
Two sound speakers are driven in phase by an audio amplifier at frequency 600Hz. The speed of sound is 340m/s. The speakers are on the y-axis, one at $y = + 1.0m$ and the other at $y = - 1.0m$. A listener begins at $y = 0$ and walks along a line parallel to the y – axis at a very large distance x away. At ${\dfrac{\theta }{2}^ \circ }$angle she will first hear a maximum $\left( {{\text{angle }}{{\text{0}}^ \circ }} \right)$ sound intensity. Find $\theta $:
Answer
570k+ views
Hint: In order to find the required solution of the given question we will apply the concept of superposition and interference. In modern physics, the double-slit experiment is a demonstration to show that light and matter display characteristics of both classically defined waves and particles
Formula Used:
$\dfrac{{yd}}{x}$
$\lambda = \dfrac{c}{f}$
Complete step-by-step solution
According to Young’s Double slit experiment, at any point on the screen at a distance ‘y’ from the center, the waves travel distances ‘${I_1}$’ and ‘${I_2}$’ to create a path difference of $\Delta I$at the point in question. There is a path difference in Young’s double-slit experiment between the two light waves from ‘${s_1}$’ and ‘${s_2}$’.
Path difference between sound from the two sources at a point of the line along which the listener travels is given as $\dfrac{{yd}}{x}$
Where ‘y’ is denoted as the y-coordinate of the point, ‘d’ is denoted as the separation between the two sources.
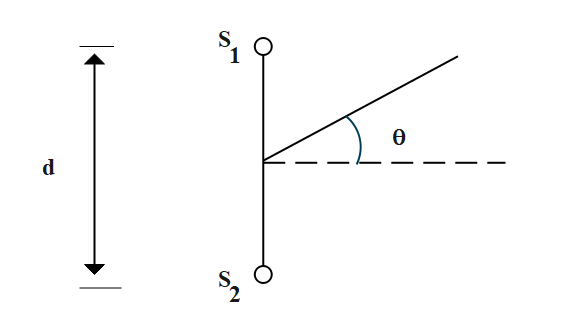
Thus, to obtain a maxima,
$\dfrac{{yd}}{x} = \lambda = \dfrac{c}{f}$
$ \Rightarrow \tan \theta = \dfrac{y}{x} = \dfrac{c}{{fd}}$
$\tan \theta = \dfrac{{340}}{{600 \times 2}}$
Applying approximation, $\tan \theta \approx \theta $
$\therefore \theta \approx {16.5^ \circ }$
Hence, the value of ‘$\theta $’ is approximately equal to ${16.5^ \circ }$.
Note: In physics, the method by which two or more light, sound, or electromagnetic waves of the same frequency combine to reinforce or cancel each other, is known as the interference of light. Interferences of light are of two types, constructive and destructive. Constructive interference results when two identical waves are superimposed in phase. Destructive interference results when two identical waves are superimposed exactly but out of phase. Superposition is defined as the combination of two waves at the same location.
Formula Used:
$\dfrac{{yd}}{x}$
$\lambda = \dfrac{c}{f}$
Complete step-by-step solution
According to Young’s Double slit experiment, at any point on the screen at a distance ‘y’ from the center, the waves travel distances ‘${I_1}$’ and ‘${I_2}$’ to create a path difference of $\Delta I$at the point in question. There is a path difference in Young’s double-slit experiment between the two light waves from ‘${s_1}$’ and ‘${s_2}$’.
Path difference between sound from the two sources at a point of the line along which the listener travels is given as $\dfrac{{yd}}{x}$
Where ‘y’ is denoted as the y-coordinate of the point, ‘d’ is denoted as the separation between the two sources.

Thus, to obtain a maxima,
$\dfrac{{yd}}{x} = \lambda = \dfrac{c}{f}$
$ \Rightarrow \tan \theta = \dfrac{y}{x} = \dfrac{c}{{fd}}$
$\tan \theta = \dfrac{{340}}{{600 \times 2}}$
Applying approximation, $\tan \theta \approx \theta $
$\therefore \theta \approx {16.5^ \circ }$
Hence, the value of ‘$\theta $’ is approximately equal to ${16.5^ \circ }$.
Note: In physics, the method by which two or more light, sound, or electromagnetic waves of the same frequency combine to reinforce or cancel each other, is known as the interference of light. Interferences of light are of two types, constructive and destructive. Constructive interference results when two identical waves are superimposed in phase. Destructive interference results when two identical waves are superimposed exactly but out of phase. Superposition is defined as the combination of two waves at the same location.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




