
Two particles of masses 'm' and '9m' are separated by a distance 'r'. At a point on the line joining them the gravitational field is zero. The gravitational potential at that point is (G = Universal constant of gravitation).
A. $\dfrac{{ - 4Gm}}{r}$
B. $\dfrac{{ - 8Gm}}{r}$
C. $\dfrac{{ - 16Gm}}{r}$
D. $\dfrac{{ - 32Gm}}{r}$
Answer
594.9k+ views
Hint: As we all know that gravitational field is zero where the force of gravitation applied by both the bodies on a unit mass placed in between the line of action of force of two bodies is equal and hence the net force at a point becomes zero.
Complete answer:
Consider the gravitational field at a point P is equal to zero which is located at a distance x from mass m. Suppose that a unit mass is placed at point P.
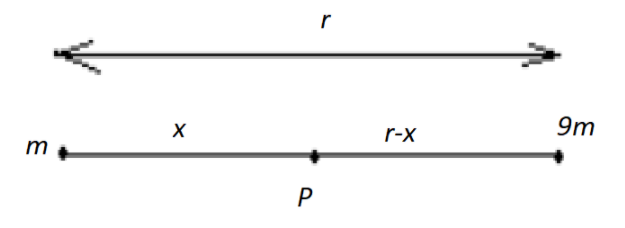
As we all know that since the gravitational field at a point P is zero, so it can be said that the gravitational pull exerted by the body of mass m on a unit mass at P i.e ${F_1}$ is equal to the gravitational pull exerted by the body of mass 9m on a unit mass i.e ${F_2}$.
Therefore, we can say that the relation becomes,
$
{F_1} = {F_2} \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{{Gm}}{{{x^2}}} = \dfrac{{G\left( {9m} \right)}}{{{{\left( {r - x} \right)}^2}}} \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{{{{\left( {r - x} \right)}^2}}}{{{x^2}}} = 9 \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{{{{\left( {r - x} \right)}^{}}}}{{{x^{}}}} = 3 \\
\Rightarrow x = \dfrac{r}{4} \\
$
Now we will find the gravitational potential at point P. So the gravitational potential ${V_P}$ at point P is,
${V_P} = - \dfrac{{Gm}}{x} - \dfrac{{G(9m)}}{{r - x}}$…… (I)
We will Substitute $x = \dfrac{r}{4}$ in equation (I) and the result would become;
$
\Rightarrow {V_P} = - \dfrac{Gm}{{\dfrac{r}{{4}}}}-\dfrac{9Gm}{{r-\dfrac{r}{{4}}}}
\Rightarrow {V_P} = - \dfrac{Gm}{{\dfrac{r}{{4}}}}-\dfrac{9Gm}{{\dfrac{3r}{{4}}}}
$
$\Rightarrow {V_P} = - \dfrac{{16\,Gm}}{r}$
At the point where the gravitational field is zero, the gravitational potential is equal to $ - \dfrac{{16\,Gm}}{r}$.
Therefore, option (C) is correct.
Note:
As we all know, the work done per unit mass that is required to move an object from another location to some reference fixed point, is called Gravitational potential. It is analogous to electric potential and here the mass plays the role of the charge.
Complete answer:
Consider the gravitational field at a point P is equal to zero which is located at a distance x from mass m. Suppose that a unit mass is placed at point P.

As we all know that since the gravitational field at a point P is zero, so it can be said that the gravitational pull exerted by the body of mass m on a unit mass at P i.e ${F_1}$ is equal to the gravitational pull exerted by the body of mass 9m on a unit mass i.e ${F_2}$.
Therefore, we can say that the relation becomes,
$
{F_1} = {F_2} \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{{Gm}}{{{x^2}}} = \dfrac{{G\left( {9m} \right)}}{{{{\left( {r - x} \right)}^2}}} \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{{{{\left( {r - x} \right)}^2}}}{{{x^2}}} = 9 \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{{{{\left( {r - x} \right)}^{}}}}{{{x^{}}}} = 3 \\
\Rightarrow x = \dfrac{r}{4} \\
$
Now we will find the gravitational potential at point P. So the gravitational potential ${V_P}$ at point P is,
${V_P} = - \dfrac{{Gm}}{x} - \dfrac{{G(9m)}}{{r - x}}$…… (I)
We will Substitute $x = \dfrac{r}{4}$ in equation (I) and the result would become;
$
\Rightarrow {V_P} = - \dfrac{Gm}{{\dfrac{r}{{4}}}}-\dfrac{9Gm}{{r-\dfrac{r}{{4}}}}
\Rightarrow {V_P} = - \dfrac{Gm}{{\dfrac{r}{{4}}}}-\dfrac{9Gm}{{\dfrac{3r}{{4}}}}
$
$\Rightarrow {V_P} = - \dfrac{{16\,Gm}}{r}$
At the point where the gravitational field is zero, the gravitational potential is equal to $ - \dfrac{{16\,Gm}}{r}$.
Therefore, option (C) is correct.
Note:
As we all know, the work done per unit mass that is required to move an object from another location to some reference fixed point, is called Gravitational potential. It is analogous to electric potential and here the mass plays the role of the charge.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




