
Two tall buildings are situated $200\,m$ apart. With what speed must a ball be thrown horizontally from the window $540\,m$above the ground in one building, so that it will enter a window $50\,m$ above the ground in the other?
Answer
499.8k+ views
Hint: This is an example of horizontal projectile motion. At every point throughout the motion the velocity vector can be represented with its x and y components. Since the acceleration is acting only downwards, the x component of the velocity should not change. In the y direction, we can simply apply the speed equation to get the velocity along the y axis.
The motion equations are
1. $v = u + at$
2. $s = ut + \dfrac{1}{2}a{t^2}$
3. $2as = {v^2} - {u^2}$
Where u is the initial velocity, v is the final velocity, s is the distance covered, t is the time taken and a is the acceleration.
Also, the final velocity is the resultant of the two components. Since the components here are along the x axis and the y axis, the angle between them is \[{90^0}\] . And so, the resultant can be calculated as
\[v = \sqrt {v_x^2 + v_y^2} \]
Complete step by step solution:
Let’s visualize the situation first.
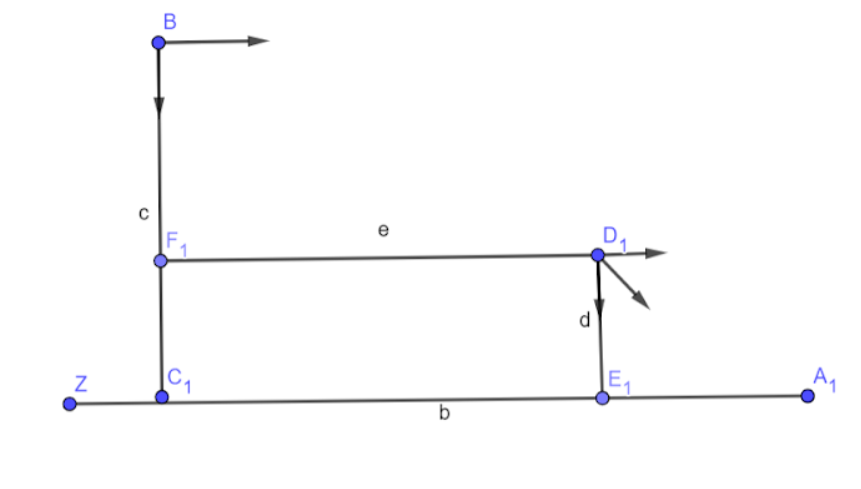
Here $B{C_1}$ represents the $540\,m$ window in one building while ${D_1}{E_1}$ represents the $50\,m$ window in the second building. ${C_1}{E_1}$ represents the distance between the two buildings and is given by ${C_1}{E_1} = 200\,m$.
In y direction,
The distance travelled by ball is given by ${s_y} = 540 - 50 = 490\,m$
The acceleration acting on the ball is given by ${a_y} = + g = 10\,m\,{s^{ - 2}}$
The initial velocity is given as ${u_y} = 0$ (since the ball is projected horizontally it will have a zero-vertical component)
Applying the speed equation $s = ut + \dfrac{1}{2}a{t^2}$ we get,
$ \Rightarrow 490 = 0 + \dfrac{1}{2} \times 9.8 \times {t^2}$
$ \Rightarrow 100 = {t^2}$
Further solving this,
$t = 10\,s$
In x direction,
The distance travelled by ball is given by ${s_x} = 200\,m$
The acceleration acting on the ball is given by ${a_x} = 0$(since there is no acceleration acting in the x direction)
The initial velocity is given as ${u_x} = u\,m\,{s^{ - 1}}$
Applying the speed equation $s = ut + \dfrac{1}{2}a{t^2}$ we get,
$ \Rightarrow 200 = u \times 10 + 0$
$ \Rightarrow u = \dfrac{{200}}{{10}}$
$ \Rightarrow u = 20\,m\,{s^{ - 1}}$
Hence the ball can be thrown at the $u = 20\,m\,{s^{ - 1}}$.
Note: Always keep a note of the direction of the acceleration. If it is the same as the motion of the object then we take + sign for acceleration. Likewise, if the direction is opposite then we take a – sign. This is also known as retardation. We use the value of g as $10\,m\,{s^{ - 2}}$ to simplify our calculations.
The motion equations are
1. $v = u + at$
2. $s = ut + \dfrac{1}{2}a{t^2}$
3. $2as = {v^2} - {u^2}$
Where u is the initial velocity, v is the final velocity, s is the distance covered, t is the time taken and a is the acceleration.
Also, the final velocity is the resultant of the two components. Since the components here are along the x axis and the y axis, the angle between them is \[{90^0}\] . And so, the resultant can be calculated as
\[v = \sqrt {v_x^2 + v_y^2} \]
Complete step by step solution:
Let’s visualize the situation first.

Here $B{C_1}$ represents the $540\,m$ window in one building while ${D_1}{E_1}$ represents the $50\,m$ window in the second building. ${C_1}{E_1}$ represents the distance between the two buildings and is given by ${C_1}{E_1} = 200\,m$.
In y direction,
The distance travelled by ball is given by ${s_y} = 540 - 50 = 490\,m$
The acceleration acting on the ball is given by ${a_y} = + g = 10\,m\,{s^{ - 2}}$
The initial velocity is given as ${u_y} = 0$ (since the ball is projected horizontally it will have a zero-vertical component)
Applying the speed equation $s = ut + \dfrac{1}{2}a{t^2}$ we get,
$ \Rightarrow 490 = 0 + \dfrac{1}{2} \times 9.8 \times {t^2}$
$ \Rightarrow 100 = {t^2}$
Further solving this,
$t = 10\,s$
In x direction,
The distance travelled by ball is given by ${s_x} = 200\,m$
The acceleration acting on the ball is given by ${a_x} = 0$(since there is no acceleration acting in the x direction)
The initial velocity is given as ${u_x} = u\,m\,{s^{ - 1}}$
Applying the speed equation $s = ut + \dfrac{1}{2}a{t^2}$ we get,
$ \Rightarrow 200 = u \times 10 + 0$
$ \Rightarrow u = \dfrac{{200}}{{10}}$
$ \Rightarrow u = 20\,m\,{s^{ - 1}}$
Hence the ball can be thrown at the $u = 20\,m\,{s^{ - 1}}$.
Note: Always keep a note of the direction of the acceleration. If it is the same as the motion of the object then we take + sign for acceleration. Likewise, if the direction is opposite then we take a – sign. This is also known as retardation. We use the value of g as $10\,m\,{s^{ - 2}}$ to simplify our calculations.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What organs are located on the left side of your body class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

How do I convert ms to kmh Give an example class 11 physics CBSE




