
Ulothrix is
(a)Attached unbranched filament
(b)Attached branched filament
(c)Colonial algae
(d)Free-floating
Answer
584.7k+ views
Hint: It is an alga that grows on a freshwater. It fixes itself on a substratum such as soil, rocks, particles, etc for its growth.
Ulothrix is an attached unbranched filament. It is a filamentous green algae genus that is commonly observed in marine water and freshwater. Individual cells have a distinct nucleus, a vacuole situated in the center, and a thin chloroplast with a minimum of one pyrenoid. It possesses a specialized cell for attachment known as holdfast and these filaments are unbranched.
Complete step-by-step answer:
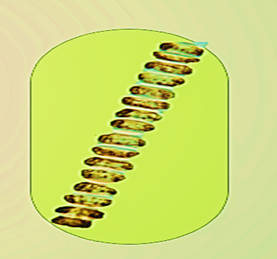
figure: Ulothrix
The above image represents the image of the algae Ulothrix.
Ulothrix can reproduce by vegetative propagation, asexual, and sexual reproduction.
-Vegetative reproduction: In vegetative reproduction, the ulothrix will undergo fragmentation. After vegetative reproduction, the fragments will undergo several divisions, and later it will form into a new filament. Each fragment will develop into a new filament.
-Asexual reproduction: It is observed that ulothrix will form zoospores, akinetes, aplanospores.
-Zoospore is a spore that can swim.
-The shrinkage of protoplasts and will form a wall all over it. This will form an aplanospores.
-Akinetes are also produced similarly as that of aplanospores but, it differs in having a thicker cell wall made of cellulose and pectin.
-Sexual reproduction: The male and female gametes are of the same size. They will undergo fusion. This is otherwise called as isogamous.
So, the correct answer is ‘Attached unbranched filament’
Note: The gametes formed during sexual reproduction may not fuse at times. These gametes will lose its flagella, form a thickly layered wall surrounding it called parthenospores and finally these parthenospores will directly form into a new plant.
Ulothrix is an attached unbranched filament. It is a filamentous green algae genus that is commonly observed in marine water and freshwater. Individual cells have a distinct nucleus, a vacuole situated in the center, and a thin chloroplast with a minimum of one pyrenoid. It possesses a specialized cell for attachment known as holdfast and these filaments are unbranched.
Complete step-by-step answer:

figure: Ulothrix
The above image represents the image of the algae Ulothrix.
Ulothrix can reproduce by vegetative propagation, asexual, and sexual reproduction.
-Vegetative reproduction: In vegetative reproduction, the ulothrix will undergo fragmentation. After vegetative reproduction, the fragments will undergo several divisions, and later it will form into a new filament. Each fragment will develop into a new filament.
-Asexual reproduction: It is observed that ulothrix will form zoospores, akinetes, aplanospores.
-Zoospore is a spore that can swim.
-The shrinkage of protoplasts and will form a wall all over it. This will form an aplanospores.
-Akinetes are also produced similarly as that of aplanospores but, it differs in having a thicker cell wall made of cellulose and pectin.
-Sexual reproduction: The male and female gametes are of the same size. They will undergo fusion. This is otherwise called as isogamous.
So, the correct answer is ‘Attached unbranched filament’
Note: The gametes formed during sexual reproduction may not fuse at times. These gametes will lose its flagella, form a thickly layered wall surrounding it called parthenospores and finally these parthenospores will directly form into a new plant.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




