
How do you use Pascal’s triangle to expand ${{\left( 2a+1 \right)}^{5}}$ ?
Answer
559.5k+ views
Hint: The process of writing Pascal’s triangle is the all the rows of the triangle starts with 1 second term of nth row is sum of first and second term of n-1 throw , third term of the row is sum of second and third term of n-1th row and this goes on and the last term is equal to 1. So total n row present in nth row
Complete step by step answer:
We know nth row of Pascal’s triangle represent the coefficients of terms present in the expansion of ${{\left( 1+x \right)}^{n-1}}$
So n+1th row will represent the coefficients of terms present in the expansion od ${{\left( 1+x \right)}^{n}}$
That means the terms present in n+1th row are $^{n}{{C}_{0}}$ , $^{n}{{C}_{1}}$, $^{n}{{C}_{2}}$ , ……
So if we have to write the expansion of ${{\left( 2a+1 \right)}^{5}}$ using Pascal’s triangle we have look into the terms of row 6
So let’s draw the Pascal’s triangle
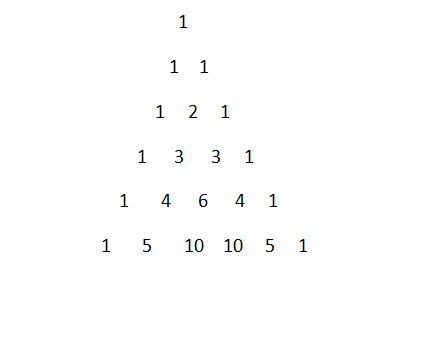
We can see the sixth row contains 1, 5, 10, 10, 5, 1
There are total 6 term present in the expansion of ${{\left( 2a+1 \right)}^{5}}$
1 is coefficient of ${{\left( 2a \right)}^{0}}$ , 5 is the coefficient of ${{\left( 2a \right)}^{1}}$ , 10 is the coefficient of ${{\left( 2a \right)}^{2}}$ and this goes on.
So the expansion of ${{\left( 2a+1 \right)}^{5}}$ is
$1\times {{\left( 2a \right)}^{0}}+5\times {{\left( 2a \right)}^{1}}+10\times {{\left( 2a \right)}^{2}}+10\times {{\left( 2a \right)}^{3}}+5\times {{\left( 2a \right)}^{4}}+1\times {{\left( 2a \right)}^{0}}$
$=1+10a+40{{a}^{2}}+80{{a}^{3}}+80{{a}^{4}}+32{{a}^{5}}$
Note:
Always keep in mind that the nth row of Pascal’s triangle represents the coefficient of terms present in the expansion of ${{\left( 1+x \right)}^{n-1}}$ so nth row contains the term $^{n-1}{{C}_{0}}$ , $^{n-1}{{C}_{1}}$ , $^{n-1}{{C}_{2}}$ ,
….., $^{n-1}{{C}_{n-1}}$ . So the nth row of Pascal’s triangle consists of total n terms.
Complete step by step answer:
We know nth row of Pascal’s triangle represent the coefficients of terms present in the expansion of ${{\left( 1+x \right)}^{n-1}}$
So n+1th row will represent the coefficients of terms present in the expansion od ${{\left( 1+x \right)}^{n}}$
That means the terms present in n+1th row are $^{n}{{C}_{0}}$ , $^{n}{{C}_{1}}$, $^{n}{{C}_{2}}$ , ……
So if we have to write the expansion of ${{\left( 2a+1 \right)}^{5}}$ using Pascal’s triangle we have look into the terms of row 6
So let’s draw the Pascal’s triangle
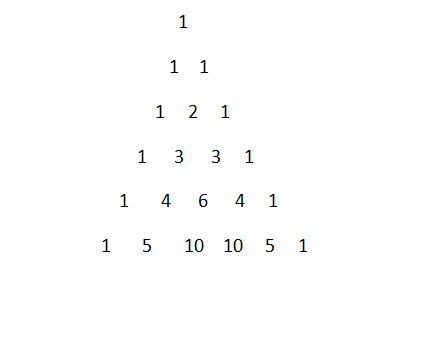
We can see the sixth row contains 1, 5, 10, 10, 5, 1
There are total 6 term present in the expansion of ${{\left( 2a+1 \right)}^{5}}$
1 is coefficient of ${{\left( 2a \right)}^{0}}$ , 5 is the coefficient of ${{\left( 2a \right)}^{1}}$ , 10 is the coefficient of ${{\left( 2a \right)}^{2}}$ and this goes on.
So the expansion of ${{\left( 2a+1 \right)}^{5}}$ is
$1\times {{\left( 2a \right)}^{0}}+5\times {{\left( 2a \right)}^{1}}+10\times {{\left( 2a \right)}^{2}}+10\times {{\left( 2a \right)}^{3}}+5\times {{\left( 2a \right)}^{4}}+1\times {{\left( 2a \right)}^{0}}$
$=1+10a+40{{a}^{2}}+80{{a}^{3}}+80{{a}^{4}}+32{{a}^{5}}$
Note:
Always keep in mind that the nth row of Pascal’s triangle represents the coefficient of terms present in the expansion of ${{\left( 1+x \right)}^{n-1}}$ so nth row contains the term $^{n-1}{{C}_{0}}$ , $^{n-1}{{C}_{1}}$ , $^{n-1}{{C}_{2}}$ ,
….., $^{n-1}{{C}_{n-1}}$ . So the nth row of Pascal’s triangle consists of total n terms.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Accountancy: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 11 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Trending doubts
Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

The draft of the Preamble of the Indian Constitution class 10 social science CBSE

Who gave "Inqilab Zindabad" slogan?

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

Who was Subhash Chandra Bose Why was he called Net class 10 english CBSE




