
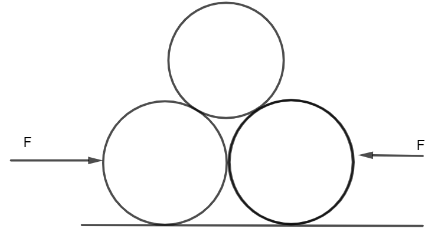
Two smooth cylindrical bars weighing W each lie next to each other in contact. A similar third bar is placed over the two bars as shown in figure. Neglecting friction, the minimum horizontal force on each lower bar necessary to keep them together is-
A. $\dfrac{W}{2}$
B. $W$
C. $\dfrac{W}{{\sqrt 3 }}$
D. $\dfrac{W}{{2\sqrt 3 }}$

Answer
505.2k+ views
Hint: Let us first get some idea about force. A force is an external agent capable of altering a body's condition of rest or motion. There is a magnitude and a direction to it. The force's direction is known as the force's direction, and the location where force is applied is known as the point where force is applied.
Complete step by step answer:
The normal force between the lower cylinders must be zero for the system to be in equilibrium, which can be done by applying an external force $F$ as shown in the diagram.Let us get some ideas about free body diagrams. A free body diagram is a diagrammatic representation of a single body or a subsystem of bodies that has been isolated from its surroundings and depicts all of the forces acting on it.
A free body diagram is a graphical image used in physics and engineering to visualise the applied forces, moments, and consequent reactions on a body under a particular condition. They show a body or a group of bodies, as well as all the applied forces, moments, and responses that act on the body (ies).
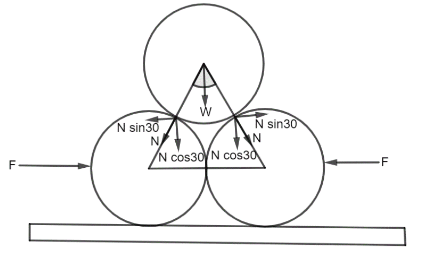
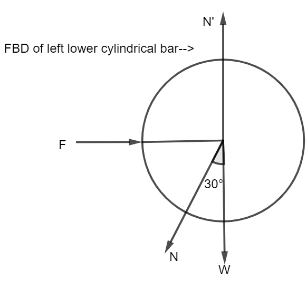
We can write the following on the basis of the free body diagram of the left lower cylindrical bar:
$F = N\,\sin {30^ \circ }$ …$(1)$
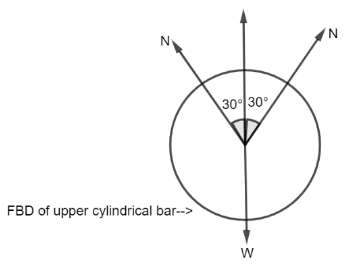
Hence, using the free body diagram of the left lower cylindrical bar as a guide, we may write:
$W = 2N\,\cos {30^ \circ }$ ….$(2)$
Now diving Eq $(1)$and Eq$(2):$ $\dfrac{{(1)}}{{(2)}}$
$\dfrac{F}{W} = \dfrac{{N\,\sin {{30}^ \circ }}}{{2N\,\cos {{30}^ \circ }}}$
$\Rightarrow F = \dfrac{{W\sin {{30}^ \circ }}}{{2\,\cos {{30}^ \circ }}}$
$\Rightarrow F = \dfrac{{W\,\tan {{30}^ \circ }}}{2}$
$\Rightarrow F = \dfrac{{W(\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }})}}{2}$
$\therefore F = \dfrac{W}{{2\sqrt 3 }}$
So,option D is correct.
Note: In order to solve this problem there are some very important points which we should keep on our finger tip. Making a free body diagram is very important here and vector resolution and breaking into components is also important for solving this problem.
Complete step by step answer:
The normal force between the lower cylinders must be zero for the system to be in equilibrium, which can be done by applying an external force $F$ as shown in the diagram.Let us get some ideas about free body diagrams. A free body diagram is a diagrammatic representation of a single body or a subsystem of bodies that has been isolated from its surroundings and depicts all of the forces acting on it.
A free body diagram is a graphical image used in physics and engineering to visualise the applied forces, moments, and consequent reactions on a body under a particular condition. They show a body or a group of bodies, as well as all the applied forces, moments, and responses that act on the body (ies).


We can write the following on the basis of the free body diagram of the left lower cylindrical bar:
$F = N\,\sin {30^ \circ }$ …$(1)$

Hence, using the free body diagram of the left lower cylindrical bar as a guide, we may write:
$W = 2N\,\cos {30^ \circ }$ ….$(2)$
Now diving Eq $(1)$and Eq$(2):$ $\dfrac{{(1)}}{{(2)}}$
$\dfrac{F}{W} = \dfrac{{N\,\sin {{30}^ \circ }}}{{2N\,\cos {{30}^ \circ }}}$
$\Rightarrow F = \dfrac{{W\sin {{30}^ \circ }}}{{2\,\cos {{30}^ \circ }}}$
$\Rightarrow F = \dfrac{{W\,\tan {{30}^ \circ }}}{2}$
$\Rightarrow F = \dfrac{{W(\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }})}}{2}$
$\therefore F = \dfrac{W}{{2\sqrt 3 }}$
So,option D is correct.
Note: In order to solve this problem there are some very important points which we should keep on our finger tip. Making a free body diagram is very important here and vector resolution and breaking into components is also important for solving this problem.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




