
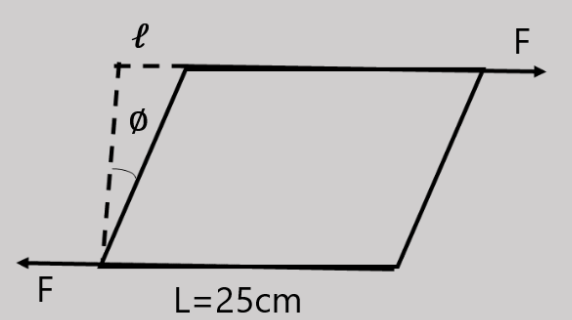
Two parallel and opposite forces, each of magnitude 4000N, are applied tangentially to the upper and lower faces of a cubical metal block of side 25cm. If the shear modulus for the metal is $8 \times {10^{10}}Pa$ , then the displacement of the upper surface relative to the lower surface will be:

Answer
595.2k+ views
Hint:The strain caused by shear stress is called angle of deformation. The angle of shear strain ($\theta $) is directly proportional to the shear force (F) applied on it and inversely proportional to the area (A) on which force applied and shear modulus (η) which is also called as modulus of rigidity.
Formula used:Angle of shear strain (θ) =$\dfrac{F}{{A\eta }}$ ;
Where,
F is applied force, A is the area on which force is applied and η is shear modulus or modulus of rigidity.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Let us first write the information given in the question.
Given,
F=4000N, Side=25cm=0.25m, η=$8 \times {10^{10}}Pa$.
Let us find the area of the side on which the shear force is applied.
Area of the side can be find by using formula,
$A = {(side)^2}$
$A = {(0.25)^2}$
$ \Rightarrow 0.0625{m^2}$
Now let us use the formula of angle of shear strain which is $\theta = \dfrac{F}{{A\eta }}$
Let us substitute the values in the formula, we get,
$\theta = \dfrac{{4000}}{{0.0625 \times 8 \times {{10}^{10}}}}$
Let us further simplify it. On simplification we get,
$\theta = 8 \times {10^{ - 7}}$
There is one more relation to angle of shear.
Angles of shear strain can also be defined as below.
θ=change in length/ original length
$\theta = \dfrac{{\Delta l}}{l}$
Let us substitute the values in this formula and obtain the change in length. We get,
$\Delta l = \theta l = (8 \times {10^{ - 7}} \times 0.25)m$
Let us simplify the expression. On simplification we get,
$\Delta l = 2 \times {10^{ - 7}}m$
Hence, the required change in length is $2 \times {10^{ - 7}}m$.
Additional information:Shear force is the force applied perpendicular to the surface, for example, force applied when the paper is cut by scissors.
Shear stress is called the force which tends to deform the material example, stress applied on pipelines by flowing fluid through it.
Note:When an external force is applied tangentially on the surface of a body such that the opposite side of the body is kept fixed. Then the shape of the body changes while the volume remains unchanged. In this case, the body is said to be sheared.
For small strain, the ratio of shear stress and shear strain is known as modulus of rigidity (η) of the body.
Formula used:Angle of shear strain (θ) =$\dfrac{F}{{A\eta }}$ ;
Where,
F is applied force, A is the area on which force is applied and η is shear modulus or modulus of rigidity.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Let us first write the information given in the question.
Given,
F=4000N, Side=25cm=0.25m, η=$8 \times {10^{10}}Pa$.
Let us find the area of the side on which the shear force is applied.
Area of the side can be find by using formula,
$A = {(side)^2}$
$A = {(0.25)^2}$
$ \Rightarrow 0.0625{m^2}$
Now let us use the formula of angle of shear strain which is $\theta = \dfrac{F}{{A\eta }}$
Let us substitute the values in the formula, we get,
$\theta = \dfrac{{4000}}{{0.0625 \times 8 \times {{10}^{10}}}}$
Let us further simplify it. On simplification we get,
$\theta = 8 \times {10^{ - 7}}$
There is one more relation to angle of shear.
Angles of shear strain can also be defined as below.
θ=change in length/ original length
$\theta = \dfrac{{\Delta l}}{l}$
Let us substitute the values in this formula and obtain the change in length. We get,
$\Delta l = \theta l = (8 \times {10^{ - 7}} \times 0.25)m$
Let us simplify the expression. On simplification we get,
$\Delta l = 2 \times {10^{ - 7}}m$
Hence, the required change in length is $2 \times {10^{ - 7}}m$.
Additional information:Shear force is the force applied perpendicular to the surface, for example, force applied when the paper is cut by scissors.
Shear stress is called the force which tends to deform the material example, stress applied on pipelines by flowing fluid through it.
Note:When an external force is applied tangentially on the surface of a body such that the opposite side of the body is kept fixed. Then the shape of the body changes while the volume remains unchanged. In this case, the body is said to be sheared.
For small strain, the ratio of shear stress and shear strain is known as modulus of rigidity (η) of the body.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




