
What do you understand by the term glycosidic linkage?
Answer
501.6k+ views
Hint: Chemical bonding is the creation of a chemical compound by forming a chemical link between two or more atoms, molecules, or ions. Chemical bonds hold the atoms in the resulting molecule together.
Chemical bonding is the attractive force that holds diverse constituents (atoms, ions, etc.) together and stabilises them through the overall loss of energy. As a result, chemical compounds are dependent on the strength of chemical bonds between their constituents; the stronger the chemical bonding between the constituents, the more stable the resulting compound.
Complete answer:
Condensation of two monosaccharides yields a disaccharide. The two cyclic structures in the disaccharide molecule are linked by glycosidic linkage and are each tied to the reactant monosaccharide molecule.
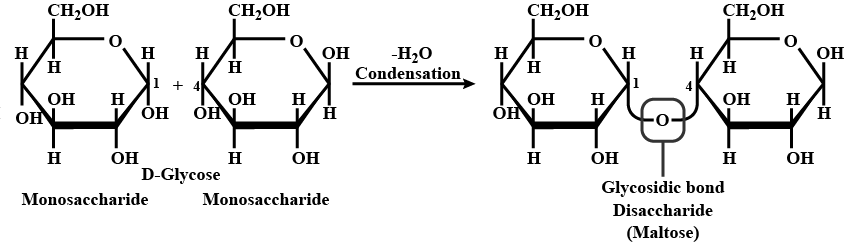
A glycosidic bond, also known as a glycosidic linkage, is a form of covalent connection that connects a carbohydrate (sugar) molecule to another group, which could be another carbohydrate or not.
The hemiacetal or hemiketal group of a saccharide forms a glycosidic link with the hydroxyl group of a molecule such as an alcohol. A glycoside is a chemical that contains a glycosidic link.
Compounds with bonds formed between hemiacetal (or hemiketal) groups of sugars and chemical groups other than hydroxyls are now referred to as -SR (thioglycosides), -SeR (selena glycosides), \[ - NR1R2\] (N-glycosides), or even \[ - CR1R2R3\] (\[CR1R2R3\] glycosides) (C-glycosides).
The chemical ROH from which the carbohydrate residue has been removed is commonly referred to as the aglycone, while the carbohydrate residue itself is sometimes referred to as the 'glycine', especially in naturally occurring glycosides.
Note:
Polysaccharides and monosaccharides-
Monosaccharides and polysaccharides are the two types of carbohydrates.
Monosaccharides have three carbon atoms or more. The most prevalent monosaccharides are hexoses, which have six carbons.
Polysaccharide is a large-scale carbohydrate molecule.
Polysaccharide is made up of a large number of monosaccharide units (several hundred).
Chemical bonding is the attractive force that holds diverse constituents (atoms, ions, etc.) together and stabilises them through the overall loss of energy. As a result, chemical compounds are dependent on the strength of chemical bonds between their constituents; the stronger the chemical bonding between the constituents, the more stable the resulting compound.
Complete answer:
Condensation of two monosaccharides yields a disaccharide. The two cyclic structures in the disaccharide molecule are linked by glycosidic linkage and are each tied to the reactant monosaccharide molecule.

A glycosidic bond, also known as a glycosidic linkage, is a form of covalent connection that connects a carbohydrate (sugar) molecule to another group, which could be another carbohydrate or not.
The hemiacetal or hemiketal group of a saccharide forms a glycosidic link with the hydroxyl group of a molecule such as an alcohol. A glycoside is a chemical that contains a glycosidic link.
Compounds with bonds formed between hemiacetal (or hemiketal) groups of sugars and chemical groups other than hydroxyls are now referred to as -SR (thioglycosides), -SeR (selena glycosides), \[ - NR1R2\] (N-glycosides), or even \[ - CR1R2R3\] (\[CR1R2R3\] glycosides) (C-glycosides).
The chemical ROH from which the carbohydrate residue has been removed is commonly referred to as the aglycone, while the carbohydrate residue itself is sometimes referred to as the 'glycine', especially in naturally occurring glycosides.
Note:
Polysaccharides and monosaccharides-
Monosaccharides and polysaccharides are the two types of carbohydrates.
Monosaccharides have three carbon atoms or more. The most prevalent monosaccharides are hexoses, which have six carbons.
Polysaccharide is a large-scale carbohydrate molecule.
Polysaccharide is made up of a large number of monosaccharide units (several hundred).
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




