
Two triangles $\vartriangle ABC$ and $\vartriangle DBC$ are on the same base BC and on the same side of BC in which $\angle A=\angle D=90{}^\circ $ . If CA and BD meet each other at E, then show that $AE\times EC=BE\times ED$ .
Answer
533.4k+ views
Hint: In this given problem, we have two triangles on the same base and they are taking place on the same side of the given base. Also with the given angles, we can clearly see that both angles are right angled triangles. Now, using vertically opposite angle properties, we can have another angle as equal. Thus we get both our triangles as similar triangles and using that property we get our proof.
Complete step by step solution:
According to the question, we are given two triangles $\vartriangle ABC$ and $\vartriangle DBC$. And they are taking place on the same base BC and also on the same side of BC. We are also given, $\angle A=\angle D=90{}^\circ $. CA and BD are meeting each other at E, and we are to prove, $AE\times EC=BE\times ED$.
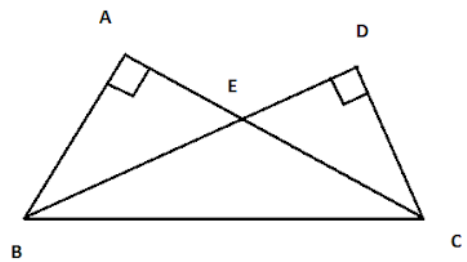
Now, considering two triangles, $\vartriangle ABC$ and $\vartriangle DBC$,
It is given that, $\angle A=\angle D=90{}^\circ $.
Again, from the given image, $\angle AEB=\angle DEC$.
Because, vertically opposite angles are equal.
Hence, we have, two triangles $\vartriangle ABC$ and $\vartriangle DBC$are similar.
This can be written as, $\vartriangle ABC \cong \vartriangle DBC$, in the AA similarity theorem .
Hence, it can be written that, $\dfrac{AE}{DE}=\dfrac{BE}{CE}$
Multiplying them and writing them altogether, we get now, $AE\times EC=BE\times ED$ (proved).
Note: We have used the properties of similar triangles here. Two triangles are said to be similar if their corresponding angles are congruent and the corresponding sides are in proportion . In other words, similar triangles are the same shape, but not necessarily the same size. The triangles are congruent if, in addition to this, their corresponding sides are of equal length.
Complete step by step solution:
According to the question, we are given two triangles $\vartriangle ABC$ and $\vartriangle DBC$. And they are taking place on the same base BC and also on the same side of BC. We are also given, $\angle A=\angle D=90{}^\circ $. CA and BD are meeting each other at E, and we are to prove, $AE\times EC=BE\times ED$.

Now, considering two triangles, $\vartriangle ABC$ and $\vartriangle DBC$,
It is given that, $\angle A=\angle D=90{}^\circ $.
Again, from the given image, $\angle AEB=\angle DEC$.
Because, vertically opposite angles are equal.
Hence, we have, two triangles $\vartriangle ABC$ and $\vartriangle DBC$are similar.
This can be written as, $\vartriangle ABC \cong \vartriangle DBC$, in the AA similarity theorem .
Hence, it can be written that, $\dfrac{AE}{DE}=\dfrac{BE}{CE}$
Multiplying them and writing them altogether, we get now, $AE\times EC=BE\times ED$ (proved).
Note: We have used the properties of similar triangles here. Two triangles are said to be similar if their corresponding angles are congruent and the corresponding sides are in proportion . In other words, similar triangles are the same shape, but not necessarily the same size. The triangles are congruent if, in addition to this, their corresponding sides are of equal length.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 8 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 8 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Master Class 8 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 7 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell

Fill the blanks with the suitable prepositions 1 The class 9 english CBSE

Who is eligible for RTE class 9 social science CBSE

Which places in India experience sunrise first and class 9 social science CBSE

What is pollution? How many types of pollution? Define it

Name 10 Living and Non living things class 9 biology CBSE




