
Two towers of 15 m and 25 m Heights respectively stand on level ground. The angles of elevation of the top from a point between the two towers on the line joining their feet are respectively 45 degree and 60 degree, and find the distance between the two towers.
Answer
492k+ views
Hint: We are given the heights of the two towers 15m and 25m from the ground level and their angles are 45 degree and 60 degree. We need to find the distance between the two towers. We will use the value of tan and using this, we will substitute it to get the final output.
Complete step by step solution:
Given that,
There are two towers 15m and 25m from the ground level. There are two angles also given i.e. 45 degree and 60 degree.
We will draw the figure from the given information as below:
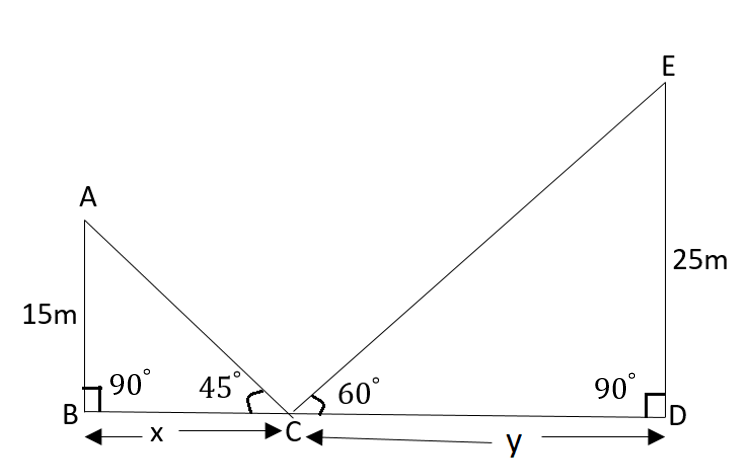
Consider a right-angled triangle, where the longest side is called the hypotenuse, and the sides opposite to the hypotenuse are referred to as the adjacent and opposite sides.
Here, we need to find the total distance of the two towers i.e. x + y.
In \[\Delta ACB\], AB = 15 m and BC = x m
\[\tan {45^ \circ } = \dfrac{{AB}}{{BC}}\]
Since the value of \[\tan {45^ \circ } = 1\] and so using this, we will get,
\[ \Rightarrow 1 = \dfrac{{15}}{x}\]
\[ \Rightarrow x = 15\]
Now, in \[\Delta DCE\], DE = 25 m and CD = y m
\[\tan {60^ \circ } = \dfrac{{DE}}{{CD}}\]
Since the value of \[\tan {60^ \circ } = \sqrt 3 \] and so using this, we will get,
\[ \Rightarrow \sqrt 3 = \dfrac{{25}}{y}\]
\[ \Rightarrow y = \dfrac{{25}}{{\sqrt 3 }}\]
Next, we will find the total distance between the towers is
\[ = x + y\]
\[ = 15 + \dfrac{{25}}{{\sqrt 3 }}\]
Multiply \[\sqrt 3 \] on both numerator and denominator, we will get,
\[ = 15 + \dfrac{{25\sqrt 3 }}{3}\]
Taking LCM as 3 here, we will get,
\[ = \dfrac{{15(3) + 25\sqrt 3 }}{3}\]
Removing the brackets, we will get,
\[ = \dfrac{{45 + 25\sqrt 3 }}{3}\]
We will use the value \[\sqrt 3 = 1.7320\] and substitute this we will get,
\[ = \dfrac{{45 + 25(1.7320)}}{3}\]
On evaluating this, we will get,
\[ = \dfrac{{45 + 43.3}}{3}\]
\[ = \dfrac{{88.3}}{3}\]
\[ = 29.43\]
Hence, the total distance between the towers is $29.43m$.
Note:
The trigonometric ratios of a triangle are also called the trigonometric functions. The angles are either measured in radians or degrees. Trigonometry can be divided into two sub-branches called plane trigonometry and spherical geometry. In this, we will study the relationship between the sides and angles of a right-angled triangle.
Complete step by step solution:
Given that,
There are two towers 15m and 25m from the ground level. There are two angles also given i.e. 45 degree and 60 degree.
We will draw the figure from the given information as below:

Consider a right-angled triangle, where the longest side is called the hypotenuse, and the sides opposite to the hypotenuse are referred to as the adjacent and opposite sides.
Here, we need to find the total distance of the two towers i.e. x + y.
In \[\Delta ACB\], AB = 15 m and BC = x m
\[\tan {45^ \circ } = \dfrac{{AB}}{{BC}}\]
Since the value of \[\tan {45^ \circ } = 1\] and so using this, we will get,
\[ \Rightarrow 1 = \dfrac{{15}}{x}\]
\[ \Rightarrow x = 15\]
Now, in \[\Delta DCE\], DE = 25 m and CD = y m
\[\tan {60^ \circ } = \dfrac{{DE}}{{CD}}\]
Since the value of \[\tan {60^ \circ } = \sqrt 3 \] and so using this, we will get,
\[ \Rightarrow \sqrt 3 = \dfrac{{25}}{y}\]
\[ \Rightarrow y = \dfrac{{25}}{{\sqrt 3 }}\]
Next, we will find the total distance between the towers is
\[ = x + y\]
\[ = 15 + \dfrac{{25}}{{\sqrt 3 }}\]
Multiply \[\sqrt 3 \] on both numerator and denominator, we will get,
\[ = 15 + \dfrac{{25\sqrt 3 }}{3}\]
Taking LCM as 3 here, we will get,
\[ = \dfrac{{15(3) + 25\sqrt 3 }}{3}\]
Removing the brackets, we will get,
\[ = \dfrac{{45 + 25\sqrt 3 }}{3}\]
We will use the value \[\sqrt 3 = 1.7320\] and substitute this we will get,
\[ = \dfrac{{45 + 25(1.7320)}}{3}\]
On evaluating this, we will get,
\[ = \dfrac{{45 + 43.3}}{3}\]
\[ = \dfrac{{88.3}}{3}\]
\[ = 29.43\]
Hence, the total distance between the towers is $29.43m$.
Note:
The trigonometric ratios of a triangle are also called the trigonometric functions. The angles are either measured in radians or degrees. Trigonometry can be divided into two sub-branches called plane trigonometry and spherical geometry. In this, we will study the relationship between the sides and angles of a right-angled triangle.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




