
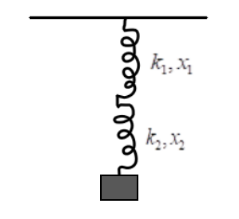
Two springs are in series combination and are attached to a block of mass $ m $ which is in equilibrium. The spring constants and the extensions in the springs are shown in the figure then the force exerted by the spring on the block is
(A) $ \dfrac{{{k_1}{k_2}}}{{{k_1} + {k_2}}}\left( {{x_1} + {x_2}} \right) $
(B) $ {k_1}{x_1} + {k_2}{x_2} $
(C) $ {k_1}{x_1} $
(D) None of these

Answer
570k+ views
Hint: Based on Hooke’s law the total force exerted on the block will be equal to the extension of both strings, and the effective spring constant. The springs are in series, the effective force constant is the inverse of the sum of the inverse of the individual spring constant or the inverse of the effective force constant is equal to the sum of the inverse of each of the spring constants.
Formula used In this solution we will be using the following formulae;
$ F = ke $ where $ F $ is the force exerted by a spring, $ k $ is the force constant, and $ e $ is the extension of spring.
$ \dfrac{1}{{{k_{eqs}}}} = \dfrac{1}{{{k_1}}} + \dfrac{1}{{{k_2}}} $ where $ {k_{eqs}} $ is the equivalent spring constant of two springs in series, $ {k_1} $ is the spring constant of one, and $ {k_2} $ is the spring constant of the other.
Complete Step-by-Step solution:
To solve this question, we note that the two springs are in series. And that the force exerted by such a spring could be considered as the product of an effective spring constant and the total extension in the springs. Generally, the force exerted by a spring is
$ F = ke $ where $ F $ is the force exerted by a spring, $ k $ is the force constant, and $ e $ is the extension of spring.
Then, for the combination of springs in series, we have
$ F = {k_{eqs}}e $ where $ {k_{eqs}} $ is the effective force constant of the network. This in itself, is given by
$ \dfrac{1}{{{k_{eqs}}}} = \dfrac{1}{{{k_1}}} + \dfrac{1}{{{k_2}}} $ where $ {k_{eqs}} $ is the equivalent spring constant of two springs in series, $ {k_1} $ is the spring constant of one, and $ {k_2} $ is the spring constant of the other.
Actually adding them, we have
$ \dfrac{1}{{{k_{eqs}}}} = \dfrac{{{k_1} + {k_2}}}{{{k_1}{k_2}}} $
$ \Rightarrow {k_{eqs}} = \dfrac{{{k_1}{k_2}}}{{{k_1} + {k_2}}} $
Hence, the force exerted would be
$ F = \dfrac{{{k_1}{k_2}}}{{{k_1} + {k_2}}}\left( {{x_1} + {x_2}} \right) $
The correct option is A.
Note:
For clarity, the $ {x_1} + {x_2} $ is the extension of the springs in total. As seen in the diagram, the upper spring is extended by $ {x_1} $ , and the extension of the upper one is $ {x_2} $ , hence, the total extension would be the addition of them both.
Formula used In this solution we will be using the following formulae;
$ F = ke $ where $ F $ is the force exerted by a spring, $ k $ is the force constant, and $ e $ is the extension of spring.
$ \dfrac{1}{{{k_{eqs}}}} = \dfrac{1}{{{k_1}}} + \dfrac{1}{{{k_2}}} $ where $ {k_{eqs}} $ is the equivalent spring constant of two springs in series, $ {k_1} $ is the spring constant of one, and $ {k_2} $ is the spring constant of the other.
Complete Step-by-Step solution:
To solve this question, we note that the two springs are in series. And that the force exerted by such a spring could be considered as the product of an effective spring constant and the total extension in the springs. Generally, the force exerted by a spring is
$ F = ke $ where $ F $ is the force exerted by a spring, $ k $ is the force constant, and $ e $ is the extension of spring.
Then, for the combination of springs in series, we have
$ F = {k_{eqs}}e $ where $ {k_{eqs}} $ is the effective force constant of the network. This in itself, is given by
$ \dfrac{1}{{{k_{eqs}}}} = \dfrac{1}{{{k_1}}} + \dfrac{1}{{{k_2}}} $ where $ {k_{eqs}} $ is the equivalent spring constant of two springs in series, $ {k_1} $ is the spring constant of one, and $ {k_2} $ is the spring constant of the other.
Actually adding them, we have
$ \dfrac{1}{{{k_{eqs}}}} = \dfrac{{{k_1} + {k_2}}}{{{k_1}{k_2}}} $
$ \Rightarrow {k_{eqs}} = \dfrac{{{k_1}{k_2}}}{{{k_1} + {k_2}}} $
Hence, the force exerted would be
$ F = \dfrac{{{k_1}{k_2}}}{{{k_1} + {k_2}}}\left( {{x_1} + {x_2}} \right) $
The correct option is A.
Note:
For clarity, the $ {x_1} + {x_2} $ is the extension of the springs in total. As seen in the diagram, the upper spring is extended by $ {x_1} $ , and the extension of the upper one is $ {x_2} $ , hence, the total extension would be the addition of them both.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

What steps did the French revolutionaries take to create class 11 social science CBSE

The transition element that has lowest enthalpy of class 11 chemistry CBSE

Can anyone list 10 advantages and disadvantages of friction




