
Two light beams superimposed each other constructively this results in:
(A). A loss of kinetic energy
(B). The destruction of the wave
(C). The reversal of the direction of the wave
(D). A larger wave
Answer
600k+ views
Hint: Waves consist of crest and troughs. When two or more sets of waves are allowed to pass through and cross another in the same medium, waves meet at a point then they superimpose on each other and the resultant effect at any point, at any instant of time is governed by the principle of superposition. The resultant wave will be the vector sum of individual waves.
Complete step by step answer:
Principle of superposition:
When two or more waves come together at some point in space then the resultant disturbance of the wave at that point is a vector sum of disturbances due to each individual wave.
Interference:
When two identical waves superimpose then according to the principle of superposition the resultant amplitude of wave at that point is a vector sum of amplitudes of each individual wave. This phenomenon is known as ‘Interference’.
There two types of interference:
Constructive Interference: When two waves of same frequency and same amplitude interfere with each other and crest of one wave coincides with crest of other wave or trough of one wave coincides with trough of other wave then this type of interference is called the ‘Constructive interference’. The resultant amplitude will be twice as amplitude of the individual wave. Therefore we get a larger wave when two waves interfere constructively.
Destructive Interference: When two waves of same frequency and same amplitude interfere with each other and crest of one wave coincides with the trough of other wave or trough of one wave coincides with crest of other wave then this type of interference is called the ‘Destructive interference’.
The following graph shows that when two waves of same frequency and amplitude interfere constructively we get a larger wave
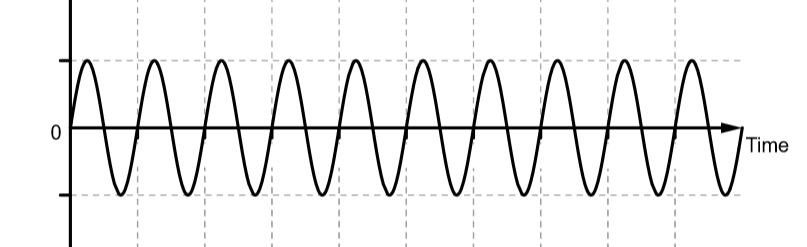
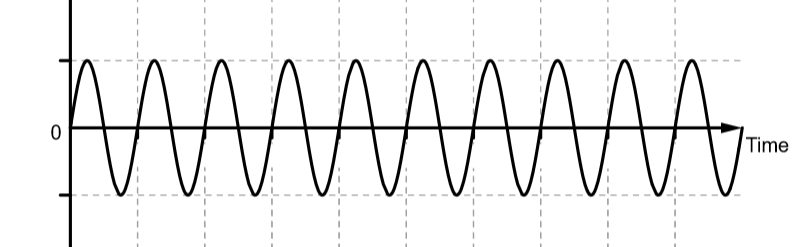
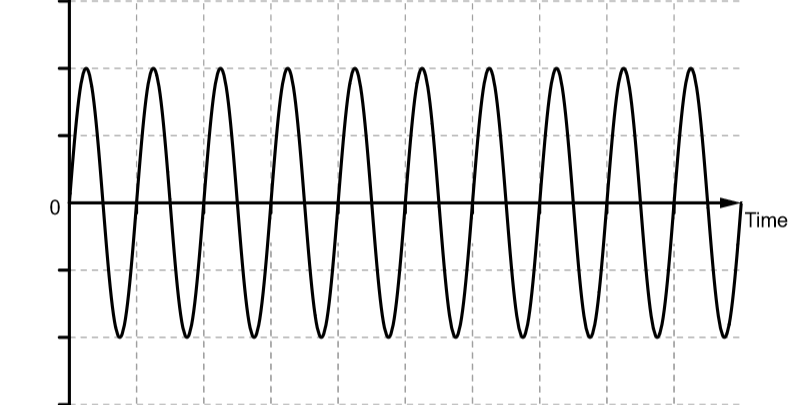
Hence, the option (D) is correct
Note: When waves of different amplitude interfere the resultant amplitude will be the vector sum of individual amplitudes. If waves of different frequencies interfere then also we get interference patterns but it will not be steady, it varies with time and in case of light we may not be able to observe that time varying pattern.
Complete step by step answer:
Principle of superposition:
When two or more waves come together at some point in space then the resultant disturbance of the wave at that point is a vector sum of disturbances due to each individual wave.
Interference:
When two identical waves superimpose then according to the principle of superposition the resultant amplitude of wave at that point is a vector sum of amplitudes of each individual wave. This phenomenon is known as ‘Interference’.
There two types of interference:
Constructive Interference: When two waves of same frequency and same amplitude interfere with each other and crest of one wave coincides with crest of other wave or trough of one wave coincides with trough of other wave then this type of interference is called the ‘Constructive interference’. The resultant amplitude will be twice as amplitude of the individual wave. Therefore we get a larger wave when two waves interfere constructively.
Destructive Interference: When two waves of same frequency and same amplitude interfere with each other and crest of one wave coincides with the trough of other wave or trough of one wave coincides with crest of other wave then this type of interference is called the ‘Destructive interference’.
The following graph shows that when two waves of same frequency and amplitude interfere constructively we get a larger wave



Hence, the option (D) is correct
Note: When waves of different amplitude interfere the resultant amplitude will be the vector sum of individual amplitudes. If waves of different frequencies interfere then also we get interference patterns but it will not be steady, it varies with time and in case of light we may not be able to observe that time varying pattern.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




