
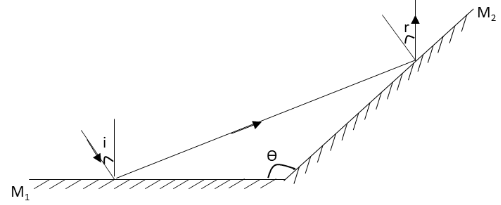
Two plane mirrors are separated by an angle of ‘\[\theta \]’ as shown in figure. If the ray strikes the mirror \[{M_1}\] at angle \[i\] then the angle \[r\] at which the ray leaves the mirror \[{M_2}\] is
A. \[r = 2\theta - i\]
B. \[r = \theta - i\]
C. \[r = \theta - 2i\]
D. \[r = 2\theta + i\]

Answer
562.8k+ views
Hint:We should first redraw the given diagram of the two plane mirror with the angle of incidence and angle of reflection and normal shown in the diagram. The values of the angle of reflection can be determined using Snell's law of reflection. Then use the theorem that the sum of all three angles in a triangle is \[180^\circ \] and calculate the angle of reflection of the ray from the second mirror.
Complete answer:
We have given that the two plane mirrors \[{M_1}\] and \[{M_2}\] are inclined at an angle \[\theta \] with each other. The ray of light strikes the mirror \[{M_1}\] at an angle of incidence \[i\] and then reflects from the mirror \[{M_1}\] and hits the mirror \[{M_2}\].This ray of light from mirror \[{M_2}\] leaves with an angle of reflection \[r\]. We have asked to calculate the value of this angle of reflection. Let us redraw the given diagram of the two mirrors as follows:

In the above diagram, \[{N_1}\] is the normal to the mirror \[{M_1}\]. Hence, according to Snell’s law, the angle of incidence and angle of reflection from the mirror \[{M_1}\] is the same. Hence, the angle between this normal, reflected ray and incident ray is the same which is \[i\].
Also the normal \[{N_1}\] is perpendicular to the mirror \[{M_1}\]. Hence, the angle between the normal and surface of the mirror is \[90^\circ \]. Thus, the angle between the reflected ray from the mirror \[{M_1}\] and the surface of the mirror is \[90^\circ - i\].In the above diagram, \[{N_2}\] is the normal to the mirror \[{M_2}\]. Hence, according to Snell’s law, the angle of incidence and angle of reflection from the mirror \[{M_2}\] must be the same. Hence, the angle between this normal, reflected ray and incident ray is the same which is \[r\].
Also the normal \[{N_2}\] is perpendicular to the mirror \[{M_2}\]. Hence, the angle between the normal and surface of the mirror is \[90^\circ \]. Thus, the angle between the incident ray on the mirror \[{M_2}\] and the surface of the mirror is \[90^\circ - r\].We know that the sum of the angles in a triangle is \[180^\circ \].Hence, the sum of the three angles in the triangle formed by the ray of light and surfaces of the two mirrors is \[180^\circ \].
\[90^\circ - i + \theta + 90^\circ - r = 180^\circ \]
\[ \Rightarrow - i + \theta - r = 0\]
\[ \therefore r = \theta - i\]
Therefore, the angle at which the ray leaves the second mirror is \[\theta - i\].
Hence, the correct option is B.
Note: The students should be careful while using the various angles in the diagram. The angles which are the same according to Snell’s law should be considered carefully. The students may get confused and consider that the angle of reflection is the angle between the reflected ray and mirror. But one should keep in mind that the angle of incidence is the angle between incident ray and normal and angle of reflection is the angle between the reflected ray and normal.
Complete answer:
We have given that the two plane mirrors \[{M_1}\] and \[{M_2}\] are inclined at an angle \[\theta \] with each other. The ray of light strikes the mirror \[{M_1}\] at an angle of incidence \[i\] and then reflects from the mirror \[{M_1}\] and hits the mirror \[{M_2}\].This ray of light from mirror \[{M_2}\] leaves with an angle of reflection \[r\]. We have asked to calculate the value of this angle of reflection. Let us redraw the given diagram of the two mirrors as follows:

In the above diagram, \[{N_1}\] is the normal to the mirror \[{M_1}\]. Hence, according to Snell’s law, the angle of incidence and angle of reflection from the mirror \[{M_1}\] is the same. Hence, the angle between this normal, reflected ray and incident ray is the same which is \[i\].
Also the normal \[{N_1}\] is perpendicular to the mirror \[{M_1}\]. Hence, the angle between the normal and surface of the mirror is \[90^\circ \]. Thus, the angle between the reflected ray from the mirror \[{M_1}\] and the surface of the mirror is \[90^\circ - i\].In the above diagram, \[{N_2}\] is the normal to the mirror \[{M_2}\]. Hence, according to Snell’s law, the angle of incidence and angle of reflection from the mirror \[{M_2}\] must be the same. Hence, the angle between this normal, reflected ray and incident ray is the same which is \[r\].
Also the normal \[{N_2}\] is perpendicular to the mirror \[{M_2}\]. Hence, the angle between the normal and surface of the mirror is \[90^\circ \]. Thus, the angle between the incident ray on the mirror \[{M_2}\] and the surface of the mirror is \[90^\circ - r\].We know that the sum of the angles in a triangle is \[180^\circ \].Hence, the sum of the three angles in the triangle formed by the ray of light and surfaces of the two mirrors is \[180^\circ \].
\[90^\circ - i + \theta + 90^\circ - r = 180^\circ \]
\[ \Rightarrow - i + \theta - r = 0\]
\[ \therefore r = \theta - i\]
Therefore, the angle at which the ray leaves the second mirror is \[\theta - i\].
Hence, the correct option is B.
Note: The students should be careful while using the various angles in the diagram. The angles which are the same according to Snell’s law should be considered carefully. The students may get confused and consider that the angle of reflection is the angle between the reflected ray and mirror. But one should keep in mind that the angle of incidence is the angle between incident ray and normal and angle of reflection is the angle between the reflected ray and normal.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




