
What is the unit which is used for the area under a velocity-time graph?
Answer
501.9k+ views
Hint: The displacement of an object traveling with a constant velocity is equal to the velocity times the amount of time the object is in motion. The area beneath the velocity-time graph is equal to the displacement of the object. The unit in which displacement is measured is meter.
Complete step by step solution:
The displacement is the area under a velocity-time graph. Velocity can be negative if an object is traveling backward. The displacement can be too negative. An area beneath the x-axis has a negative value. An area up the x-axis has a positive value. Be careful when measuring the total displacement; when summing the displacements, get to combine the plus and minus signs of the displacements.
The graph of the v-t graph is shown below:
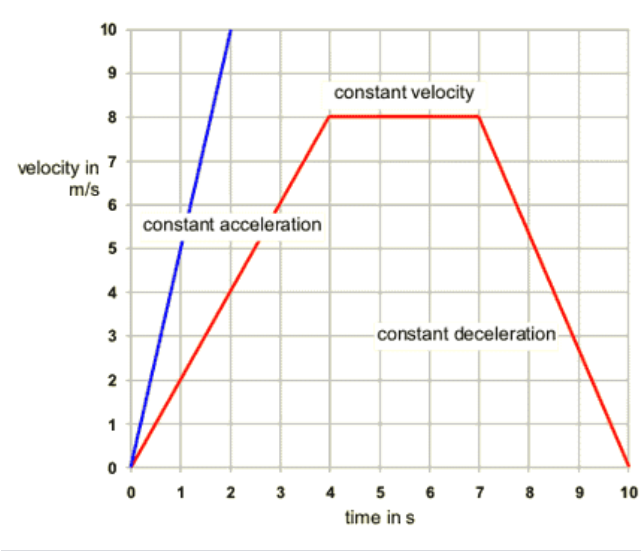
If the graph's appearance can be split into simple geometric frames, the total area beneath the line can be calculated by summing the areas of those shapes.
To determine the displacement when the velocity is not fixed, a velocity-time graph is needed. Usually, velocity is sketched on the vertical axis, and time is sketched on the horizontal axis.
The area below a velocity-time graph is a description of the displacement. If the area is up a time interval, then the displacement during that time interval can be estimated by the area under the graph limited by the time interval. The area beneath a velocity-time graph provides the displacement, and the unit of displacement is the meter.
Note: In a velocity-time graph, acceleration is expressed by the slope, or steepness, of the graph line. Suppose the line slopes upward, velocity increases, so acceleration is positive. If the line is horizontal, velocity is constant, and acceleration is zero. If the line slopes downward, velocity is reducing, and acceleration is negative. Negative acceleration is termed deceleration.
Complete step by step solution:
The displacement is the area under a velocity-time graph. Velocity can be negative if an object is traveling backward. The displacement can be too negative. An area beneath the x-axis has a negative value. An area up the x-axis has a positive value. Be careful when measuring the total displacement; when summing the displacements, get to combine the plus and minus signs of the displacements.
The graph of the v-t graph is shown below:

If the graph's appearance can be split into simple geometric frames, the total area beneath the line can be calculated by summing the areas of those shapes.
To determine the displacement when the velocity is not fixed, a velocity-time graph is needed. Usually, velocity is sketched on the vertical axis, and time is sketched on the horizontal axis.
The area below a velocity-time graph is a description of the displacement. If the area is up a time interval, then the displacement during that time interval can be estimated by the area under the graph limited by the time interval. The area beneath a velocity-time graph provides the displacement, and the unit of displacement is the meter.
Note: In a velocity-time graph, acceleration is expressed by the slope, or steepness, of the graph line. Suppose the line slopes upward, velocity increases, so acceleration is positive. If the line is horizontal, velocity is constant, and acceleration is zero. If the line slopes downward, velocity is reducing, and acceleration is negative. Negative acceleration is termed deceleration.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




