
How many unpaired electrons does an atom of sulfur have in its ground state?
Answer
558.9k+ views
Hint: For calculating the number of unpaired electrons in the ground state of any atom we have to know about the atomic number because the atomic number of any element is equal to the number of protons or number of electrons present in that atom.
Complete step by step answer:
In the periodic table element Sulfur (${\text{S}}$) is located at ‘VI A’ group in the p – block of the periodic table and it is denoted as ${}_{{\text{16}}}^{{\text{32}}}{\text{S}}$.
- Upper quantity which is mention in ${}_{{\text{16}}}^{{\text{32}}}{\text{S}}$describes the Atomic mass (${\text{A}}$) and lower quantity describes the Atomic number (${\text{Z}}$) of the sulfur element.
- As we know that relation between Atomic number (${\text{Z}}$) of the atom and number of electrons present inside in it is as follow:
Atomic Number (${\text{Z}}$) = No. of electrons = No. of protons
So that in sulphur (${\text{S}}$) $16$ electrons are present as the atomic number of gallium is also $16$.
- Now electronic configuration of sulphur is shown as ${\text{1}}{{\text{s}}^{\text{2}}}{\text{,2}}{{\text{s}}^{\text{2}}}{\text{2}}{{\text{p}}^{\text{6}}}{\text{,3}}{{\text{s}}^{\text{2}}}{\text{3}}{{\text{p}}^{\text{4}}}$ ($2,8,6$) and from this it is clear that in the outermost shell six electrons are present.
- And two out of six electrons are present in the s – orbital in the paired form and remaining electrons are present in the p-orbital. Now in the p – orbital two electrons are present in the paired form and two are present unpaired which are shown as follow:
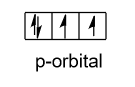
Hence, two electrons are present in the sulphur atom in ground state.
Note: Some of you may think that why two electrons of p-orbital are not present in the paired form, so the reason is that according to the Hund’s rule only after single filling of orbitals, pairing of electrons will take place.
Complete step by step answer:
In the periodic table element Sulfur (${\text{S}}$) is located at ‘VI A’ group in the p – block of the periodic table and it is denoted as ${}_{{\text{16}}}^{{\text{32}}}{\text{S}}$.
- Upper quantity which is mention in ${}_{{\text{16}}}^{{\text{32}}}{\text{S}}$describes the Atomic mass (${\text{A}}$) and lower quantity describes the Atomic number (${\text{Z}}$) of the sulfur element.
- As we know that relation between Atomic number (${\text{Z}}$) of the atom and number of electrons present inside in it is as follow:
Atomic Number (${\text{Z}}$) = No. of electrons = No. of protons
So that in sulphur (${\text{S}}$) $16$ electrons are present as the atomic number of gallium is also $16$.
- Now electronic configuration of sulphur is shown as ${\text{1}}{{\text{s}}^{\text{2}}}{\text{,2}}{{\text{s}}^{\text{2}}}{\text{2}}{{\text{p}}^{\text{6}}}{\text{,3}}{{\text{s}}^{\text{2}}}{\text{3}}{{\text{p}}^{\text{4}}}$ ($2,8,6$) and from this it is clear that in the outermost shell six electrons are present.
- And two out of six electrons are present in the s – orbital in the paired form and remaining electrons are present in the p-orbital. Now in the p – orbital two electrons are present in the paired form and two are present unpaired which are shown as follow:

Hence, two electrons are present in the sulphur atom in ground state.
Note: Some of you may think that why two electrons of p-orbital are not present in the paired form, so the reason is that according to the Hund’s rule only after single filling of orbitals, pairing of electrons will take place.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




