
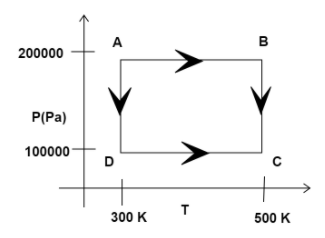
Two moles of Helium gas are taken over the cycle $ABCDA$ as shown in the P-T diagram. The net work done on the gas in the cycle $ABCDA$ IS:
A.$0$
B.$276R$
C.$1076R$
D.$1094R$

Answer
556.8k+ views
Hint: To find the work done in the process, we need to find the work done at respective stages that is work done in$AB$, $BC$, $CD$,$DA$. The summation of the work done at this stage will give us the total work done by the gas.
Formula used:
$W = nR\Delta T$
$W = $ Work done
$n = $ Number of moles
$R = $ Universal Gas constant
$\Delta T = $ Change in temperature.
$W = nRT\ln (\dfrac{{{P_1}}}{{{P_2}}})$
$W = $ Work done
$n = $ Number of moles
$R = $ Universal Gas constant
$\Delta T = $ Change in temperature
${P_1} = $ Pressure at point $1$
${P_2} = $ Pressure at point $2$
Complete step by step answer:
We know, this is a cyclic process as in this the starting and the ending point are same.
Now, let us consider stage$AB$:
As we can see from the diagram, the pressure remains constant but the temperature changes.
Therefore, the work done in $AB$is
${W_{AB}} = nR\Delta T$
Now, putting the values we get:
${W_{AB}} = 2 \times R \times (500 - 300) = 400R$
In case of $BC$, the process takes place at constant temperature, but changing pressure.
Thus, we know, the formula for work done in $BC$ is written as:
${W_{BC}} = nRT\ln (\dfrac{{{P_B}}}{{{P_C}}})$
Now, putting the values, we get:
${W_{BC}} = 2 \times R \times 500 \times \ln (2) = 690R$
Again, in case of$CA$, as we can see from the diagram, the pressure remains constant but the temperature changes.
Thus, work done by$CA$, is given by:
${W_{CA}} = 2 \times R \times (300 - 500) = - 400R$
Now, again:
In case of $DA$, the work done is:
${W_{DA}} = n \times R \times T \times \ln (\dfrac{{{P_D}}}{{{P_A}}})$
On putting the values, we get:
${W_{DA}} = 2 \times R \times 500 \times \ln (0.5) = - 414R$
Therefore, total work done by the system is:
$W = {W_{AB}} + {W_{BC}} + {W_{CD}} + {W_{DA}}$
Now, putting the values as obtained above:
$W = 400R + 690R - 400R - 414R$
Therefore, the obtain work done is $276R$
Thus, option (B) is correct.
Note:
Since in stage $AD$ and $CB$ as we can see from the diagram, the pressure remains constant but the temperature changes, they are known as isochoric process and in case of $AB$ and $DA$ , the pressure remains constant but the temperature changes, the process is known as isobaric process.
Formula used:
$W = nR\Delta T$
$W = $ Work done
$n = $ Number of moles
$R = $ Universal Gas constant
$\Delta T = $ Change in temperature.
$W = nRT\ln (\dfrac{{{P_1}}}{{{P_2}}})$
$W = $ Work done
$n = $ Number of moles
$R = $ Universal Gas constant
$\Delta T = $ Change in temperature
${P_1} = $ Pressure at point $1$
${P_2} = $ Pressure at point $2$
Complete step by step answer:
We know, this is a cyclic process as in this the starting and the ending point are same.
Now, let us consider stage$AB$:
As we can see from the diagram, the pressure remains constant but the temperature changes.
Therefore, the work done in $AB$is
${W_{AB}} = nR\Delta T$
Now, putting the values we get:
${W_{AB}} = 2 \times R \times (500 - 300) = 400R$
In case of $BC$, the process takes place at constant temperature, but changing pressure.
Thus, we know, the formula for work done in $BC$ is written as:
${W_{BC}} = nRT\ln (\dfrac{{{P_B}}}{{{P_C}}})$
Now, putting the values, we get:
${W_{BC}} = 2 \times R \times 500 \times \ln (2) = 690R$
Again, in case of$CA$, as we can see from the diagram, the pressure remains constant but the temperature changes.
Thus, work done by$CA$, is given by:
${W_{CA}} = 2 \times R \times (300 - 500) = - 400R$
Now, again:
In case of $DA$, the work done is:
${W_{DA}} = n \times R \times T \times \ln (\dfrac{{{P_D}}}{{{P_A}}})$
On putting the values, we get:
${W_{DA}} = 2 \times R \times 500 \times \ln (0.5) = - 414R$
Therefore, total work done by the system is:
$W = {W_{AB}} + {W_{BC}} + {W_{CD}} + {W_{DA}}$
Now, putting the values as obtained above:
$W = 400R + 690R - 400R - 414R$
Therefore, the obtain work done is $276R$
Thus, option (B) is correct.
Note:
Since in stage $AD$ and $CB$ as we can see from the diagram, the pressure remains constant but the temperature changes, they are known as isochoric process and in case of $AB$ and $DA$ , the pressure remains constant but the temperature changes, the process is known as isobaric process.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




