
Use curved arrow notations to show the formation of reactive intermediates formed when the following covalent bonds undergo heterolytic cleavage.
a. $C{H_3} - SC{H_3}$
b. $C{H_3} - CN$
c. $C{H_3} - Cu$
Answer
520.8k+ views
Hint : Molecules or ions which are short-lived highly reactive molecules and consist of high energy are known as reactive intermediates. These are formed within a chemical reaction and due to high reactivity, the intermediates quickly convert to form a more stable intermediate. Some examples of reactive intermediate are: carbocation, carbanions, free radicals, etc.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
Reactive intermediate formed on cleavage of a covalent bond are as follows:
Homolytic cleavage of a covalent bond: It is the breaking of covalent bond in such a manner that electrons are equally divided between the atoms and each one will have an unshared electron known as radical. The reactive intermediate formed in homolytic cleavage of bond is known as free radical.
Heterolytic cleavage of covalent bond: It is the breaking of covalent bond in such a manner that originally shared pair of electrons remain with one of the atoms of a molecule. So, the atom which gains electrons becomes electron rich and acquires a negative charge whereas the other atom which donated the electron pair becomes electron deficient and acquires a positive charge. Hence, reactive intermediates formed in the heterolytic cleavage of covalent bonds are carbocation and carbanion.
For the given covalent bonds, the heterolytic cleavage takes place as follows:
a. $C{H_3} - SC{H_3}$: The heterolytic cleavage of dimethyl sulphate take place to form methylium ion and methanethiolate ion. The reaction takes place as follows:
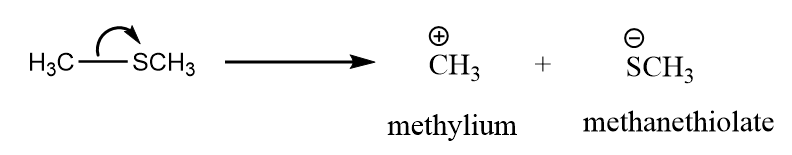
So, the reactive intermediate formed is carbocation.
b. $C{H_3} - CN$: The heterolytic cleavage of acetonitrile takes place to form methylium ion and cyanide ion. The reaction takes place as follows:
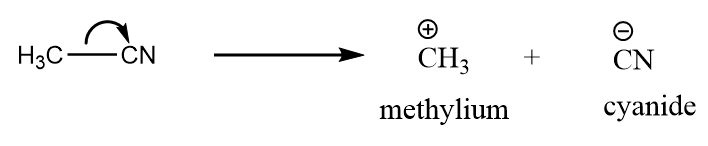
So, the reactive intermediate formed is carbocation.
c. $C{H_3} - Cu$: The heterolytic cleavage of methyl copper takes place to form methanide ion and copper(I) ion. The reaction takes place as follows:
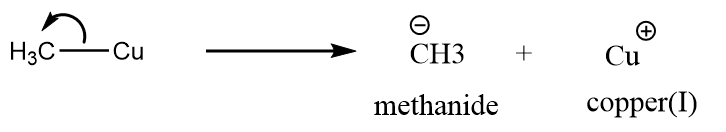
So, the reactive intermediate formed is carbanion.
Note :
It is important to note that in heterolytic cleavage, electron pairs are always shifted towards more electronegative elements i.e., negative charge will always be formed on the atom which is comparatively more electronegative. Among given compounds, sulphur and cyanide groups are more electronegative so will acquire a negative charge whereas copper is an electropositive metal and is less electronegative than carbon, so will acquire a positive charge.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
Reactive intermediate formed on cleavage of a covalent bond are as follows:
Homolytic cleavage of a covalent bond: It is the breaking of covalent bond in such a manner that electrons are equally divided between the atoms and each one will have an unshared electron known as radical. The reactive intermediate formed in homolytic cleavage of bond is known as free radical.
Heterolytic cleavage of covalent bond: It is the breaking of covalent bond in such a manner that originally shared pair of electrons remain with one of the atoms of a molecule. So, the atom which gains electrons becomes electron rich and acquires a negative charge whereas the other atom which donated the electron pair becomes electron deficient and acquires a positive charge. Hence, reactive intermediates formed in the heterolytic cleavage of covalent bonds are carbocation and carbanion.
For the given covalent bonds, the heterolytic cleavage takes place as follows:
a. $C{H_3} - SC{H_3}$: The heterolytic cleavage of dimethyl sulphate take place to form methylium ion and methanethiolate ion. The reaction takes place as follows:

So, the reactive intermediate formed is carbocation.
b. $C{H_3} - CN$: The heterolytic cleavage of acetonitrile takes place to form methylium ion and cyanide ion. The reaction takes place as follows:

So, the reactive intermediate formed is carbocation.
c. $C{H_3} - Cu$: The heterolytic cleavage of methyl copper takes place to form methanide ion and copper(I) ion. The reaction takes place as follows:

So, the reactive intermediate formed is carbanion.
Note :
It is important to note that in heterolytic cleavage, electron pairs are always shifted towards more electronegative elements i.e., negative charge will always be formed on the atom which is comparatively more electronegative. Among given compounds, sulphur and cyanide groups are more electronegative so will acquire a negative charge whereas copper is an electropositive metal and is less electronegative than carbon, so will acquire a positive charge.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

What steps did the French revolutionaries take to create class 11 social science CBSE

The transition element that has lowest enthalpy of class 11 chemistry CBSE

Can anyone list 10 advantages and disadvantages of friction




