
What type of lens is converging and which type of mirror is converging?
A. convex mirror, convex lens
B. concave mirror, concave lens
C. convex mirror, concave lens
D. concave mirror, convex lens
E. all mirrors are diverging
Answer
593.7k+ views
Hint: A converging lens or mirror, will converge the parallel rays coming from infinity to a point on the principal axis. For a converging mirror, the real image will form on the same side of the mirror, from where object rays are coming. Similarly, for a converging lens, the real image will form on the other side of the lens as compared to the direction from the incident rays.
Complete step by step answer:
A converging lens or a converging mirror, will converge parallel rays coming from an object at infinity to a point on the principal axis. The image formed will be a real image.
Let’s understand what happens, when parallel rays from infinity are incident on a concave mirror.

We find that the rays reflect from the concave mirror, and according to the reflection laws the rays converge to a point on the principal axis. The image formed is a real image and this image is formed on the same side of the mirror. Hence, the concave mirror is a converging mirror.
Similarly, for a concave mirror, let’s see what happens when parallel rays from infinity are incident on a convex mirror.
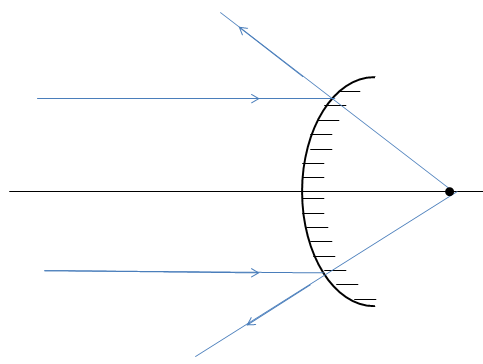
Here, we see that the rays diverge away from the principal axis. Upon extending the rays diverging out, we find these rays seem to converge at a point behind the mirror. Since, this doesn’t happen actually, it’s a virtual image that is formed.
Now, considering a convex lens, let’s see what happens when parallel rays are incident on it.
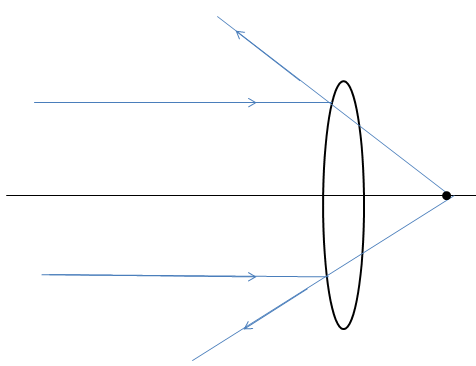
Here, we see that the rays are incident from convex lenses as parallel rays. These rays seem to converge to a point after refracting through the lens. Hence, this type of lens is known as a converging lens.
Now let’s consider the case of a concave lens.
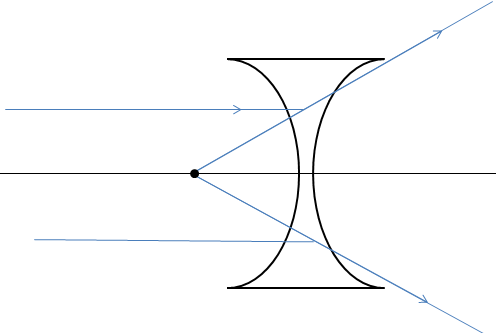
When the rays are incident on the concave lens from infinity, the parallel rays seem to diverge as they refract through the lens. Here, when we extend the rays backwards, they seem to be emerging from a point. This point is where the virtual image is formed.
Hence, the correct answer is option D.
Note:
It’s important to remember that all the parallel rays will definitely converge to a point. However, only in the case of a Convex lens and Concave mirror, the image formed will be a real image that we can project onto a screen. Hence, they are known as converging lens and mirror respectively.
In the case of the diverging lens, the rays will seem to diverge from a point on the axis, which is where the virtual image is made. This image cannot be projected on a screen.
Complete step by step answer:
A converging lens or a converging mirror, will converge parallel rays coming from an object at infinity to a point on the principal axis. The image formed will be a real image.
Let’s understand what happens, when parallel rays from infinity are incident on a concave mirror.

We find that the rays reflect from the concave mirror, and according to the reflection laws the rays converge to a point on the principal axis. The image formed is a real image and this image is formed on the same side of the mirror. Hence, the concave mirror is a converging mirror.
Similarly, for a concave mirror, let’s see what happens when parallel rays from infinity are incident on a convex mirror.

Here, we see that the rays diverge away from the principal axis. Upon extending the rays diverging out, we find these rays seem to converge at a point behind the mirror. Since, this doesn’t happen actually, it’s a virtual image that is formed.
Now, considering a convex lens, let’s see what happens when parallel rays are incident on it.

Here, we see that the rays are incident from convex lenses as parallel rays. These rays seem to converge to a point after refracting through the lens. Hence, this type of lens is known as a converging lens.
Now let’s consider the case of a concave lens.

When the rays are incident on the concave lens from infinity, the parallel rays seem to diverge as they refract through the lens. Here, when we extend the rays backwards, they seem to be emerging from a point. This point is where the virtual image is formed.
Hence, the correct answer is option D.
Note:
It’s important to remember that all the parallel rays will definitely converge to a point. However, only in the case of a Convex lens and Concave mirror, the image formed will be a real image that we can project onto a screen. Hence, they are known as converging lens and mirror respectively.
In the case of the diverging lens, the rays will seem to diverge from a point on the axis, which is where the virtual image is made. This image cannot be projected on a screen.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




