{n}}={{a}^{n}}+n{{a}^{n-1}}b+\dfrac{n\left( n-1 \right)}{2!}{{b}^{2}}{{a}^{n-2}}+..........+{{b}^{n}}$ we get,
$\Rightarrow {{\left( x+2 \right)}^{5}}={{x}^{5}}+5{{x}^{4}}\cdot 2+\dfrac{5\left( 5-1 \right)}{2!}{{x}^{3}}{{\left( 2 \right)}^{2}}+\dfrac{5\left( 5-1 \right)}{2!}{{x}^{2}}{{\left( 2 \right)}^{3}}+5x{{\left( 2 \right)}^{4}}+\left( {{2}^{5}} \right)$ $\Rightarrow {{\left( x+2 \right)}^{5}}={{x}^{5}}+10{{x}^{4}}+10\cdot 4{{x}^{3}}+10\cdot 8{{x}^{2}}+5\cdot 16x+32$ $ {{\left( x+2 \right)}^{5}}={{x}^{5}}+10{{x}^{4}}+40{{x}^{3}}+80{{x}^{2}}+80x+32$
Hence we get the expanded form of given expression ${{\left( x+2 \right)}^{5}}$ which is, ${{\left( x+2 \right)}^{5}}={{x}^{5}}+10{{x}^{4}}+40{{x}^{3}}+80{{x}^{2}}+80x+32$
We can also solve the above expression by using direct Pascal's triangle formula. Pascal's triangle is a never ending equilateral triangle of numbers that follows a rule of adding the two numbers above to get the number below. Here two of the sides are “all $1\grave{\ }s''$ and because the triangle is infinite, there is no “bottom side”.
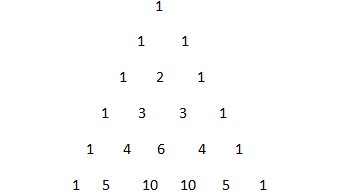
The 5th row of Pascal's triangle is: $1,5,10,10,5,1$. These values are the coefficients in a binomial expansion to the 5th power:
$\Rightarrow {{\left( a+b \right)}^{5}}={{a}^{5}}+5{{a}^{4}}b+10{{a}^{3}}{{b}^{2}}+10{{a}^{2}}{{b}^{3}}+5a{{b}^{4}}+{{b}^{5}}$
Notice this pattern of the exponents: the exponents of $a$ starts at $5$ and goes to $0$ and $b$ starts at $0$ and goes to $5$.
We will apply this in rule ${{\left( a+b \right)}^{5}}={{a}^{5}}+5{{a}^{4}}b+10{{a}^{3}}{{b}^{2}}+10{{a}^{2}}{{b}^{3}}+5a{{b}^{4}}+{{b}^{5}}$ to solve ${{\left( x+2 \right)}^{5}}$:
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow {{\left( x+2 \right)}^{5}}={{x}^{5}}+5{{x}^{4}}\left( 2 \right)+10{{x}^{^{3}}}{{\left( 2 \right)}^{2}}+10{{x}^{2}}{{\left( 2 \right)}^{3}}+5x{{\left( 2 \right)}^{4}}+{{2}^{5}} \\
& \Rightarrow {{x}^{5}}+10{{x}^{4}}+40{{x}^{3}}+80{{x}^{2}}+80x+32 \\
\end{align}$
Hence by using the binomial expansion formula ${{\left( a+b \right)}^{n}}{{=}^{n}}{{c}_{0}}{{a}^{n}}{{b}^{0}}{{+}^{n}}{{c}_{1}}{{a}^{n-1}}{{b}^{1}}+...............{{+}^{n}}{{c}_{n}}{{a}^{0}}{{b}^{n}}$ we get the expansion of ${{\left( x+2 \right)}^{5}}$is ${{x}^{5}}+10{{x}^{4}}+40{{x}^{3}}+80{{x}^{2}}+80x+32$
Note:
Here we can go wrong by writing the wrong binomial expansion formula, sometimes students make mistakes in the powers of $a$and b. Therefore by using the above two methods binomial expansion and Pascal's triangle formula we can easily expand any expression.
Complete step by step solution:
The formula of binomial expansion is: ${{\left( a+b \right)}^{n}}{{=}^{n}}{{c}_{0}}{{a}^{n}}{{b}^{0}}{{+}^{n}}{{c}_{1}}{{a}^{n-1}}{{b}^{1}}+...............{{+}^{n}}{{c}_{n}}{{a}^{0}}{{b}^{n}}$ where $a$ and \[b\] are integers and the $^{n}{{c}_{k}}=\dfrac{n!}{k!\left( n-k \right)!}$, where $n$ is equal to power of the expansion and $k$ is equal to picks and this is the combinations general formula. So we can also write binomial expansion by putting the values of combinations. Therefore the formula becomes: ${{\left( a+b \right)}^{n}}={{a}^{n}}+n{{a}^{n-1}}b+\dfrac{n\left( n-1 \right)}{2!}{{b}^{2}}{{a}^{n-2}}+..........+{{b}^{n}}$. So by using this above expression we will solve our given expression${{\left( x+2 \right)}^{5}}$. Now we will expand this expression by using this ${{\left( a+b \right)}^{n}}={{a}^{n}}+n{{a}^{n-1}}b+\dfrac{n\left( n-1 \right)}{2!}{{b}^{2}}{{a}^{n-2}}+..........+{{b}^{n}}$ we get,
$\Rightarrow {{\left( x+2 \right)}^{5}}={{x}^{5}}+5{{x}^{4}}\cdot 2+\dfrac{5\left( 5-1 \right)}{2!}{{x}^{3}}{{\left( 2 \right)}^{2}}+\dfrac{5\left( 5-1 \right)}{2!}{{x}^{2}}{{\left( 2 \right)}^{3}}+5x{{\left( 2 \right)}^{4}}+\left( {{2}^{5}} \right)$ $\Rightarrow {{\left( x+2 \right)}^{5}}={{x}^{5}}+10{{x}^{4}}+10\cdot 4{{x}^{3}}+10\cdot 8{{x}^{2}}+5\cdot 16x+32$ $ {{\left( x+2 \right)}^{5}}={{x}^{5}}+10{{x}^{4}}+40{{x}^{3}}+80{{x}^{2}}+80x+32$
Hence we get the expanded form of given expression ${{\left( x+2 \right)}^{5}}$ which is, ${{\left( x+2 \right)}^{5}}={{x}^{5}}+10{{x}^{4}}+40{{x}^{3}}+80{{x}^{2}}+80x+32$
We can also solve the above expression by using direct Pascal's triangle formula. Pascal's triangle is a never ending equilateral triangle of numbers that follows a rule of adding the two numbers above to get the number below. Here two of the sides are “all $1\grave{\ }s''$ and because the triangle is infinite, there is no “bottom side”.
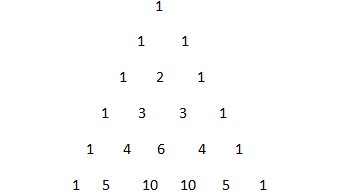
The 5th row of Pascal's triangle is: $1,5,10,10,5,1$. These values are the coefficients in a binomial expansion to the 5th power:
$\Rightarrow {{\left( a+b \right)}^{5}}={{a}^{5}}+5{{a}^{4}}b+10{{a}^{3}}{{b}^{2}}+10{{a}^{2}}{{b}^{3}}+5a{{b}^{4}}+{{b}^{5}}$
Notice this pattern of the exponents: the exponents of $a$ starts at $5$ and goes to $0$ and $b$ starts at $0$ and goes to $5$.
We will apply this in rule ${{\left( a+b \right)}^{5}}={{a}^{5}}+5{{a}^{4}}b+10{{a}^{3}}{{b}^{2}}+10{{a}^{2}}{{b}^{3}}+5a{{b}^{4}}+{{b}^{5}}$ to solve ${{\left( x+2 \right)}^{5}}$:
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow {{\left( x+2 \right)}^{5}}={{x}^{5}}+5{{x}^{4}}\left( 2 \right)+10{{x}^{^{3}}}{{\left( 2 \right)}^{2}}+10{{x}^{2}}{{\left( 2 \right)}^{3}}+5x{{\left( 2 \right)}^{4}}+{{2}^{5}} \\
& \Rightarrow {{x}^{5}}+10{{x}^{4}}+40{{x}^{3}}+80{{x}^{2}}+80x+32 \\
\end{align}$
Hence by using the binomial expansion formula ${{\left( a+b \right)}^{n}}{{=}^{n}}{{c}_{0}}{{a}^{n}}{{b}^{0}}{{+}^{n}}{{c}_{1}}{{a}^{n-1}}{{b}^{1}}+...............{{+}^{n}}{{c}_{n}}{{a}^{0}}{{b}^{n}}$ we get the expansion of ${{\left( x+2 \right)}^{5}}$is ${{x}^{5}}+10{{x}^{4}}+40{{x}^{3}}+80{{x}^{2}}+80x+32$
Note:
Here we can go wrong by writing the wrong binomial expansion formula, sometimes students make mistakes in the powers of $a$and b. Therefore by using the above two methods binomial expansion and Pascal's triangle formula we can easily expand any expression.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




