
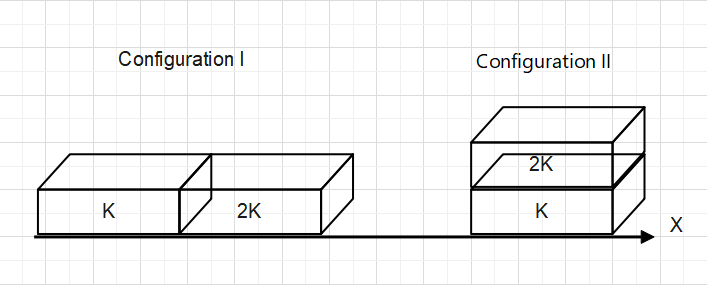
Two rectangular blocks, having identical dimensions, can be arranged either in configuration I or in configuration II as shown in the figure.One of the blocks has thermal conductivity K and the other has 2K. The temperature difference between the ends along the x-axis is the same in both configurations. It takes 9 s to transport a certain amount of heat from the hot end to the cold end in configuration I. The time to transport the same amount of heat in configuration II is.

Answer
515.1k+ views
Hint: Firstly, we have to find the equivalent thermal Resistance for both the configurations. Then, with the help of heat transfer through conduction mode, you have to deduce a proportional expression for time.So, as to calculate the time for configuration II.
Formula Used:
Here, 2 formulas are used. One is thermal resistance. That is, \[R=\dfrac{l}{KA}\].
Where $l$ is the length of object in metre (‘m’), K is the thermal conductivity in ‘$\left( \dfrac{w}{k\centerdot m} \right)$’ and A is the cross-sectional area in ‘${{m}^{2}}$’ perpendicular to the path of heat flow.
While, Other is heat transfer through conduction. That is,$Q=\dfrac{\left( {{T}_{1}}-{{T}_{2}} \right)}{R}t$
Where, ‘${{T}_{1}}$’ is the temperature of object having ${{K}_{1}}$conductivity and ‘ \[{{T}_{2}}\]’ is the temperature of object having \[{{K}_{2}}\] conductivity.
‘t’ is the time required in the process.
Complete step-by-step solution:
It is given that the temperature difference is same in both the configurations.
So,\[{{H}_{I}}={{H}_{II}}\]
Now, In configuration I
total thermal resistance :-
\[{{R}_{eq}}=\dfrac{l}{KA}+\dfrac{l}{2KA}\]
\[{{R}_{eq}}=\dfrac{1}{3}\dfrac{l}{KA}\]
Now, In Configuration II
total thermal resistance :-
\[R{{'}_{eq}}=\left( \dfrac{1\times \dfrac{1}{2}}{1+\dfrac{1}{2}} \right)\dfrac{l}{KA}\]
\[R{{'}_{eq}}=\dfrac{1}{3}\dfrac{l}{KA}\]
Since, We have this formula also :-
$Q=\dfrac{\left( {{T}_{1}}-{{T}_{2}} \right)}{R}t$
So, If Q and $\left( {{T}_{1}}-{{T}_{2}} \right)$ are constant. Then, we can conclude that
$t\propto R$
Therefore, $\dfrac{{{t}_{2}}}{{{t}_{1}}}=\dfrac{{{R}_{2}}}{{{R}_{1}}}$
${{t}_{2}}=\dfrac{2}{9}\times 9$
And the result is ${{t}_{2}}=2\sec $
Hence, the time required to transport the same amount of heat in configuration II is 2 sec.
Note:Always solve these types of questions in a manner as prescribed above to get the correct result. Also, we are using the formula of heat transfer through conduction mode only. So, don't use any other formula for heat transfer. As the formula becomes different through a different mode of transfer.
Formula Used:
Here, 2 formulas are used. One is thermal resistance. That is, \[R=\dfrac{l}{KA}\].
Where $l$ is the length of object in metre (‘m’), K is the thermal conductivity in ‘$\left( \dfrac{w}{k\centerdot m} \right)$’ and A is the cross-sectional area in ‘${{m}^{2}}$’ perpendicular to the path of heat flow.
While, Other is heat transfer through conduction. That is,$Q=\dfrac{\left( {{T}_{1}}-{{T}_{2}} \right)}{R}t$
Where, ‘${{T}_{1}}$’ is the temperature of object having ${{K}_{1}}$conductivity and ‘ \[{{T}_{2}}\]’ is the temperature of object having \[{{K}_{2}}\] conductivity.
‘t’ is the time required in the process.
Complete step-by-step solution:
It is given that the temperature difference is same in both the configurations.
So,\[{{H}_{I}}={{H}_{II}}\]
Now, In configuration I
total thermal resistance :-
\[{{R}_{eq}}=\dfrac{l}{KA}+\dfrac{l}{2KA}\]
\[{{R}_{eq}}=\dfrac{1}{3}\dfrac{l}{KA}\]
Now, In Configuration II
total thermal resistance :-
\[R{{'}_{eq}}=\left( \dfrac{1\times \dfrac{1}{2}}{1+\dfrac{1}{2}} \right)\dfrac{l}{KA}\]
\[R{{'}_{eq}}=\dfrac{1}{3}\dfrac{l}{KA}\]
Since, We have this formula also :-
$Q=\dfrac{\left( {{T}_{1}}-{{T}_{2}} \right)}{R}t$
So, If Q and $\left( {{T}_{1}}-{{T}_{2}} \right)$ are constant. Then, we can conclude that
$t\propto R$
Therefore, $\dfrac{{{t}_{2}}}{{{t}_{1}}}=\dfrac{{{R}_{2}}}{{{R}_{1}}}$
${{t}_{2}}=\dfrac{2}{9}\times 9$
And the result is ${{t}_{2}}=2\sec $
Hence, the time required to transport the same amount of heat in configuration II is 2 sec.
Note:Always solve these types of questions in a manner as prescribed above to get the correct result. Also, we are using the formula of heat transfer through conduction mode only. So, don't use any other formula for heat transfer. As the formula becomes different through a different mode of transfer.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




