
Two springs A and B having spring constants ${K_A}$ and ${K_B}{\text{ }}\left( {{K_A} = 2{K_B}} \right)$ are stretched by applying force of equal magnitude. If the energy stored in spring A is ${E_A}$ then energy stored in B will be
$\eqalign{
& {\text{A}}{\text{. }}2{E_A} \cr
& {\text{B}}{\text{. }}\dfrac{{{{\text{E}}_A}}}{4} \cr
& {\text{C}}{\text{. }}\dfrac{{{{\text{E}}_A}}}{2} \cr
& {\text{D}}{\text{. 4}}{{\text{E}}_A} \cr} $
Answer
588.6k+ views
Hint: When a force of equal magnitude is applied on both the springs, the springs will undergo elongation. The force is such that it is K times the elongation of the spring. Use the mathematical expression for this spring force and the energy stored in the spring by rearranging them to establish a relation between them. And thus find the required answer.
Formula used:
$F = - Kx$
$E = - \dfrac{1}{2}K{x^2}$
Complete step by step answer:
Consider a spring system as shown in figure below. One end of the spring is attached to a fixed vertical support and the other to a block which can move on a horizontal table. Let us assume x=0 denotes the position of the block when the spring is in its natural length. We shall calculate the work done on the block by the spring force as the block moves from x=0 to $x = {x_1}$.
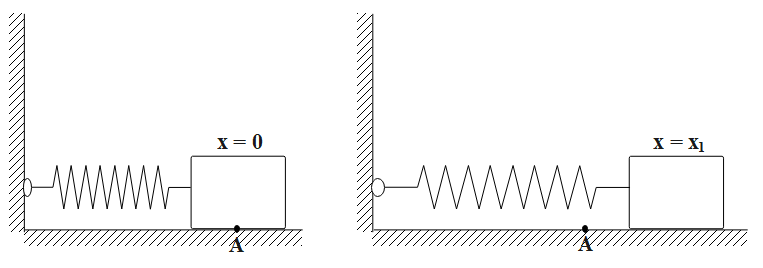
The force on the block is K times the elongation of the spring. Mathematically, the force on the spring or the spring force is:
$F = - Kx \cdots \cdots \cdots \cdots \left( 1 \right)$
But the elongation changes as the block moves and so does the force. We cannot take $\overrightarrow F $ out of the integration $\int {\overrightarrow F } .d\overrightarrow r $, when integrating for the work done. We have to write the work done during a small interval in which the block moves from x to x+dx. The force in this interval is kx and the displacement is dx. The force and the displacement are in opposite directions. So,
$\overrightarrow F .d\overrightarrow r = - Fdx = - Kxdx$
During this interval the total work do as the block is displaced from x=0 to $x = {x_1}$ is:
$W = \int\limits_0^{{x_1}} { - Kxdx} = \left[ { - \dfrac{1}{2}K{x^2}} \right]_0^{{x_1}} = - \dfrac{1}{2}Kx_1^2$
From work energy theorem we know that the work done on a system by the resultant force is equal to the change in the system’s kinetic energy, i.e.,
$E = - \dfrac{1}{2}K{x^2} \cdots \cdots \cdots \cdots \cdots \left( 2 \right)$
Rearranging equation (1) and (2) we get:
$\eqalign{
& E = - \dfrac{F}{{2K}} \cr
& \Rightarrow E \propto \dfrac{1}{K} \cdots \cdots \cdots \cdots \cdots \left( 3 \right) \cr} $
Now, in the given question it is provided to us that ${K_A} = 2{K_B}$ where A and B are two springs having spring constants ${K_A}$ and ${K_B}$respectively.
Taking ratio of energies stored in spring A and B by using equation (3) we get:
$\eqalign{
& \dfrac{{{E_A}}}{{{E_B}}} = \dfrac{{{K_B}}}{{{K_A}}} \cr
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{E_A}}}{{{E_B}}} = \dfrac{{{K_B}}}{{2{K_B}}}{\text{ }}\left[ {\because {K_A} = 2{K_B}\left( {given} \right)} \right] \cr
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{E_A}}}{{{E_B}}} = \dfrac{1}{2}{\text{ }} \cr
& \therefore {{\text{E}}_B} = 2{E_A} \cr} $
Therefore the correct option is A, i.e., if the energy stored in spring A is ${E_A}$ then energy stored in B will be $2{E_A}$.
Note:
The negative sign in the equation for energy, force and work done only symbolises that the direction of force and displacement are opposite with respect to each other. So students must not be confused with it otherwise. Additionally, the work done on a system by an individual force is not equal to the change in the kinetic energy; the sum of the work done by all the forces acting on the system is equal to the change in its kinetic energy.
Formula used:
$F = - Kx$
$E = - \dfrac{1}{2}K{x^2}$
Complete step by step answer:
Consider a spring system as shown in figure below. One end of the spring is attached to a fixed vertical support and the other to a block which can move on a horizontal table. Let us assume x=0 denotes the position of the block when the spring is in its natural length. We shall calculate the work done on the block by the spring force as the block moves from x=0 to $x = {x_1}$.

The force on the block is K times the elongation of the spring. Mathematically, the force on the spring or the spring force is:
$F = - Kx \cdots \cdots \cdots \cdots \left( 1 \right)$
But the elongation changes as the block moves and so does the force. We cannot take $\overrightarrow F $ out of the integration $\int {\overrightarrow F } .d\overrightarrow r $, when integrating for the work done. We have to write the work done during a small interval in which the block moves from x to x+dx. The force in this interval is kx and the displacement is dx. The force and the displacement are in opposite directions. So,
$\overrightarrow F .d\overrightarrow r = - Fdx = - Kxdx$
During this interval the total work do as the block is displaced from x=0 to $x = {x_1}$ is:
$W = \int\limits_0^{{x_1}} { - Kxdx} = \left[ { - \dfrac{1}{2}K{x^2}} \right]_0^{{x_1}} = - \dfrac{1}{2}Kx_1^2$
From work energy theorem we know that the work done on a system by the resultant force is equal to the change in the system’s kinetic energy, i.e.,
$E = - \dfrac{1}{2}K{x^2} \cdots \cdots \cdots \cdots \cdots \left( 2 \right)$
Rearranging equation (1) and (2) we get:
$\eqalign{
& E = - \dfrac{F}{{2K}} \cr
& \Rightarrow E \propto \dfrac{1}{K} \cdots \cdots \cdots \cdots \cdots \left( 3 \right) \cr} $
Now, in the given question it is provided to us that ${K_A} = 2{K_B}$ where A and B are two springs having spring constants ${K_A}$ and ${K_B}$respectively.
Taking ratio of energies stored in spring A and B by using equation (3) we get:
$\eqalign{
& \dfrac{{{E_A}}}{{{E_B}}} = \dfrac{{{K_B}}}{{{K_A}}} \cr
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{E_A}}}{{{E_B}}} = \dfrac{{{K_B}}}{{2{K_B}}}{\text{ }}\left[ {\because {K_A} = 2{K_B}\left( {given} \right)} \right] \cr
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{E_A}}}{{{E_B}}} = \dfrac{1}{2}{\text{ }} \cr
& \therefore {{\text{E}}_B} = 2{E_A} \cr} $
Therefore the correct option is A, i.e., if the energy stored in spring A is ${E_A}$ then energy stored in B will be $2{E_A}$.
Note:
The negative sign in the equation for energy, force and work done only symbolises that the direction of force and displacement are opposite with respect to each other. So students must not be confused with it otherwise. Additionally, the work done on a system by an individual force is not equal to the change in the kinetic energy; the sum of the work done by all the forces acting on the system is equal to the change in its kinetic energy.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

Actinoid contraction is more than lanthanoid contraction class 11 chemistry CBSE

The transition element that has lowest enthalpy of class 11 chemistry CBSE

Can anyone list 10 advantages and disadvantages of friction

State the laws of reflection of light




