
Two loudspeakers $ M $ and $ N $ are located $ 20m $ apart and emit sound at frequencies $ 118\;Hz $ and $ 121\;Hz $ respectively. A car is initially at a point $ P,\;1800\;m $ away from the midpoint $ Q $ of the line $ MN $ and moves towards Q constantly at $ 60km{h^{ - 1}} $ along perpendicular bisector of $ MN $ . It crosses $ Q $ and eventually reaches a point $ R,1800 $ away from $ Q $ . Let $ \nu \left( t \right)\; $ represent the beat frequency measured by a person sitting in the car at time $ t $ . Let $ {v_P} $ , $ {v_Q} $ and $ {v_R} $ be the beat frequencies measured at locations $ P,Q,R\; $ respectively. The speed of sound in air is $ 300m{s^{ - 1}} $ . Which of the following statement (s) is (are) true regarding the sound heard by the person?
(A) A plot below represents schematically the variation of beat frequency with time
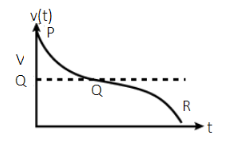
(B) The rate of change in beat frequency is maximum when the car reaches point $ Q $ .
(C) $ {v_P} + {v_R} = 2{v_Q} $
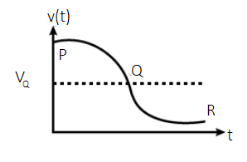
(D) The plot below shows the variation for beat frequency with time.
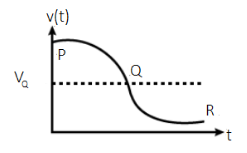


Answer
533.1k+ views
Hint :In order to solve this question, we are first going to consider all the information given, then after finding the apparent frequencies of the loudspeakers at the distance $ P $ and $ Q $ , we get the idea of the relation of the frequencies at different points and also the point where the frequency is maximum.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
Here, we are given with the two loudspeakers, $ M $ and $ N $
Distance between them is, $ d = 20m $
Frequency by loudspeaker $ M $ , $ {\nu _M} = 118Hz $
Frequency for loudspeaker $ N $ , $ {\nu _N} = 121Hz $
Now the point $ P,\;1800\;m $ away from the midpoint $ Q $ of the line $ MN $ ,
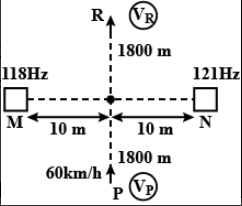
Thus, apparent frequency of $ M $ and $ N $ at $ P $ is:
$ {\nu _M}' = \dfrac{{v + {v_0}}}{v}{\nu _M} $ ,putting the values of the velocities in this equation, we get
$ {\nu _M}' = \dfrac{{330 + \dfrac{{50}}{3}}}{{330}} \times 118 \\
\Rightarrow {\nu _M}' = \dfrac{{1040}}{{990}}118 \\ $
Also, $ {\nu _N}' = \dfrac{{v + {v_0}}}{v}{\nu _N} $
Putting the values in this equation,
$ {\nu _N}' = \dfrac{{330 + \dfrac{{50}}{3}}}{{330}} \times 121 \\
\Rightarrow {\nu _N}' = \dfrac{{1040}}{{990}}121 \\ $
Thus, frequency at $ P $ is
$ {\nu _P} = {\nu _M}' - {\nu _N}' = \dfrac{{1040}}{{330}}Hz $
Thus, apparent frequency of $ M $ and $ N $ at $ R $ is:
$ {\nu _M}' = \dfrac{{v - {v_0}}}{v}{\nu _M} $
Putting the values, we get
$ {\nu _M}' = \dfrac{{330 - \dfrac{{50}}{3}}}{{330}} \times 118 \\
\Rightarrow {\nu _M}' = \dfrac{{940}}{{990}}118 \\ $
Also, $ {\nu _N}' = \dfrac{{v - {v_0}}}{v}{\nu _N} $ ,
Putting values, we get
$ {\nu _N}' = \dfrac{{330 - \dfrac{{50}}{3}}}{{330}} \times 121 \\
\Rightarrow {\nu _N}' = \dfrac{{940}}{{990}}121 \\ $
Thus, apparent frequency is
$ {\nu _R} = {\nu _N}' - {\nu _M}' = \dfrac{{940}}{{330}}Hz $
Now, beat frequency at $ Q $ is calculated as
$ {v_Q} = 121 - 118 = 3Hz $
Now, if we check option (C),
$ {v_P} + {v_R} = 2{\nu _Q} \\
6 = 2 \times 3 \\ $
Also, $ \dfrac{{d\nu }}{{dt}} $ is maximum at $ Q $ ,
Hence, the correct options are (B),(C),(D), i.e.,
The rate of change in beat frequency is maximum when the car reaches point $ Q $ .
$ {v_P} + {v_R} = 2{v_Q} $
The plot below shows the variation for beat frequency with time.
Note :
It is important to note that at the point of maximum rate of change of frequency, the double derivative is zero thus, indicating that the point is a maxima point. Also the apparent frequencies at the points at larger distances is less as compared to those points which are nearer.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
Here, we are given with the two loudspeakers, $ M $ and $ N $
Distance between them is, $ d = 20m $
Frequency by loudspeaker $ M $ , $ {\nu _M} = 118Hz $
Frequency for loudspeaker $ N $ , $ {\nu _N} = 121Hz $
Now the point $ P,\;1800\;m $ away from the midpoint $ Q $ of the line $ MN $ ,

Thus, apparent frequency of $ M $ and $ N $ at $ P $ is:
$ {\nu _M}' = \dfrac{{v + {v_0}}}{v}{\nu _M} $ ,putting the values of the velocities in this equation, we get
$ {\nu _M}' = \dfrac{{330 + \dfrac{{50}}{3}}}{{330}} \times 118 \\
\Rightarrow {\nu _M}' = \dfrac{{1040}}{{990}}118 \\ $
Also, $ {\nu _N}' = \dfrac{{v + {v_0}}}{v}{\nu _N} $
Putting the values in this equation,
$ {\nu _N}' = \dfrac{{330 + \dfrac{{50}}{3}}}{{330}} \times 121 \\
\Rightarrow {\nu _N}' = \dfrac{{1040}}{{990}}121 \\ $
Thus, frequency at $ P $ is
$ {\nu _P} = {\nu _M}' - {\nu _N}' = \dfrac{{1040}}{{330}}Hz $
Thus, apparent frequency of $ M $ and $ N $ at $ R $ is:
$ {\nu _M}' = \dfrac{{v - {v_0}}}{v}{\nu _M} $
Putting the values, we get
$ {\nu _M}' = \dfrac{{330 - \dfrac{{50}}{3}}}{{330}} \times 118 \\
\Rightarrow {\nu _M}' = \dfrac{{940}}{{990}}118 \\ $
Also, $ {\nu _N}' = \dfrac{{v - {v_0}}}{v}{\nu _N} $ ,
Putting values, we get
$ {\nu _N}' = \dfrac{{330 - \dfrac{{50}}{3}}}{{330}} \times 121 \\
\Rightarrow {\nu _N}' = \dfrac{{940}}{{990}}121 \\ $
Thus, apparent frequency is
$ {\nu _R} = {\nu _N}' - {\nu _M}' = \dfrac{{940}}{{330}}Hz $
Now, beat frequency at $ Q $ is calculated as
$ {v_Q} = 121 - 118 = 3Hz $
Now, if we check option (C),
$ {v_P} + {v_R} = 2{\nu _Q} \\
6 = 2 \times 3 \\ $
Also, $ \dfrac{{d\nu }}{{dt}} $ is maximum at $ Q $ ,
Hence, the correct options are (B),(C),(D), i.e.,
The rate of change in beat frequency is maximum when the car reaches point $ Q $ .
$ {v_P} + {v_R} = 2{v_Q} $
The plot below shows the variation for beat frequency with time.

Note :
It is important to note that at the point of maximum rate of change of frequency, the double derivative is zero thus, indicating that the point is a maxima point. Also the apparent frequencies at the points at larger distances is less as compared to those points which are nearer.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




