
Two parallel chords of a circle whose diameter \[13cm\] are \[5cm\text{ }and\text{ }12cm\] . find the distance between them if they lie on opposite of the centre and when they lie on the same side of centre.
Answer
512.4k+ views
Hint: First of all we will make the diagram of the given condition, to understand the condition very well. Then by using the properties of the circle and Pythagoras theorem to find out the length of the triangle.
Complete step by step answer:
Moving ahead with the question, we had a circle whose diameter is \[13cm\] .
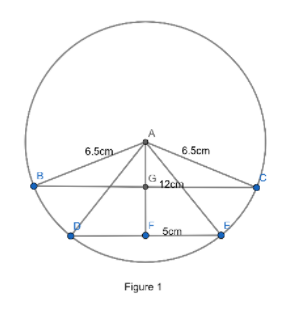
Let us first make the chords which are on the same side of centre as shown in figure 1. So according to the question we had to find out the distance between two chords i.e. between line segments marked as $ GF $ .
So let first find the $ AG $ and $ AF $ length using the triangle priority in $ \Delta ABG $ and $ \Delta ADF $ , and finally subtract $ AF $ and $ AG $ which will give us $ GF $ .
As by the circle property we know that whenever a line is dropped perpendicular to the chord from the centre of the circle then that line will cut the chord in two equal parts. So we can say that point $ G $ and $ F $ are the midpoint of chord $ BC $ and $ DE $ respectively.
So in the right angle triangle $ \Delta AGB $ right angle at $ G $ , length of $ AB=6.5cm $ which is equal to radius of circle. And the length of $ BG=6cm $ as it is half of the chord length $ BC $ . So by applying Pythagoras theorem in $ \Delta AGB $ we will get the unknown length $ AG $ , i.e.;
\[\begin{align}
& {{H}^{2}}={{P}^{2}}+{{B}^{2}} \\
& {{\left( 6.5 \right)}^{2}}={{\left( AG \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( 6 \right)}^{2}} \\
\end{align}\]
On simplifying above equation, we will get;
\[\begin{align}
& 42.25={{\left( AG \right)}^{2}}+36 \\
& {{\left( AG \right)}^{2}}=42.25-36 \\
& {{\left( AG \right)}^{2}}=6.25 \\
& AG=\sqrt{6.25} \\
& AG=2.5cm \\
\end{align}\]
So we got \[AG=2.5cm\] . Now moving further in the same way to find the length of $ AF $ .
So in the right angle triangle $ \Delta AFD $ right angle at $ F $ , length of $ AD=6.5cm $ which is equal to radius of circle. And the length of $ DF=2.5cm $ as it is half of the chord length $ DE $ . So by applying Pythagoras theorem in $ \Delta AFD $ we will get the unknown length $ AF $ , i.e.;
\[\begin{align}
& {{H}^{2}}={{P}^{2}}+{{B}^{2}} \\
& {{\left( 6.5 \right)}^{2}}={{\left( AF \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( 2.5 \right)}^{2}} \\
\end{align}\]
On simplifying above equation, we will get;
\[\begin{align}
& 42.25={{\left( AF \right)}^{2}}+6.25 \\
& {{\left( AF \right)}^{2}}=42.25-6.25 \\
& {{\left( AF \right)}^{2}}=36 \\
& AF=\sqrt{36} \\
& AF=6cm \\
\end{align}\]
So we got \[AF=6cm\]
So to find the distance between two chords is as already mentioned is \[AF-AG\] which will give us the length of $ GF $ which is the distance between the chords when both are on the same side of centre. So distance between the chord is;
\[GF=AF-AG\]
By putting the value of $ AF $ and $ AG $ , we will get;
\[\begin{align}
& GF=AF-AG \\
& GF=6-2.25 \\
& GF=3.75cm \\
\end{align}\]
So the distance between two chords when they are on the same side of centre is $ GF $ which is equal to $ 3.75cm $ .
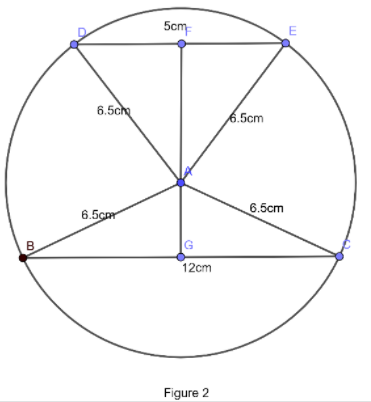
Now when two chords are opposite to the centre is, as shown in figure 2. Going with the same procedure we did when chords are on the same side, as now we also need to find the distance between the chords which is now the length of $ GF $ . Which we can get when we can add the length of $ AF $ and $ AG $ .
As by the circle property we know that whenever a line is dropped perpendicular to the chord from the centre of the circle then that line will cut the chord in two equal parts. So we can say that point $ G $ and $ F $ are the midpoint of chord $ BC $ and $ DE $ respectively.
So in the right angle triangle $ \Delta AGB $ right angle at $ G $ , length of $ AB=6.5cm $ which is equal to radius of circle. And the length of $ BG=6cm $ as it is half of the chord length $ BC $ . So by applying Pythagoras theorem in $ \Delta AGB $ we will get the unknown length $ AG $ , i.e.;
\[\begin{align}
& {{H}^{2}}={{P}^{2}}+{{B}^{2}} \\
& {{\left( 6.5 \right)}^{2}}={{\left( AG \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( 6 \right)}^{2}} \\
\end{align}\]
On simplifying above equation, we will get;
\[\begin{align}
& 42.25={{\left( AG \right)}^{2}}+36 \\
& {{\left( AG \right)}^{2}}=42.25-36 \\
& {{\left( AG \right)}^{2}}=6.25 \\
& AG=\sqrt{6.25} \\
& AG=2.5cm \\
\end{align}\]
So we got \[AG=2.5cm\] . Now moving further in the same way to find the length of $ AF $ .
So in the right angle triangle $ \Delta AFD $ right angle at $ F $ , length of $ AD=6.5cm $ which is equal to radius of circle. And the length of $ DF=2.5cm $ as it is half of the chord length $ DE $ . So by applying Phthagoras theorem in $ \Delta AFD $ we will get the unknown length $ AF $ , i.e.;
\[\begin{align}
& {{H}^{2}}={{P}^{2}}+{{B}^{2}} \\
& {{\left( 6.5 \right)}^{2}}={{\left( AF \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( 2.5 \right)}^{2}} \\
\end{align}\]
On simplifying above equation, we will get;
\[\begin{align}
& 42.25={{\left( AF \right)}^{2}}+6.25 \\
& {{\left( AF \right)}^{2}}=42.25-6.25 \\
& {{\left( AF \right)}^{2}}=36 \\
& AF=\sqrt{36} \\
& AF=6cm \\
\end{align}\]
So we got \[AF=6cm\]
So to find the distance between two chords is as already mentioned is \[AF+AG\] which will give us the length of $ GF $ which is the distance between the chords when both are on the same side of centre. So distance between the chord is;
\[GF=AF+AG\]
By putting the value of $ AF $ and $ AG $ , we will get;
\[\begin{align}
& GF=AF+AG \\
& GF=6+2.25 \\
& GF=8.25cm \\
\end{align}\]
So the distance between two chords when they are on the same side of the centre is $ GF $ which is equal to \[8.25cm\] .
Hence the answer is \[8.25cm\] and \[3.75cm\] , which is the distance between the chords if they lie on opposite of the centre and when they lie on the same side of centre.
Note: The distance between two lines is found by dropping the perpendicular between them, so we joined the centre point with a chord such that they are perpendicular to each other, which ultimately makes the right angle between the line joining the two chords.
Complete step by step answer:
Moving ahead with the question, we had a circle whose diameter is \[13cm\] .

Let us first make the chords which are on the same side of centre as shown in figure 1. So according to the question we had to find out the distance between two chords i.e. between line segments marked as $ GF $ .
So let first find the $ AG $ and $ AF $ length using the triangle priority in $ \Delta ABG $ and $ \Delta ADF $ , and finally subtract $ AF $ and $ AG $ which will give us $ GF $ .
As by the circle property we know that whenever a line is dropped perpendicular to the chord from the centre of the circle then that line will cut the chord in two equal parts. So we can say that point $ G $ and $ F $ are the midpoint of chord $ BC $ and $ DE $ respectively.
So in the right angle triangle $ \Delta AGB $ right angle at $ G $ , length of $ AB=6.5cm $ which is equal to radius of circle. And the length of $ BG=6cm $ as it is half of the chord length $ BC $ . So by applying Pythagoras theorem in $ \Delta AGB $ we will get the unknown length $ AG $ , i.e.;
\[\begin{align}
& {{H}^{2}}={{P}^{2}}+{{B}^{2}} \\
& {{\left( 6.5 \right)}^{2}}={{\left( AG \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( 6 \right)}^{2}} \\
\end{align}\]
On simplifying above equation, we will get;
\[\begin{align}
& 42.25={{\left( AG \right)}^{2}}+36 \\
& {{\left( AG \right)}^{2}}=42.25-36 \\
& {{\left( AG \right)}^{2}}=6.25 \\
& AG=\sqrt{6.25} \\
& AG=2.5cm \\
\end{align}\]
So we got \[AG=2.5cm\] . Now moving further in the same way to find the length of $ AF $ .
So in the right angle triangle $ \Delta AFD $ right angle at $ F $ , length of $ AD=6.5cm $ which is equal to radius of circle. And the length of $ DF=2.5cm $ as it is half of the chord length $ DE $ . So by applying Pythagoras theorem in $ \Delta AFD $ we will get the unknown length $ AF $ , i.e.;
\[\begin{align}
& {{H}^{2}}={{P}^{2}}+{{B}^{2}} \\
& {{\left( 6.5 \right)}^{2}}={{\left( AF \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( 2.5 \right)}^{2}} \\
\end{align}\]
On simplifying above equation, we will get;
\[\begin{align}
& 42.25={{\left( AF \right)}^{2}}+6.25 \\
& {{\left( AF \right)}^{2}}=42.25-6.25 \\
& {{\left( AF \right)}^{2}}=36 \\
& AF=\sqrt{36} \\
& AF=6cm \\
\end{align}\]
So we got \[AF=6cm\]
So to find the distance between two chords is as already mentioned is \[AF-AG\] which will give us the length of $ GF $ which is the distance between the chords when both are on the same side of centre. So distance between the chord is;
\[GF=AF-AG\]
By putting the value of $ AF $ and $ AG $ , we will get;
\[\begin{align}
& GF=AF-AG \\
& GF=6-2.25 \\
& GF=3.75cm \\
\end{align}\]
So the distance between two chords when they are on the same side of centre is $ GF $ which is equal to $ 3.75cm $ .

Now when two chords are opposite to the centre is, as shown in figure 2. Going with the same procedure we did when chords are on the same side, as now we also need to find the distance between the chords which is now the length of $ GF $ . Which we can get when we can add the length of $ AF $ and $ AG $ .
As by the circle property we know that whenever a line is dropped perpendicular to the chord from the centre of the circle then that line will cut the chord in two equal parts. So we can say that point $ G $ and $ F $ are the midpoint of chord $ BC $ and $ DE $ respectively.
So in the right angle triangle $ \Delta AGB $ right angle at $ G $ , length of $ AB=6.5cm $ which is equal to radius of circle. And the length of $ BG=6cm $ as it is half of the chord length $ BC $ . So by applying Pythagoras theorem in $ \Delta AGB $ we will get the unknown length $ AG $ , i.e.;
\[\begin{align}
& {{H}^{2}}={{P}^{2}}+{{B}^{2}} \\
& {{\left( 6.5 \right)}^{2}}={{\left( AG \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( 6 \right)}^{2}} \\
\end{align}\]
On simplifying above equation, we will get;
\[\begin{align}
& 42.25={{\left( AG \right)}^{2}}+36 \\
& {{\left( AG \right)}^{2}}=42.25-36 \\
& {{\left( AG \right)}^{2}}=6.25 \\
& AG=\sqrt{6.25} \\
& AG=2.5cm \\
\end{align}\]
So we got \[AG=2.5cm\] . Now moving further in the same way to find the length of $ AF $ .
So in the right angle triangle $ \Delta AFD $ right angle at $ F $ , length of $ AD=6.5cm $ which is equal to radius of circle. And the length of $ DF=2.5cm $ as it is half of the chord length $ DE $ . So by applying Phthagoras theorem in $ \Delta AFD $ we will get the unknown length $ AF $ , i.e.;
\[\begin{align}
& {{H}^{2}}={{P}^{2}}+{{B}^{2}} \\
& {{\left( 6.5 \right)}^{2}}={{\left( AF \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( 2.5 \right)}^{2}} \\
\end{align}\]
On simplifying above equation, we will get;
\[\begin{align}
& 42.25={{\left( AF \right)}^{2}}+6.25 \\
& {{\left( AF \right)}^{2}}=42.25-6.25 \\
& {{\left( AF \right)}^{2}}=36 \\
& AF=\sqrt{36} \\
& AF=6cm \\
\end{align}\]
So we got \[AF=6cm\]
So to find the distance between two chords is as already mentioned is \[AF+AG\] which will give us the length of $ GF $ which is the distance between the chords when both are on the same side of centre. So distance between the chord is;
\[GF=AF+AG\]
By putting the value of $ AF $ and $ AG $ , we will get;
\[\begin{align}
& GF=AF+AG \\
& GF=6+2.25 \\
& GF=8.25cm \\
\end{align}\]
So the distance between two chords when they are on the same side of the centre is $ GF $ which is equal to \[8.25cm\] .
Hence the answer is \[8.25cm\] and \[3.75cm\] , which is the distance between the chords if they lie on opposite of the centre and when they lie on the same side of centre.
Note: The distance between two lines is found by dropping the perpendicular between them, so we joined the centre point with a chord such that they are perpendicular to each other, which ultimately makes the right angle between the line joining the two chords.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




