
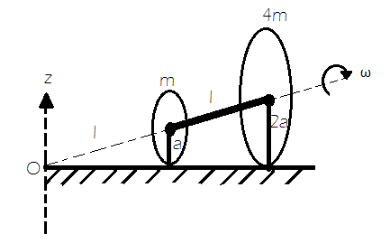
Two thin circular discs of mass $ m $ and $ 4m $ , having radii of $ a $ and $ 2a $ , respectively, are rigidly fixed by a massless, rigid rod of length $ l = \sqrt {24} a $ through their centres. This assembly is laid on a firm and flat surface, and set rolling without slipping on the surface so that the angular speed about the axis of the rod is $ \omega $ . The angular momentum of the entire assembly about the point $ 'O' $ is $ \vec L $ (see the figure). Which of the following statement(s) is (are) true?
(A) The magnitude of the $ z - $ component of $ \vec L $ is $ 55m{a^2}\omega $ .
(B) The magnitude of angular momentum of centre of mass of the assembly about point $ O $ is $ 81m{a^2}\omega $ .
(C) The centre of mass of the assembly rotates about the $ z - $ axis with an angular speed of $ \dfrac{\omega }{5} $ .
(D) The magnitude of the angular momentum of the assembly about its centre of mass is $ \dfrac{{17m{a^2}\omega }}{2} $

Answer
516.6k+ views
Hint :In order to solve this question, we are going to first consider the masses and the radii of the discs given after which the angular speed is taken and then, the velocity of the centre of lower disc is calculated , then, angular velocity of centre of mass and angular momentum are calculated.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
There are two circular discs given of masses, $ m $ and $ 4m $ , having radii of $ a $ and $ 2a $ , respectively
Length of the rod is $ l = \sqrt {24} a $
The angular speed about the axis of the rod is $ \omega $
Let the axis of the horizontal be inclined at an angle equal to $ \theta $
From the figure,
$ \cos \theta = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt {{l^2} + {a^2}} }} = \dfrac{{\sqrt {24} }}{5} $
Velocity of the point P, where point P is the centre of the lower disk
$ a\omega = 1\Omega $
This implies,
$ \Omega = \dfrac{{a\omega }}{1} $
Angular velocity of centre of mass w.r.t. $ z - $ axis is $ \Omega \cos \theta $
Thus, the angular momentum is given by
$ {L_{D - CM}} = \dfrac{{m{a^2}}}{2}\omega + \dfrac{{4m{{\left( {2a} \right)}^2}}}{2}\omega = \dfrac{{17m{a^2}\omega }}{2} $
Hence, the options (C) and (D) form the correct answer.
Note :
The center of mass of a distribution of mass in space is the unique point where the weighted relative position of the distributed mass sums to zero. The most important point here is the velocity of the centre of the lower disc and the calculation of angular speed of the centre of mass of the system.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
There are two circular discs given of masses, $ m $ and $ 4m $ , having radii of $ a $ and $ 2a $ , respectively
Length of the rod is $ l = \sqrt {24} a $
The angular speed about the axis of the rod is $ \omega $
Let the axis of the horizontal be inclined at an angle equal to $ \theta $
From the figure,
$ \cos \theta = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt {{l^2} + {a^2}} }} = \dfrac{{\sqrt {24} }}{5} $
Velocity of the point P, where point P is the centre of the lower disk
$ a\omega = 1\Omega $
This implies,
$ \Omega = \dfrac{{a\omega }}{1} $
Angular velocity of centre of mass w.r.t. $ z - $ axis is $ \Omega \cos \theta $
Thus, the angular momentum is given by
$ {L_{D - CM}} = \dfrac{{m{a^2}}}{2}\omega + \dfrac{{4m{{\left( {2a} \right)}^2}}}{2}\omega = \dfrac{{17m{a^2}\omega }}{2} $
Hence, the options (C) and (D) form the correct answer.
Note :
The center of mass of a distribution of mass in space is the unique point where the weighted relative position of the distributed mass sums to zero. The most important point here is the velocity of the centre of the lower disc and the calculation of angular speed of the centre of mass of the system.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




