
Two points O $\left( 0,0 \right)$ and A $\left( 3,\sqrt{3} \right)$ along with another point P form an equilateral triangle. Find the coordinate of P.
Answer
606.3k+ views
Hint: Here we may first calculate the length of one side of the triangle using the given two points then equate it to the length of the sides PA and PO. Since, it’s an equilateral triangle so, the length of all the sides are equal.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Here the two given points are O $\left( 0,0 \right)$ and A $\left( 3,\sqrt{3} \right)$.
Therefore length of OA can be calculated using length formula which is given as:
According to length formula length between any two points is = $\sqrt{{{\left( {{x}_{2}}-{{x}_{2}} \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( {{y}_{2}}-{{y}_{1}} \right)}^{2}}}$
So, using this formula we have:
OA =$\sqrt{{{\left( 3-0 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( \sqrt{3}-0 \right)}^{2}}}$
= $\sqrt{{{\left( 3 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( \sqrt{3} \right)}^{2}}}$
= $\sqrt{9+3}$
= $\sqrt{12}$
So, OA = $2\sqrt{3}\,\,units............(1)$
Let us take the coordinates of point P to be (a,b).
Now we may find the length of the sides PA and PO using distance formula.
So, PA = $\sqrt{{{\left( 3-a \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( \sqrt{3}-b \right)}^{2}}}.............\left( 2 \right)$
Similarly using distance formula to calculate the length of PO, we get:
PO =$\sqrt{{{\left( 0-a \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( 0-b \right)}^{2}}}$
Or, PO = $\sqrt{{{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}}................(3)$
Since, triangle AOP is an equilateral triangle so all the sides are equal i.e. :
OA = PO = PA
First consider the case when:
OA = PO
We may substitute here the lengths of OA and PO from equations (1) and (3) and get:
$2\sqrt{3}=\sqrt{{{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}}$
On squaring both sides we get:
$12={{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}............(4)$
Now, also we have:
PO = PA
So, again putting values of PO and PA from equations (3) and (2) and squaring both sides we get:
${{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}=9+{{a}^{2}}-6a+3+{{b}^{2}}-2\sqrt{3b}$
Or, ${{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}-{{a}^{2}}-{{b}^{2}}+6a+2\sqrt{3b}-9-3=0$
Or, $6a+2\sqrt{3}b-12=0$
Or, $2\sqrt{3}b=12-6a$
So, from this we can write b as:
$\begin{align}
& b=\dfrac{12-6a}{2\sqrt{3}} \\
& b\,=\dfrac{6-3a}{\sqrt{3}}.............(5) \\
\end{align}$
On substituting value of b from equation (5) in equation (4) we get:
$12={{a}^{2}}+{{\left( \tfrac{\left( 6-3a \right)}{\sqrt{3}} \right)}^{2}}$
Or, \[12={{a}^{2}}\dfrac{36+9{{a}^{2}}-36a}{3}\]
Or, $12\times 3=12{{a}^{2}}-36a+36$
Or, $12a\left( a-6 \right)=0$
From here we can get value of a as:
a=0 or a = 6
On putting a =0 in equation (5) , we get:
$\begin{align}
& b=\dfrac{6-3\times 0}{\sqrt{3}} \\
& \,\,\,\,=\dfrac{6}{\sqrt{3}} \\
& \,\,\,\,=2\sqrt{3} \\
\end{align}$
On putting a = 6 in equation (5) we get:
$\begin{align}
& b=\dfrac{6-3\times 6}{\sqrt{3}} \\
& \,\,\,\,=\dfrac{-12}{\sqrt{3}} \\
& \,\,\,\,=-4\sqrt{3} \\
\end{align}$
Therefore, the point P can be $\left( 0,2\sqrt{3} \right)$ or $\left( 6,-4\sqrt{3} \right)$.
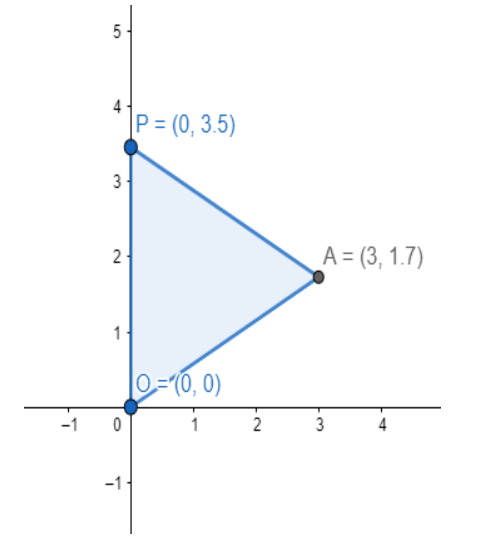
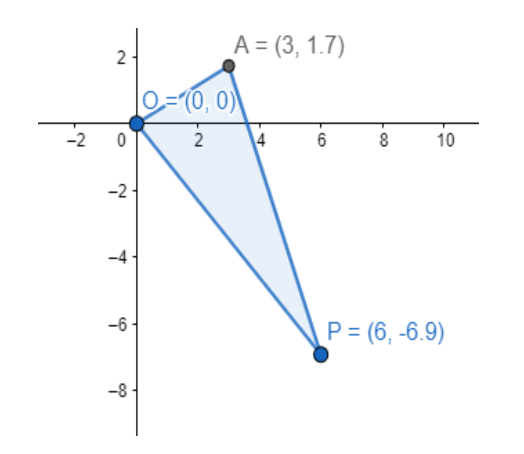
Note: Students should note here that as we obtain a quadratic equation in ‘a’ so, we get two values of a. These two values of a give two values of b correspondingly.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Here the two given points are O $\left( 0,0 \right)$ and A $\left( 3,\sqrt{3} \right)$.
Therefore length of OA can be calculated using length formula which is given as:
According to length formula length between any two points is = $\sqrt{{{\left( {{x}_{2}}-{{x}_{2}} \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( {{y}_{2}}-{{y}_{1}} \right)}^{2}}}$
So, using this formula we have:
OA =$\sqrt{{{\left( 3-0 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( \sqrt{3}-0 \right)}^{2}}}$
= $\sqrt{{{\left( 3 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( \sqrt{3} \right)}^{2}}}$
= $\sqrt{9+3}$
= $\sqrt{12}$
So, OA = $2\sqrt{3}\,\,units............(1)$
Let us take the coordinates of point P to be (a,b).
Now we may find the length of the sides PA and PO using distance formula.
So, PA = $\sqrt{{{\left( 3-a \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( \sqrt{3}-b \right)}^{2}}}.............\left( 2 \right)$
Similarly using distance formula to calculate the length of PO, we get:
PO =$\sqrt{{{\left( 0-a \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( 0-b \right)}^{2}}}$
Or, PO = $\sqrt{{{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}}................(3)$
Since, triangle AOP is an equilateral triangle so all the sides are equal i.e. :
OA = PO = PA
First consider the case when:
OA = PO
We may substitute here the lengths of OA and PO from equations (1) and (3) and get:
$2\sqrt{3}=\sqrt{{{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}}$
On squaring both sides we get:
$12={{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}............(4)$
Now, also we have:
PO = PA
So, again putting values of PO and PA from equations (3) and (2) and squaring both sides we get:
${{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}=9+{{a}^{2}}-6a+3+{{b}^{2}}-2\sqrt{3b}$
Or, ${{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}-{{a}^{2}}-{{b}^{2}}+6a+2\sqrt{3b}-9-3=0$
Or, $6a+2\sqrt{3}b-12=0$
Or, $2\sqrt{3}b=12-6a$
So, from this we can write b as:
$\begin{align}
& b=\dfrac{12-6a}{2\sqrt{3}} \\
& b\,=\dfrac{6-3a}{\sqrt{3}}.............(5) \\
\end{align}$
On substituting value of b from equation (5) in equation (4) we get:
$12={{a}^{2}}+{{\left( \tfrac{\left( 6-3a \right)}{\sqrt{3}} \right)}^{2}}$
Or, \[12={{a}^{2}}\dfrac{36+9{{a}^{2}}-36a}{3}\]
Or, $12\times 3=12{{a}^{2}}-36a+36$
Or, $12a\left( a-6 \right)=0$
From here we can get value of a as:
a=0 or a = 6
On putting a =0 in equation (5) , we get:
$\begin{align}
& b=\dfrac{6-3\times 0}{\sqrt{3}} \\
& \,\,\,\,=\dfrac{6}{\sqrt{3}} \\
& \,\,\,\,=2\sqrt{3} \\
\end{align}$
On putting a = 6 in equation (5) we get:
$\begin{align}
& b=\dfrac{6-3\times 6}{\sqrt{3}} \\
& \,\,\,\,=\dfrac{-12}{\sqrt{3}} \\
& \,\,\,\,=-4\sqrt{3} \\
\end{align}$
Therefore, the point P can be $\left( 0,2\sqrt{3} \right)$ or $\left( 6,-4\sqrt{3} \right)$.


Note: Students should note here that as we obtain a quadratic equation in ‘a’ so, we get two values of a. These two values of a give two values of b correspondingly.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




