
Two light strings of length $4cm$ and $3cm$ are tied to a bob of weight $50gm$. The free ends of the strings are tied to pegs in the same horizontal line and separated by $5cm$. The ratio of the tension in the longer string to that in the shorter string is:
(A). $4:3$
(B). $3:4$
(C). $4:5$
(D). $5:4$
Answer
564.6k+ views
Hint: The strings are attached to a horizontal support and tied to a bob. The forces acting on the bob must be the tensions in the strings and the force of gravity. Forces can be resolved into their components in perpendicular directions. Using Newton’s second law and making equations for forces acting in x-direction and y-direction, we can calculate the ratio by solving the equations and using properties of right-angled triangles.
Formulae used:
${{T}_{1}}\cos \theta +{{T}_{2}}\sin \theta =mg$
$\dfrac{{{T}_{1}}}{{{T}_{2}}}=\cot \theta $
$\cot \theta =\dfrac{\cos \theta }{\sin \theta }$
Complete step-by-step solution:
Given, two strings are tied to a bob. The system of strings and bob is isolated. Tension is a pulling force that acts along the axis. It operates in continuous objects like strings, rods, etc.
Resolving the forces acting on the system, we get,

Since the triplet of $3cm,\,4cm\,,\,5cm$ is a Pythagorean triplet, therefore, $\angle BAC={{90}^{o}}$.
For forces acting in the y-direction,
${{T}_{1}}\cos \theta +{{T}_{2}}\sin \theta -mg=0$
$\Rightarrow {{T}_{1}}\cos \theta +{{T}_{2}}\sin \theta =mg$ - (1)
For forces acting in the x-direction,
${{T}_{1}}\sin \theta ={{T}_{2}}\cos \theta $
$\therefore \dfrac{{{T}_{1}}}{{{T}_{2}}}=\cot \theta $ - (2)
We know that
$\cot \theta =\dfrac{\cos \theta }{\sin \theta }$ - (3)
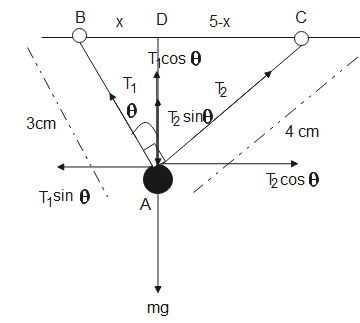
$\begin{align}
& \Delta ABD \\
& \cos \theta =\dfrac{AD}{3} \\
\end{align}$
$\begin{align}
& \Delta ACD \\
& \sin \theta =\dfrac{AD}{4} \\
\end{align}$
Substituting the above values in eq (3), we have,
$\begin{align}
& \cot \theta =\dfrac{\dfrac{AD}{3}}{\dfrac{AD}{4}} \\
& \Rightarrow \cot \theta =\dfrac{4}{3} \\
\end{align}$
Substituting in eq (2), we get,
$\therefore \dfrac{{{T}_{1}}}{{{T}_{2}}}=\dfrac{4}{3}$
Therefore, the ratio of the tension in the strings is $\dfrac{4}{3}$. Hence, the correct option is (A).
Note:
Pythagorean triplet is a set of three numbers that obey the Pythagoras theorem. When a perpendicular is dropped from the opposite vertex to the hypotenuse, it divides it into two equal parts so it meets it at the midpoint. Forces acting in the opposite direction are subtracted. By Newton’s third law, tension acts equal and opposite on the string as well as on the object attached to it.
Formulae used:
${{T}_{1}}\cos \theta +{{T}_{2}}\sin \theta =mg$
$\dfrac{{{T}_{1}}}{{{T}_{2}}}=\cot \theta $
$\cot \theta =\dfrac{\cos \theta }{\sin \theta }$
Complete step-by-step solution:

Given, two strings are tied to a bob. The system of strings and bob is isolated. Tension is a pulling force that acts along the axis. It operates in continuous objects like strings, rods, etc.
Resolving the forces acting on the system, we get,

Since the triplet of $3cm,\,4cm\,,\,5cm$ is a Pythagorean triplet, therefore, $\angle BAC={{90}^{o}}$.
For forces acting in the y-direction,
${{T}_{1}}\cos \theta +{{T}_{2}}\sin \theta -mg=0$
$\Rightarrow {{T}_{1}}\cos \theta +{{T}_{2}}\sin \theta =mg$ - (1)
For forces acting in the x-direction,
${{T}_{1}}\sin \theta ={{T}_{2}}\cos \theta $
$\therefore \dfrac{{{T}_{1}}}{{{T}_{2}}}=\cot \theta $ - (2)
We know that
$\cot \theta =\dfrac{\cos \theta }{\sin \theta }$ - (3)

$\begin{align}
& \Delta ABD \\
& \cos \theta =\dfrac{AD}{3} \\
\end{align}$
$\begin{align}
& \Delta ACD \\
& \sin \theta =\dfrac{AD}{4} \\
\end{align}$
Substituting the above values in eq (3), we have,
$\begin{align}
& \cot \theta =\dfrac{\dfrac{AD}{3}}{\dfrac{AD}{4}} \\
& \Rightarrow \cot \theta =\dfrac{4}{3} \\
\end{align}$
Substituting in eq (2), we get,
$\therefore \dfrac{{{T}_{1}}}{{{T}_{2}}}=\dfrac{4}{3}$
Therefore, the ratio of the tension in the strings is $\dfrac{4}{3}$. Hence, the correct option is (A).
Note:
Pythagorean triplet is a set of three numbers that obey the Pythagoras theorem. When a perpendicular is dropped from the opposite vertex to the hypotenuse, it divides it into two equal parts so it meets it at the midpoint. Forces acting in the opposite direction are subtracted. By Newton’s third law, tension acts equal and opposite on the string as well as on the object attached to it.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




