
Two sources of sound ${S_1}$ and ${S_2}$, emitting waves of equal wavelength $20.0{\text{ }}cm$, are placed with a separation of $20.0{\text{ }}cm$ between them. A detector can be moved on a line parallel to ${S_1}{S_{}}$ and at a distance of $20.0{\text{ }}cm$ from it. Initially, the detector is equidistant from the two sources. Assuming that the waves emitted by the sources are in phase, find the minimum distance through which the detector should be shifted to detect a minimum of sound.
Answer
508.8k+ views
Hint: First of all we have to construct a figure. We have to assume that the waves meet at D which is $x$ distance from O. From geometry we have to find the path difference. Also from the minimum condition of waves we have to find path differences. After that by equating both terms we will eventually have our result.
Complete step by step answer:
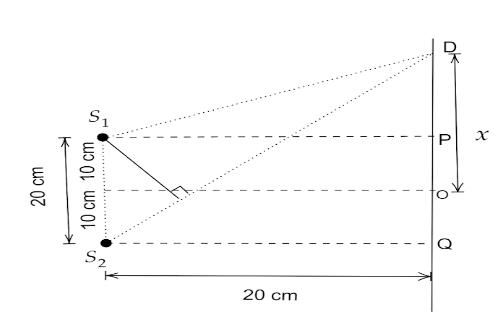
From the given figure we have to find out the phase difference $\Delta x$. According to given data $\lambda = 20\,cm$ and distance between $DQ$ and ${S_1}{S_2}$ is $20\,cm$ also ${S_1}{S_2} = 20{\text{ }}cm$. Let the distance between $D$ and $o$ is $x$ $cm$.
Then $PD = \left( {x - 10} \right)$ and $QD = \left( {x + 10} \right)$
From $\Delta {S_1}PD$ and $\Delta {S_2}QD$ we get,
${S_1}D = \sqrt {{{\left( {{S_1}P} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {PD} \right)}^2}} $ from Pythagoras Theorem,
$\Rightarrow {S_1}D = \sqrt {{{\left( {20} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {x - 10} \right)}^2}} $ and
$\Rightarrow {S_2}D = \sqrt {{{\left( {{S_2}Q} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {QD} \right)}^2}} $
$\Rightarrow {S_2}D = \sqrt {{{\left( {20} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {x + 10} \right)}^2}} $
The path difference $\Delta x$ is,
$\Delta x$=${S_2}D$-${S_1}D$
$ \Rightarrow \Delta x = \sqrt {{{\left( {20} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {x + 10} \right)}^2}} - \sqrt {{{\left( {20} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {x - 10} \right)}^2}} - - - - - \left( 1 \right)$
Path difference is defined as,
$\Delta x = \dfrac{{(2n + 1)\lambda }}{2}$
For minima, $n = 0$
$\therefore \Delta x = \dfrac{\lambda }{2}$
Substituting the value $\lambda $ we get,
$\Delta x = \dfrac{{20}}{2} = 10 - - - - \left( 2 \right)$
From equation $\left( 1 \right)$ and $\left( 2 \right)$ we get,
$\sqrt {{{\left( {20} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {x + 10} \right)}^2}} - \sqrt {{{\left( {20} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {x - 10} \right)}^2}} = 10$
$ \Rightarrow \sqrt {{{\left( {20} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {x + 10} \right)}^2}} = 10 + \sqrt {{{\left( {20} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {x - 10} \right)}^2}} $
Squaring both sides we get,
$400 + {x^2} + 100 + 20x = 100 + 400 + {x^2} - 20x + 100 + 20\sqrt {{{\left( {20} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {x - 10} \right)}^2}} $
By eliminating some terms we get,
$40x - 100 = 20\sqrt {{{\left( {20} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {x - 10} \right)}^2}} $
Again, squaring both sides we get,
$1600{x^2} + 10000 - 8000x = 400\left( {500 + {x^2} - 20x} \right) \\
\Rightarrow 1200{x^2} = 200000 $
Now the value of $x = 12.9$
Hence, the minimum distance through which the detector should be shifted to detect a minimum of sound is $12.9{\text{ }}cm$.
Note: We must use Pythagoras Theorem in the above figure. While solving the equations we must be sure that we do not cancel out any value of variable. For a minimum condition the value of $n = 0$.We have to assume that the waves meet $x$distance from the midpoint of detector $DQ$.
Complete step by step answer:

From the given figure we have to find out the phase difference $\Delta x$. According to given data $\lambda = 20\,cm$ and distance between $DQ$ and ${S_1}{S_2}$ is $20\,cm$ also ${S_1}{S_2} = 20{\text{ }}cm$. Let the distance between $D$ and $o$ is $x$ $cm$.
Then $PD = \left( {x - 10} \right)$ and $QD = \left( {x + 10} \right)$
From $\Delta {S_1}PD$ and $\Delta {S_2}QD$ we get,
${S_1}D = \sqrt {{{\left( {{S_1}P} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {PD} \right)}^2}} $ from Pythagoras Theorem,
$\Rightarrow {S_1}D = \sqrt {{{\left( {20} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {x - 10} \right)}^2}} $ and
$\Rightarrow {S_2}D = \sqrt {{{\left( {{S_2}Q} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {QD} \right)}^2}} $
$\Rightarrow {S_2}D = \sqrt {{{\left( {20} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {x + 10} \right)}^2}} $
The path difference $\Delta x$ is,
$\Delta x$=${S_2}D$-${S_1}D$
$ \Rightarrow \Delta x = \sqrt {{{\left( {20} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {x + 10} \right)}^2}} - \sqrt {{{\left( {20} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {x - 10} \right)}^2}} - - - - - \left( 1 \right)$
Path difference is defined as,
$\Delta x = \dfrac{{(2n + 1)\lambda }}{2}$
For minima, $n = 0$
$\therefore \Delta x = \dfrac{\lambda }{2}$
Substituting the value $\lambda $ we get,
$\Delta x = \dfrac{{20}}{2} = 10 - - - - \left( 2 \right)$
From equation $\left( 1 \right)$ and $\left( 2 \right)$ we get,
$\sqrt {{{\left( {20} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {x + 10} \right)}^2}} - \sqrt {{{\left( {20} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {x - 10} \right)}^2}} = 10$
$ \Rightarrow \sqrt {{{\left( {20} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {x + 10} \right)}^2}} = 10 + \sqrt {{{\left( {20} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {x - 10} \right)}^2}} $
Squaring both sides we get,
$400 + {x^2} + 100 + 20x = 100 + 400 + {x^2} - 20x + 100 + 20\sqrt {{{\left( {20} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {x - 10} \right)}^2}} $
By eliminating some terms we get,
$40x - 100 = 20\sqrt {{{\left( {20} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {x - 10} \right)}^2}} $
Again, squaring both sides we get,
$1600{x^2} + 10000 - 8000x = 400\left( {500 + {x^2} - 20x} \right) \\
\Rightarrow 1200{x^2} = 200000 $
Now the value of $x = 12.9$
Hence, the minimum distance through which the detector should be shifted to detect a minimum of sound is $12.9{\text{ }}cm$.
Note: We must use Pythagoras Theorem in the above figure. While solving the equations we must be sure that we do not cancel out any value of variable. For a minimum condition the value of $n = 0$.We have to assume that the waves meet $x$distance from the midpoint of detector $DQ$.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




