
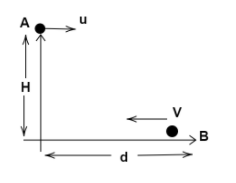
Two particles $A$ and $B$ are placed as shown in the figure. The particle $A$, on the top of the tower, is projected horizontally with a velocity $u$and the particle $B$ is projected along the surface towards the tower, simultaneously. If both particles meet each other, then the speed of projection of particle $B$ is [ignore any friction]
A.$d\sqrt {\dfrac{g}{{2H}}} u$
B.$d\sqrt {\dfrac{g}{{2H}}}$
C.$d\sqrt {\dfrac{g}{{2H}}} - u$
D.$u$

Answer
556.8k+ views
Hint: In the diagram as both the objects are moving with different velocities, we need to solve the question considering the non-inertial frame of reference. We need to write the equation of particle in the x-direction and then write the direction of motion of a particle in the Y direction. Then we need to use the two equations to solve the question.
Complete step by step answer:
As we can see from the diagram that object $A$ moves with velocity $u$ and object $B$ moves with velocity $v$.
Since object $A$is thrown horizontally and object $B$ is thrown upwards, they must meet at a point.
Therefore, we consider non-inertial frame of reference of $B$, thus the relative velocity of $A$ with respect to $B$ is written as: $v + u$
We know the velocity of an object when multiplied by time, giving us the distance travelled by it.
Therefore, in the x-axis,
$(v + u)t = d$
On rearranging the equation, we get:
$t = d/(u + v)$
On squaring both sides, we get:
${t^2} = {d^2}/{(u + v)^2}$
Now, let us consider the Y-axis:
The distance travelled can be obtained as:
$s = {u_o}t + \dfrac{1}{2}a{t^2}$
Where $s$ is the distance travelled in the Y-axis, $a$ is the acceleration, ${u_o}$is the initial velocity.
Now, in this case, ${u_o}$ is zero as the object is thrown.
Thus,
$H = \dfrac{1}{2}a{t^2}$
In this case, the acceleration implies the acceleration due to gravity.
Now, substituting the value of ${t^2}$as obtained from the equation of X-axis, we get:
$H = \dfrac{1}{2}g({d^2}/{(u + v)^2})$
Thus,
On solving the equation, we obtain:
$v = d\sqrt {\dfrac{g}{{2H}}} - u$
This is the required solution.
Option (C ) Is correct.
Note:
Non-inertial frame of reference is used when a body accelerates with respect to the inertial frame. In the case of the inertial frame, the laws of motion remain the same, whereas in the case of the non-inertial frame the laws of motion vary from one frame to another. In the non-inertial frame, it gives rise to pseudo force.
Complete step by step answer:
As we can see from the diagram that object $A$ moves with velocity $u$ and object $B$ moves with velocity $v$.
Since object $A$is thrown horizontally and object $B$ is thrown upwards, they must meet at a point.
Therefore, we consider non-inertial frame of reference of $B$, thus the relative velocity of $A$ with respect to $B$ is written as: $v + u$
We know the velocity of an object when multiplied by time, giving us the distance travelled by it.
Therefore, in the x-axis,
$(v + u)t = d$
On rearranging the equation, we get:
$t = d/(u + v)$
On squaring both sides, we get:
${t^2} = {d^2}/{(u + v)^2}$
Now, let us consider the Y-axis:
The distance travelled can be obtained as:
$s = {u_o}t + \dfrac{1}{2}a{t^2}$
Where $s$ is the distance travelled in the Y-axis, $a$ is the acceleration, ${u_o}$is the initial velocity.
Now, in this case, ${u_o}$ is zero as the object is thrown.
Thus,
$H = \dfrac{1}{2}a{t^2}$
In this case, the acceleration implies the acceleration due to gravity.
Now, substituting the value of ${t^2}$as obtained from the equation of X-axis, we get:
$H = \dfrac{1}{2}g({d^2}/{(u + v)^2})$
Thus,
On solving the equation, we obtain:
$v = d\sqrt {\dfrac{g}{{2H}}} - u$
This is the required solution.
Option (C ) Is correct.
Note:
Non-inertial frame of reference is used when a body accelerates with respect to the inertial frame. In the case of the inertial frame, the laws of motion remain the same, whereas in the case of the non-inertial frame the laws of motion vary from one frame to another. In the non-inertial frame, it gives rise to pseudo force.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




