
Uniform rod $AB$ is hinged at the end $A$ is horizontal position as shown in the figure. The other end is connected to a block through a massless string as shown. The pulley is smooth and massless. Masses of this block and the rod are the same and is equal to $m$. Then the acceleration of the block just after release from this position is.
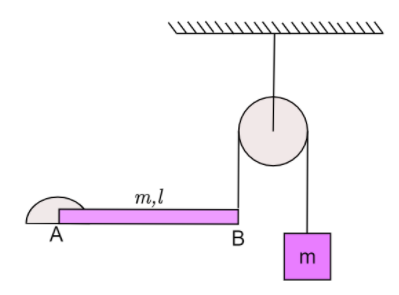
A. $6g/13$
B. $g/4$
C. $3g/8$
D. $3g/26$

Answer
559.2k+ views
Hint: Initially when the block is released from the position, it moves downwards, this causes tension to build up in the string connecting the block and the rod. Since initially, the rod $AB$ is horizontal, it experiences a force in the vertical direction. Thus its acceleration will also be in the upward direction. This acceleration will be equal to the acceleration of the block.
Complete step by step answer:
It is given in the question that,
Mass of the block is equal to the mass of the rod, that is $m$.
The length of the rod is $l$,
Let the acceleration of the block be $a$ and the angular acceleration of the rod be $\alpha$.
The block and the rod are connected via a string. Since the pulley is frictionless, and initially the rod is kept horizontal therefore the acceleration of both, the rod and the block is same.
The acceleration of the rod is given by,
$a = l\alpha$
Which is also equal to the acceleration of the block.
On drawing and analysing the free body diagram of the block, we observe that-
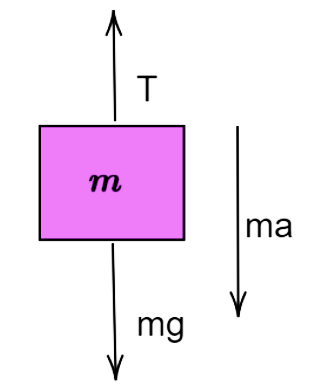
Let $T$ be the tension in the string and $g$ be the acceleration due to gravity, then,
$mg - T = ma$
Or,
$T = mg - ma$ ___________(1)
Now, let us consider the free body diagram of the rod.
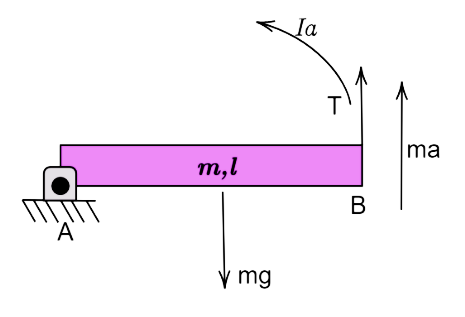
The torque acting about the end A is given by,
$\tau = I\alpha$
Where $I$ is the moment of inertia of the rod.
The acceleration of the rod is,
$l \times \alpha = a$
Therefore,
$\alpha = \dfrac{a}{l}$
The moment of inertia, of a rod about one of its ends is given by,
$I = \dfrac{{m{l^2}}}{3}$
Therefore torque about A,
$\tau = \dfrac{{am{l^2}}}{{3l}} = \dfrac{{aml}}{3}$
Now balancing the torque about end A in the rod while taking anticlockwise positive, we have-
$\tau = T \times l - mg \times \dfrac{l}{2}$
Putting values,
$\dfrac{{aml}}{3} = Tl - \dfrac{{mgl}}{2}$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{{am}}{3} = T - \dfrac{{mg}}{2}$
The acceleration is given by,
$a = \dfrac{{3\left( {2T - mg} \right)}}{{2m}}$
Now from equation (1) we have,
$T = mg - ma$
Substituting the value of $a$,
$a = \dfrac{{6(mg - ma) - 3mg}}{{2m}}$
$\Rightarrow 2ma = 3mg - 6ma$
$\Rightarrow 8a = 3g$
$\Rightarrow a = \dfrac{{3g}}{8}$
Thus, acceleration of the block is $\dfrac{{3g}}{8}$ and option (C) is correct.
Note: For equilibrium of a non-point-object (or a body where all forces are not collinear) there can be two types of equations that form after drawing the free body diagram. They are the balancing of force and the balancing of the moment. In this question, we have balanced the moment of the rod to find its acceleration.
Complete step by step answer:
It is given in the question that,
Mass of the block is equal to the mass of the rod, that is $m$.
The length of the rod is $l$,
Let the acceleration of the block be $a$ and the angular acceleration of the rod be $\alpha$.
The block and the rod are connected via a string. Since the pulley is frictionless, and initially the rod is kept horizontal therefore the acceleration of both, the rod and the block is same.
The acceleration of the rod is given by,
$a = l\alpha$
Which is also equal to the acceleration of the block.
On drawing and analysing the free body diagram of the block, we observe that-

Let $T$ be the tension in the string and $g$ be the acceleration due to gravity, then,
$mg - T = ma$
Or,
$T = mg - ma$ ___________(1)
Now, let us consider the free body diagram of the rod.

The torque acting about the end A is given by,
$\tau = I\alpha$
Where $I$ is the moment of inertia of the rod.
The acceleration of the rod is,
$l \times \alpha = a$
Therefore,
$\alpha = \dfrac{a}{l}$
The moment of inertia, of a rod about one of its ends is given by,
$I = \dfrac{{m{l^2}}}{3}$
Therefore torque about A,
$\tau = \dfrac{{am{l^2}}}{{3l}} = \dfrac{{aml}}{3}$
Now balancing the torque about end A in the rod while taking anticlockwise positive, we have-
$\tau = T \times l - mg \times \dfrac{l}{2}$
Putting values,
$\dfrac{{aml}}{3} = Tl - \dfrac{{mgl}}{2}$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{{am}}{3} = T - \dfrac{{mg}}{2}$
The acceleration is given by,
$a = \dfrac{{3\left( {2T - mg} \right)}}{{2m}}$
Now from equation (1) we have,
$T = mg - ma$
Substituting the value of $a$,
$a = \dfrac{{6(mg - ma) - 3mg}}{{2m}}$
$\Rightarrow 2ma = 3mg - 6ma$
$\Rightarrow 8a = 3g$
$\Rightarrow a = \dfrac{{3g}}{8}$
Thus, acceleration of the block is $\dfrac{{3g}}{8}$ and option (C) is correct.
Note: For equilibrium of a non-point-object (or a body where all forces are not collinear) there can be two types of equations that form after drawing the free body diagram. They are the balancing of force and the balancing of the moment. In this question, we have balanced the moment of the rod to find its acceleration.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




