
Two sources A and B are sounding notes of frequency 660Hz. A listener moves from A to B with a constant velocity u. If the speed of sound is \[330m{{s}^{-1}}\]. What must be the value of u so that he hears 8 beats per second?
(A). \[2.8m{{s}^{-1}}\]
(B). \[2m{{s}^{-1}}\]
(C). \[3.0m{{s}^{-1}}\]
(D). \[3.5m{{s}^{-1}}\]
Answer
603.3k+ views
Hint: Since the listener is moving, we can apply the Doppler effect here. From the change in frequency, we can find out the velocity of the listener. We can use the Doppler effect equation to find out the velocity of the listener.
Formula used: \[\text{apparent frequency = original frequency}\left[ \dfrac{\text{Relative velocity between sound and listener}}{\text{Relative velocity between sound and source}} \right]\]
Complete step by step answer:
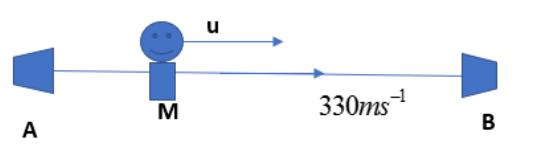
Since the sources are at rest and the listener is moving with a velocity u, we have to consider the Doppler effect here. The change in frequency according to the motion is known as the Doppler effect. The apparent frequency can be written as,
\[\text{apparent frequency = original frequency}\left[ \dfrac{\text{Relative velocity between sound and listener}}{\text{Relative velocity between sound and source}} \right]\]
Here we can write the apparent frequency of A as \[{{f}_{A}}\].
Original frequency is 660 Hz. The relative velocity between sound and listener will be \[(330-u)m{{s}^{-1}}\] and the relative velocity between sound and source will be \[330m{{s}^{-1}}\]since the source is not moving. We can assign these values to find the apparent frequency of source A.
\[{{f}_{A}}=660\left( \dfrac{330-u}{330} \right)\]…………………..(1)
Next, we can find out the apparent frequency of B, \[{{f}_{B}}\].
Here the relative velocity between sound and listener will be \[(330+u)m{{s}^{-1}}\] and the relative velocity between sound and source will be \[330m{{s}^{-1}}\]since the source is not moving. We can assign these values to the \[{{f}_{B}}\].
\[{{f}_{B}}=660\left( \dfrac{330+u}{330} \right)\]…………………..(2)
Since the positive sign in the numerator of \[{{f}_{B}}\], it will be greater than the \[{{f}_{A}}\].
As we know, the change in apparent frequency can be written as the number of beats per second. Here we required 8 beats per second.
\[{{f}_{B}}-{{f}_{A}}=8\]………………………….(3)
Now we can assign equation (1) and equation (2) into the equation (3).
\[660\left( \dfrac{330+u}{330} \right)-660\left( \dfrac{330-u}{330} \right)=8\]
\[\dfrac{660}{330}\left( 330+u-330+u \right)=8\]
\[\dfrac{660}{330}\left( 2u \right)=8\]
\[4u=8\]
\[u=2m{{s}^{-1}}\]
Therefore, the correct option is B.
Additional information:
Due to the movement of an object (either source or listener) frequency will change accordingly. This is known as the Doppler effect. It has been widely used in military services, medical science, astrophysics, etc. To check the speed of the moving vehicle, we will send a sound wave of known frequency towards the moving vehicle. This will get reflected from the object. We can detect the change in frequency of this reflected wave using a monitoring machine. This type of change in frequency is known as Doppler shift.
Note: To find the apparent frequency of the sound wave, we have to take the relative velocity between sound and source and the relative velocity between sound and listener. Since they are relative velocity, the signs are also important. In the first case, the listener is moving away from the source A. So the velocity will be the difference between them. In the second case, the listener is moving towards the source B. So the velocity will be the sum of these two velocities.
Formula used: \[\text{apparent frequency = original frequency}\left[ \dfrac{\text{Relative velocity between sound and listener}}{\text{Relative velocity between sound and source}} \right]\]
Complete step by step answer:

Since the sources are at rest and the listener is moving with a velocity u, we have to consider the Doppler effect here. The change in frequency according to the motion is known as the Doppler effect. The apparent frequency can be written as,
\[\text{apparent frequency = original frequency}\left[ \dfrac{\text{Relative velocity between sound and listener}}{\text{Relative velocity between sound and source}} \right]\]
Here we can write the apparent frequency of A as \[{{f}_{A}}\].
Original frequency is 660 Hz. The relative velocity between sound and listener will be \[(330-u)m{{s}^{-1}}\] and the relative velocity between sound and source will be \[330m{{s}^{-1}}\]since the source is not moving. We can assign these values to find the apparent frequency of source A.
\[{{f}_{A}}=660\left( \dfrac{330-u}{330} \right)\]…………………..(1)
Next, we can find out the apparent frequency of B, \[{{f}_{B}}\].
Here the relative velocity between sound and listener will be \[(330+u)m{{s}^{-1}}\] and the relative velocity between sound and source will be \[330m{{s}^{-1}}\]since the source is not moving. We can assign these values to the \[{{f}_{B}}\].
\[{{f}_{B}}=660\left( \dfrac{330+u}{330} \right)\]…………………..(2)
Since the positive sign in the numerator of \[{{f}_{B}}\], it will be greater than the \[{{f}_{A}}\].
As we know, the change in apparent frequency can be written as the number of beats per second. Here we required 8 beats per second.
\[{{f}_{B}}-{{f}_{A}}=8\]………………………….(3)
Now we can assign equation (1) and equation (2) into the equation (3).
\[660\left( \dfrac{330+u}{330} \right)-660\left( \dfrac{330-u}{330} \right)=8\]
\[\dfrac{660}{330}\left( 330+u-330+u \right)=8\]
\[\dfrac{660}{330}\left( 2u \right)=8\]
\[4u=8\]
\[u=2m{{s}^{-1}}\]
Therefore, the correct option is B.
Additional information:
Due to the movement of an object (either source or listener) frequency will change accordingly. This is known as the Doppler effect. It has been widely used in military services, medical science, astrophysics, etc. To check the speed of the moving vehicle, we will send a sound wave of known frequency towards the moving vehicle. This will get reflected from the object. We can detect the change in frequency of this reflected wave using a monitoring machine. This type of change in frequency is known as Doppler shift.
Note: To find the apparent frequency of the sound wave, we have to take the relative velocity between sound and source and the relative velocity between sound and listener. Since they are relative velocity, the signs are also important. In the first case, the listener is moving away from the source A. So the velocity will be the difference between them. In the second case, the listener is moving towards the source B. So the velocity will be the sum of these two velocities.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




